Abstract
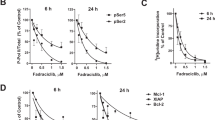
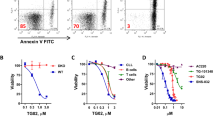
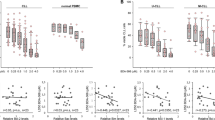
A new class of cell cycle inhibitors is currently entering clinical trials. These drugs exert their activity by inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk) and induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells. Roscovitine, a cdk2-inhibitor that is in preclinical evaluation, induced apoptosis in B-CLL cells at doses that were not cytotoxic for normal human B cells. At 20 μ M, Roscovitine induced apoptosis in 21 of 28 B-CLL samples and was equally effective in zap-70-positive or -negative samples. Caspase-3 was cleaved in B-CLL cells exposed to Roscovitine and the pancaspase inhibitor z.VAD.fmk-blocked Roscovitine-induced apoptosis. Expression of the proapoptotic protein Bak was increased and Bax cleavage and conformational change was observed in Roscovitine-treated B-CLL cells. Antiapoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and XIAP were downregulated, but the expression of Bcl-2 remained unchanged. In contrast to previous reports in cancer cell lines, Roscovitine treatment was not accompanied by nuclear accumulation of p53. Cyc202 (R-Roscovitine) is in early clinical trials in cancer patients. Given its powerful effects on zap-70-positive and -negative B-CLL cells, but not on normal lymphocytes, Roscovitine might be an attractive drug to be tested in this incurable disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA . Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin 2000; 50: 7–33.
Caligaris-Cappio F, Hamblin TJ . B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a bird of a different feather. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 399–408.
Granziero L, Ghia P, Circosta P, Gottardi D, Strola G, Geuna M et al. Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001; 97: 2777–2783.
Wendtner CM, Schmitt B, Wilhelm M, Dreger P, Montserrat E, Emmerich B et al. Redefining the therapeutic goals in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: towards an evidence-based, risk-adapted therapy. Ann Oncol 1999; 10: 505–509.
Mavromatis B, Cheson BD . Monoclonal antibody therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1874–1881.
Dreger P, Montserrat E . Autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 985–992.
Kitada S, Andresen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S et al. Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses. Blood 1998; 91: 3379–3389.
Schimmer AD, Munk-Pedersen I, Minden MD, Reed JC . Bcl-2 and apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2003; 4: 211–218.
Pedersen IM, Kitada S, Leoni LM, Zapata JM, Karras JG, Tsukada N et al. Protection of CLL B cells by a follicular dendritic cell line is dependent on induction of Mcl-1. Blood 2002; 100: 1795–1801.
Thomas A, El Rouby S, Reed JC, Krajewski S, Silber R, Potmesil M et al. Drug induced apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: relationship between p53 gene. Oncogene 1996; 12: 1055–1062.
Bannerji R, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Pearson M, Young D, Reed JC et al. Apoptotic-regulatory complement-protecting protein expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: relationship to in vivo rituximab resistance. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1466–1471.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, Yu X et al. Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1639–1647.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1765.
Vrhovac R, Delmer A, Tang R, Marie JP, Zittuon R, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F . Prognostic significance of the cell cycle inhibitor p27 in chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1998; 91: 4694–4700.
Byrd JC, Shinn C, Waselenko JK, Fuchss EJ, Lehman TA, Nguyen PL et al. Flavopiridol induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via activation of caspase 3 without evidence of bcl-2 modulation or dependence of functional p53. Blood 1998; 92: 3804–3816.
Kitada S, Zapata JM, Andreeff M, Reed JC . Protein kinase inhibitors flavopiridol and 7-hydroxy-staurosporine down-regulate antiapoptosis proteins in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2000; 96: 393–397.
Kouroukis CT, Belch A, Crump M, Eisenhauer E, Gascoyne RD, Meyer R et al. National Cancer Institute of Canada. Flavopiridol in untreated or relapsed mantle-cell lymphoma: results of a phase II study of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1740–1745.
Vesely J, Havlicek L, Strnad M, Blow JJ, Donella-Deana A, Pinna L et al. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues. Eur J Biochem 1994; 224: 771–786.
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP, Blow JJ, Inagaki N et al. Biochemical and cellular effects of Roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem 1997; 243: 527–536.
Mgbonyebi OP, Russo J, Russo IH . Roscovitine induces cell death and morphological changes indicative of apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 1999; 15: 1903–1910.
Edamatsu H, Gau CL, Nemoto T, Guo L, Tamanoi F . Cdk inhibitors, Roscovitine and olomoucine, synergize with farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTI) to induce efficient apoptosis of human cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3059–3068.
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M, Cohen P . The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors; an update. Biochem J 2003; 371: 199–204.
