Abstract
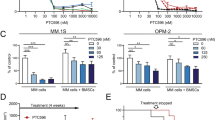
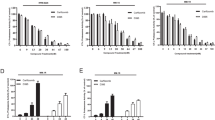
The proteasome inhibitor PSI is potently cytotoxic in vitro against human chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and acute myeloid leukemias (AML). Here, we have tested proteasome inhibitor I (PSI) in a panel of 11 human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines and found that it has antiproliferative activity, with an IC50 between 4.5 and 557 nM at 48 h. PSI potentiated the toxicity of a number of chemotherapeutic agents in myeloid leukemia but not in MM cell lines, while in combination with therapeutic proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (Bortezomib) it had a synergistic effect. PSI suppressed the growth of AML cell lines more effectively than PS-341. CFU-GM colony assays revealed that CD34+ bone marrow progenitors from CML and AML patients were more sensitive to PSI than those from normal subjects (IC50: 5, 15 and 50 nM for AML, CML and normal, respectively). Moreover, the growth of normal primitive progenitors (LTC-IC) was unaffected by 15 nM PSI (P=0.576). PSI-induced cell death required RNA transcription and protein synthesis, but not DNA replication, was accompanied by the upregulation of Bcl-2 and modest reduction of Bax and Bcl-XL proteins, and involved the activation of caspases 2, 3, 7 and 8. These findings lend additional support to preclinical investigations with PSI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J . The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 349–360.
Stock D, Ditzel L, Baumeister W, Huber R, Lowe J . Catalytic mechanism of the 20S proteasome of Thermplasma acidophilum revealed by X-ray crystallography. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 1995; 60: 525–532.
Kitagawa H, Tani E, Ikemoto H, Ozaki I, Nakano A, Omura S . Proteasome inhibitors induce mitochondria-independent apoptosis in human glioma cells. FEBS Lett 1999; 443: 181–186.
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD et al. Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2615–2622.
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V et al. Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 1995; 269: 682–685.
Drexler HCA . Activation of the cell death program by inhibition of proteasome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 855–860.
Nalepa G, Harper JW . Therapeutic anti-cancer targets upstream of the proteasome. Cancer Treatment Rev 2003; 29 (Suppl I): 49–57.
Almond JB, Cohen GM . The proteasome: a novel target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 2002; 16: 433–443.
Soligo D, Servida F, Delia D, Fontanella E, Lamorte G, Caneva L et al. The apoptogenic response of human myeloid leukaemia cell lines and of normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitor cells to the proteasome inhibitor PSI. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 126–135.
Sayers TJ, Brooks AD, Koh CY, Ma W, Seki N, Raziuddin A et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 sensitizes neoplastic cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by reducing levels of c-FLIP. Blood 2003; 102: 303–310.
Richardson P . Clinical update: proteasome inhibitors in hematologic malignancies. Cancer Treat Rev 2003; 29: 33–39.
Yu C, Rahmani M, Conrad D, Subler M, Dent P, Grant S . The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl+ cells sensitive and resistant to STI571. Blood 2003; 102: 3765–3774.
Ishiyama M, Tominaga H, Shiga M, Sasamoto K, Ohkura Y, Ueno K . A combined assay of cell viability and in vitro cytotoxicity with a high water-soluble tetrazolium salt, neutral red and crystal violet. Biol Pharm Bull 1996; 11: 1518–1520.
Kern DH, Morgan CR, Hildebrand-Zanki SU . In vitro pharmacodynamics of 1-beta-arabinofuranosylcytosine: synergy of antitumor activity with cis-diamminechloroplatinum. Cancer Res 1988; 48: 117–121.
Romanelli S, Perego P, Pratesi G, Carenini N, Tortoreto M, Zuino F . In vitro and in vivo interactions between cisplatin and topotecan in ovarian carcinoma systems. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1988; 41: 385–390.
Eaves AC, Cashman JD, Gaboury LA, Kalousek DK, Eaves CJ . Unregulated proliferation of primitive chronic myeloid leukemia progenitors in the presence of normal marrow adherent cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986; 83: 5306–5310.
Sutherland HJ, Lansdorp PM, Henkelman DH, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ . Functional characterization of individual human hematopoietic stem cells cultured at limiting dilution on supportive marrow stromal layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 3584–3588.
Taswell C . Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol 1981; 126: 1614–1619.
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D, Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ, Adams J et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3071–3076.
Ma MH, Yang HH, Parker K, Manyak S, Friedman JM, Altamirano C et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 markedly enhances sensitivity of multiple myeloma tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1136–1144.
Crowley J, Jacobson J, Alexanian R . Standard-dose therapy for multiple myeloma: The Southwest Oncology Group experience. Semin Hematol 2001; 38: 203–208.
Zheng B, Georgakis GV, Li Y, Bharti A, McConkey D, Aggarwal BB et al. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in Hodgkin disease cell lines is independent of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB mutations or activation of the CD30, CD40, and RANK receptors. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 3207–3215.
