Abstract
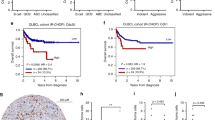
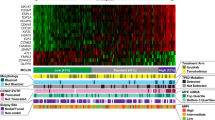
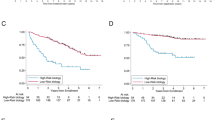
Nodal mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a well-defined entity, but non-nodal leukemic cyclin D1 positive lymphoproliferative disorders have been reported and their relationship with MCL remains controversial and their prognosis heterogeneous. We prospectively studied the expression of cyclin D1 in CD5 positive leukemic B lymphoproliferative disorders at diagnosis and identified 65 cases overexpressing cyclin D1. We did not distinguish any clinical or biological criteria allowing one to identify a non-MCL group. Multivariate analysis identified age, anemia and p27kip1 expression as independent prognostic factors of survival. By univariate analysis, p27kip1 high expression proved to be the strongest predictor of prolonged survival. The median survival of p27 low expressors was 30 months, while it was not reached for p27 high expressors. A high level of p27 expression was often found associated with the absence of nodal involvement and the presence of somatic mutations, but neither of them was restricted to the p27 high expression group. In conclusion, we hypothesize that MCL and these cyclin D1 positive leukemic lymphoproliferative disorders represent a continuous spectrum of diseases. Determination of p27 expression level appears as a routine applicable test allowing identification of a subset of patients who could be considered for different therapeutic approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barista I, Romaguera JE, Cabanillas F . Mantle-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol 2001; 2: 141–148.
Garcia-Conde J, Cabanillas F . Mantle cell lymphoma: a lymphoproliferative disorder associated with aberrant function of the cell cycle. Leukemia 1996; 10: s78–s83.
Velders GA, Kluin-Nelemans JC, De Boer CJ, Hermans J, Noordijk EM, Schuuring E et al. Mantle-cell lymphoma: a population-based clinical study. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 1269–1274.
Molina TJ, Delmer A, Cymbalista F, Le Tourneau A, Perrot JY, Ramond S et al. Mantle cell lymphoma, in leukaemic phase with prominent splenomegaly. A report of eight cases with similar clinical presentation and aggressive outcome. Virchows Arch 2000; 437: 591–598.
Levy V, Ugo V, Delmer A, Tang R, Ramond S, Perrot J et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression allows identification of an aggressive subset of leukemic lymphoproliferative disorder. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1343–1351.
Criel A, Pittaluga S, Verhoef G, Wlodarska I, Meeus P, Mecucci C et al. Small B cell NHL and their leukemic counterpart: differences in subtyping and assessment of leukemic spread. Leukemia 1996; 10: 848–853.
Swerdlow SH, Zukerberg LR, Yang WI, Harris NL, Williams ME . The morphologic spectrum of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas with BCL1/cyclin D1 gene rearrangements. Am J Surg Pathol 1996; 20: 627–640.
Dascalescu C, Gressin R, Callanan M, Sotto JJ, Leroux D . t(11;14)(q13;q32): chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or mantle cell leukaemia? Br J Haematol 1996; 95: 572–573.
Neilson JR, Fegan CD, Milligan DW . Mantle cell leukaemia? Br J Haematol 1996; 93: 494–495.
Montserrat E . Chronic lymphoproliferative disorders. Curr Opin Oncol 1997; 9: 34–41.
Wong KF, Chan JK, So JC, Yu PH . Mantle cell lymphoma in leukemic phase: characterization of its broad cytologic spectrum with emphasis on the importance of distinction from other chronic lymphoproliferative disorders. Cancer 1999; 86: 850–857.
Orchard J, Garand R, Davis Z, Babbage G, Sahota S, Matutes E et al. A sub-set of t(11;14) lymphoma with mantle cell features displays mutated IgVH genes and includes patients with good prognosis, non-nodal disease. Blood 2003; 27: 27.
Bosch F, Lopez-Guillermo A, Campo E, Ribera JM, Conde E, Piris MA et al. Mantle cell lymphoma: presenting features, response to therapy, and prognostic factors. Cancer 1998; 82: 567–575.
Hernandez L, Fest T, Cazorla M, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bosch F, Peinado MA et al. p53 gene mutations and protein overexpression are associated with aggressive variants of mantle cell lymphomas. Blood 1996; 87: 3351–3359.
Bernard M, Gressin R, Lefrere F, Drenou B, Branger B, Caulet-Maugendre S et al. Blastic variant of mantle cell lymphoma: a rare but highly aggressive subtype. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1785–1791.