McClue SJ, Blake D, Clarke R, Cowan A, Cummings L, Fischer PM et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor properties of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-Roscovitine). Int J Cancer 2002; 102: 463–468.
Ljungman M, Paulsen MT . The cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor Roscovitine inhibits RNA synthesis and triggers nuclear accumulation of p53 that is unmodified at Ser15 and Lys382. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 60: 785–789.
David-Pfeuty T . Potent inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 induce nuclear accumulation of wild type p53 and nucleolar fragmentation in human untransformed and tumor derived cells. Oncogene 1998; 18: 7409–7422.
Decker T, Schneller F, Sparwasser T, Tretter T, Lipford GB, Wagner H et al. Immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides cause proliferation, cytokine secretion and an immunogenic phenotype in B-CLL patients. Blood 2000; 95: 999–1006.
Bogner C, Schneller F, Hipp S, Ringshausen I, Peschel C, Decker T . Cycling B-CLL cells are highly susceptible to inhibition of the proteasome: involvement of p27, early D-type cyclins, Bax and caspase dependent and independent pathways. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 218–225.
Mackman N, Brand K, Edgington TS . Lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcriptional activation of the human tissue factor gene in THP-1 monocytic cells requires both activator protein 1 and nuclear factor kappa B binding sites. J Exp Med 1991; 174: 1517–1526.
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kremer M, Keller G, Nathrath M, Gamboa-Dominguez A, Meneses A et al. p53 mutations in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma from Mexico: association with large cell morphology and advanced disease. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 2095–2105.
Decker T, Hipp S, Ringshausen I, Bogner C, Oelsner M, Schneller F et al. Rapamycin-induced G1 arrest in cycling B-CLL cells is associated with reduced expression of cyclin D3, cyclin E, cyclin A, and survivin. Blood 2003; 101: 278–285.
Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA . Preclinical and clinical development of cyclin-dependent kinase modulators. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92: 376–387.
Senderowicz AM . Development of cyclin-dependent kinase modulators as novel therapeutic approaches for hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1–9.
Herr I, Debatin KM . Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood 2001; 98: 2603–2614.
Pettitt AR, Cawley JC . Caspases influence the mode but not the extent of cell death induced by purine analogues in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2000; 109: 800–804.
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Lopez-Guilermo A, Marce S, Esteve J, Campo E et al. Complement-mediated cell death induced by rituximab in B-CLL lymphoproliferative disorders is mediated in vitro by a caspase-independent mechanism involving the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood 2001; 98: 2771–2777.
Cory S, Adams JM . The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 647–666.
Gojo I, Zhang B, Fenton RG . The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through transcriptional repression and down-regulation of MCL-1. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3527–3538.
Wood DE, Newcomb EN . Cleavage of Bax enhances its cell death function. Exp Cell Res 2000; 256: 375–382.
Bouillet P, Strasser A . BH3-only proteins – evolutionarily conserved pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members essential for initiating programmed cell death. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 1567–1574.
Gross A, Jockel J, Wie MC, Korsmeyer SJ . Enforced dimerization of Bax results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J 2000; 17: 878–3885.
Griffiths GJ, Dubrez L, Morgan CP, Jones NA, Whitehouse J, Corfe BM et al. Cell damage-induced conformational changes of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak in vivo precede the onset of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 903–914.
Dewson G, Snowden RT, Almond JB, Dyer MJS, Cohen GM . Conformational change and mitochondrial translocation of Bax accompany proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells. Oncogene 2002; 22: 2643–2654.
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Lopez-Guilermo A, Marce S, Bosch F, Campo E et al. Spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis is mediated by conformational changes of Bax and Bak in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1810–1816.
Fischer PM, Gianella-Borradori A . CDK inhibitors in clinical development for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 2003; 12: 955–970.
Whittaker SR, Poele RT, Walton MI . Gene expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 2002; 43 (abstr. 3302).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant from the Technical University of Munich (KKF H30-97) and a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DE 771.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahntow, I., Schneller, F., Oelsner, M. et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Roscovitine induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 18, 747–755 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403295
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403295
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting MCL-1 sensitizes human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Reduction of phosphorylated Thr-161 Cdk1 level participates in roscovitine-induced Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis in rat eggs cultured in vitro
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2015)
-
A first-in-human, phase 1, dose-escalation study of dinaciclib, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, administered weekly in subjects with advanced malignancies
Journal of Translational Medicine (2013)
-
Inhibition of polyamine oxidase prevented cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in HCT 116 colon carcinoma cells
Apoptosis (2013)
-
Polyamine depletion enhances the roscovitine-induced apoptosis through the activation of mitochondria in HCT116 colon carcinoma cells
Amino Acids (2012)