Dimmeler S, Breitschopf K, Haendeler J, Zeiher AM . Dephosphorylation targets Bcl-2 for ubiquitin-dependent degradation: a link between the apoptosome and the proteasome pathway. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1815–1822.
Hu W, Kavanagh JJ . Anticancer therapy targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol 2003; 4: 721–729.
Lenz HJ . Clinical update: proteasome inhibitors in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 2003; 29: 41–48.
Ding Q, Bruce-Keller AJ, Chen Q, Keller JN . Analysis of gene expression in neural cells subject to chronic proteasome inhibition. Free Rad Biol Med 2004; 36: 445–455.
Drexler HCA . Programmed cell death and the proteasome. Apoptosis 1998; 3: 1–7.
Naujokat C, Sezer O, Zinke H, Leclere A, Hauptmann S, Possinger K . Proteasome inhibitors induce caspase-dependent apoptosis and accumulation of p21WAF1/Cip1 in human immature leukemic cells. Eur J Haematol 2000; 65: 221–236.
Henderson CJ, Aleo E, Fontanini A, Maestro R, Paroni G, Brancolini C . Caspase activation and apoptosis in response to proteasome inhibitors. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 1240–1254.
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Richardson PG, Poulaki V, Tai YT, Chauhan D et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 potentiates sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to conventional chempotherapeutic agents: therapeutic applications. Blood 2003; 101: 2377–2380.
Mack PC, Davies AM, Lara PN, Gumerlock PH, Gandara DR . Integration of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (Velcade) into the therapeutic approach to lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2003; 41 (Suppl 1): S89–S96.
Fahy BN, Schlieman MG, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ . Schedule-dependent molecular effects of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res 2003; 113: 88–95.
Bogner C, Ringshausen I, Schneller F, Fend F, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Hacker G et al. Inhibition of the proteasome induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 260–268.
Ikezoe T, Yang Y, Saito T, Koeffler HP, Taguchi H . Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 down-regulates prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and induces growth arrest and apoptosis of androgen-dependent human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Sci 2004; 95: 266–270.
Johnson TR, Stone K, Nikrad M, Yeh T, Zong WX, Thompson CB et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 overcomes TRAIL resistance in Bax and caspase 9-negative or Bcl-xL overexpressing cells. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4953–4963.
Kamat AM, Karashima T, Davis DW, Lashinger L, Bar-Eli M, Millikan R et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib synergizes with gemcitabine to block the growth of human 253JB-V bladder tumors in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3: 279–290.
Davis NB, Taber DA, Ansari RH, Ryan CW, George C, Vokes EE et al. Phase II trial of PS-341 in patients with renal cell cancer: a University of Chicago phase II consortium study. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 115–119.
Wójcik C, Stoklosa T, Giermasz A, Golab J, Zagozdzon R, Kawiak J et al. Apoptosis induced in L1210 leukaemia cells by an inhibitor of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Apoptosis 1997; 2: 455–462.
Baumgartner B, Weber M, Quirling M, Fischer C, Page S, Adam M et al. Increased IkappaB kinase activity is associated with activated NF-kappaB in acute myeloid blasts. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2062–2071.
Barlogie B, Shaughnessy J, Tricot G, Jacobson J, Zangari M, Anaissie E et al. Treatment of multiple myeloma. Blood 2004; 103: 20–32.
Gatto S, Scappini B, Pham L, Onida F, Milella M, Ball G et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in Bcr/Abl-positive cell lines sensitive and resistant to imatinib mesylate. Haematologica 2003; 88: 853–863.
Guzman ML, Swiderski CF, Howard DS, Grimes BA, Rossi RM, Szilvassy SJ et al. Preferential induction of apoptosis for primary human leukemic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 16220–16225.
Fernandez Y, Verhaegen M, Miller TP, Rush JL, Steiner P, Opipari AW et al. Differential regulation of Noxa in normal melanocytes and melanoma cells by proteasome inhibition: therapeutic implications. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6294–6304.
Orlowski RZ . The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Diff 1999; 6: 303–313.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by grants of the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC), National Research Council (CNR, Grant CU03.00416) and the Italian Ministry of Health (Ricerca Finalizzata).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Servida, F., Soligo, D., Delia, D. et al. Sensitivity of human multiple myelomas and myeloid leukemias to the proteasome inhibitor I. Leukemia 19, 2324–2331 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403987
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403987
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
(Immuno)proteasomes as therapeutic target in acute leukemia
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2017)
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of the novel antimyeloma agents perifosine, bortezomib and lenalidomide against different cell lines
Investigational New Drugs (2012)
-
Leukemia stem cells
Annals of Hematology (2011)
-
Up-regulation of p21 and TNF-α is mediated in lycorine-induced death of HL-60 cells
Cancer Cell International (2010)
-
Critical molecular pathways in cancer stem cells of chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2010)