Pinyol M, Cobo F, Bea S, Jares P, Nayach I, Fernandez PL et al. p16(INK4a) gene inactivation by deletions, mutations, and hypermethylation is associated with transformed and aggressive variants of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Blood 1998; 91: 2977–2984.
Swerdlow SH, Williams ME . From centrocytic to mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic and molecular review of 3 decades. Hum Pathol 2002; 33: 7–20.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Magnac C, Porcher R, Davi F, Nataf J, Payelle-Brogard B, Tang RP et al. Predictive value of serum thymidine kinase level for Ig-V mutational status in B-CLL. Leukemia 2003; 17: 133–137.
Hummel M, Tamaru J, Kalvelage B, Stein H . Mantle cell (previously centrocytic) lymphomas express VH genes with no or very little somatic mutations like the physiologic cells of the follicle mantle. Blood 1994; 84: 403–407.
Thorselius M, Walsh S, Eriksson I, Thunberg U, Johnson A, Backlin C et al. Somatic hypermutation and V(H) gene usage in mantle cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 2002; 68: 217–224.
Camacho FI, Algara P, Rodriguez A, Ruiz-Ballesteros E, Mollejo M, Martinez N et al. Molecular heterogeneity in MCL defined by the use of specific VH genes and the frequency of somatic mutations. Blood 2003; 101: 4042–4046.
Kienle D, Kroeber A, Katzenberger T, Ott G, Leupolt E, Barth TF et al. VH mutation status and VDJ rearrangement structure in mantle cell lymphoma: correlation with genomic aberrations, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Blood 2003; 3: 3.
Walsh SH, Thorselius M, Johnson A, Soderberg O, Jerkeman M, Bjorck E et al. Mutated VH genes and preferential VH3-21 use define new subsets of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2003; 101: 4047–4054.
Andersen NS, Donovan JW, Borus JS, Poor CM, Neuberg D, Aster JC et al. Failure of immunologic purging in mantle cell lymphoma assessed by polymerase chain reaction detection of minimal residual disease. Blood 1997; 90: 4212–4221.
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon M, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM et al. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-β and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994; 8: 9–22.
Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM . Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science 1996; 272: 877–880.
Sgambato A, Cittadini A, Faraglia B, Weinstein IB . Multiple functions of p27(Kip1) and its alterations in tumor cells: a review. J Cell Physiol 2000; 183: 18–27.
Slingerland J, Pagano M . Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell Physiol 2000; 183: 10–17.
Kudoh S, Kumaravel TS, Kuramavel B, Eguchi M, Asaoku H, Dohy H et al. Protein expression of cell cycle regulator, p27Kip1, correlates with histopathological grade of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 1999; 90: 1262–1269.
Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC et al. p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am J Pathol 1999; 154: 313–323.
Sanchez-Beato M, Saez AI, Martinez-Montero JC, Sol Mateo M, Sanchez-Verde L, Villuendas R et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27KIP1 in lymphoid tissue: p27KIP1 expression is inversely proportional to the proliferative index. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: 151–160.
Steeg PS, Abrams JS . Cancer prognostics: past, present and p27. Nat Med 1997; 3: 152–154.
Izban KF, Alkan S, Singleton TP, Hsi ED . Multiparameter immunohistochemical analysis of the cell cycle proteins cyclin D1, Ki-67, p21WAF1, p27KIP1, and p53 in mantle cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000; 124: 1457–1462.
Kremer M, Dirnhofer S, Nickl A, Hoefler H, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Fend F . p27(Kip1) immunostaining for the differential diagnosis of small b-cell neoplasms in trephine bone marrow biopsies. Mod Pathol 2001; 14: 1022–1029.
Vrhovac R, Delmer A, T&ang RP, Parie JP, Zittoun R, Marie JP . Prognostic significance of the cell cycle inhibitor p27kip1 in chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1998; 91: 4694–4700.
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JWE (eds). Mature B-cell neoplasms. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press, 2001, p 346.
Matutes E, Owusu-Ankomah K, Morilla R, Garcia Marco J, Houlihan A, Que TH et al. The immunological profile of B-cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia 1994; 8: 1640–1645.
Mitelman F . ISCN (1995) An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Basel: S Karger, 1995.
Uchimaru K, Taniguchi T, Yoshikawa M, Asano S, Arnold A, Fujita T et al. Detection of cyclin D1 (bcl-1, PRAD1) overexpression by a simple competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay in t(11;14)(q13;q32)-bearing B-cell malignancies and/or mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 1997; 89: 965–974.
Leonard JP, Schattner EJ, Coleman M . Biology and management of mantle cell lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol 2001; 13: 342–347.
Argatoff LH, Connors JM, Klasa RJ, Horsman DE, Gascoyne RD . Mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 80 cases. Blood 1997; 89: 2067–2078.
Savilo E, Campo E, Mollejo M, Pinyol M, Piris MA, Zukerberg LR et al. Absence of cyclin D1 protein expression in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Mod Pathol 1998; 11: 601–606.
Oertel J, Kingreen D, Busemann C, Stein H, Dorken B . Morphologic diagnosis of leukaemic B-lymphoproliferative disorders and the role of cyclin D1 expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2002; 128: 182–188.
Gong JZ, Lagoo AS, Peters D, Horvatinovich J, Benz P, Buckley PJ . Value of CD23 determination by flow cytometry in differentiating mantle cell lymphoma from chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 2001; 116: 893–897.
DiRaimondo F, Albitar M, Huh Y, O'Brien S, Montillo M, Tedeschi A et al. The clinical and diagnostic relevance of CD23 expression in the chronic lymphoproliferative disease. Cancer 2002; 94: 1721–1730.
Stilgenbauer S, Bullinger L, Lichter P, Dohner H . Genetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: genomic aberrations and V(H) gene mutation status in pathogenesis and clinical course. Leukemia 2002; 16: 993–1007.
Fais F, Ghiotto F, Hashimoto S, Sellars B, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated antigen receptors. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1515–1525.
Evans WE, Cheok M, Yang W, Sherr CJ . Expression arrays illuminate a way forward for mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 100–102.
Rivard N, L'Allemain G, Bartek J, Pouyssegur J . Abrogation of p27Kip1 by cDNA antisense suppresses quiescence (G0 state) in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 18337–18341.
Sanhes L, Tang R, Delmer A, DeCaprio JA, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F . Fludarabine-induced apoptosis of B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells includes early cleavage of p27kip1 by caspases. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1104–1111.
LaBaer J, Garrett MD, Stevenson LF, Slingerland JM, Sandhu C, Chou HS et al. New functional activities for the p21 family of CDK inhibitors. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 847–862.
Montagnoli A, Fiore F, Eytan E, Carrano AC, Draetta GF, Hershko A et al. Ubiquitination of p27 is regulated by Cdk-dependent phosphorylation and trimeric complex formation. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 1181–1189.
Sheaff RJ, Groudine M, Gordon M, Roberts JM, Clurman BE . Cyclin E-CDK2 is a regulator of p27Kip1. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 1464–1478.
Xu X, Nakano T, Wick S, Dubay M, Brizuela L . Mechanism of Cdk2/Cyclin E inhibition by p27 and p27 phosphorylation. Biochemistry 1999; 38: 8713–8722.
Sherr CJ . The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 3689–3695.
Alessandrini A, Chiaur DS, Pagano M . Regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 by degradation and phosphorylation. Leukemia 1997; 11: 342–345.
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M . SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1: 193–199.
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Davies-Hill T, Fend F, Calzada-Wack J, Sorbara L, Campo E et al. Sequestration of p27Kip1 protein by cyclin D1 in typical and blastic variants of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL): implications for pathogenesis. Blood 2003; 101: 3181–3187.
Tsvetkov LM, Yeh KH, Lee SJ, Sun H, Zhang H . p27(Kip1) ubiquitination and degradation is regulated by the SCF(Skp2) complex through phosphorylated Thr187 in p27. Curr Biol 1999; 9: 661–664.
Lim MS, Adamson A, Lin Z, Perez-Ordonez B, Jordan RC, Tripp S et al. Expression of Skp2, a p27(Kip1) ubiquitin ligase, in malignant lymphoma: correlation with p27(Kip1) and proliferation index. Blood 2002; 100: 2950–2956.
Chiarle R, Budel LM, Skolnik J, Frizzera G, Chilosi M, Corato A et al. Increased proteasome degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 is associated with a decreased overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2000; 95: 619–626.
Chiarle R, Fan Y, Piva R, Boggino H, Skolnik J, Novero D et al. S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma inversely correlates with p27 expression and defines cells in S phase. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 1457–1466.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support of PHRC97 ‘Etude multicentrique des SLPC inclassables’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Letestu, R., Ugo, V., Valensi, F. et al. Prognostic impact of p27KIP1 expression in cyclin D1 positive lymphoproliferative disorders. Leukemia 18, 953–961 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403337
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403337
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Potential effects of CRM1 inhibition in mantle cell lymphoma
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research (2012)
-
Topoisomerase IIα as a prognostic factor in mantle cell lymphoma
Leukemia (2004)