Abstract
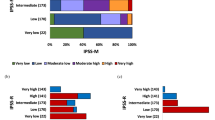
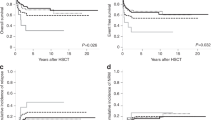
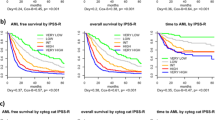
We retrospectively studied 227 patients with MDS (1) to identify the prognostic factors of survival and acute leukemia evolution in Korean patients with MDS, (2) to apply different prognostic scoring systems to the same group of patients, and (3) to compare the FAB with the WHO classification. Six scoring systems were applied to the patients, and the FAB and WHO classifications were compared. The patients’ median age was 57 years. The median survival time was 21 months, and age, dysgranulopoiesis and the IPSS cytogenetic groups were independent prognostic factors for survival. Acute leukemia occurred in 34 patients, and the cumulative incidence was 27.1% at 3 years. Marrow blast percentage was the only independent prognostic factor for acute leukemia evolution. Most scoring systems successfully discriminated risk groups for survival and acute leukemia evolution, but patient distribution into risk groups varied according to the scoring systems. Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and RAEB II seemed to have different prognoses from RA or RARS and RAEB I, respectively. In summary, our MDS patients had different disease natures from those of Western countries regarding clinical features, prognostic factors and cytogenetic profiles. Although the WHO classification seems to improve the FAB classification, further studies are warranted to validate the utility of the WHO classification before it is accepted for routine clinical use. Our study has the limitations of retrospective analysis, and our results should be verified in future prospective studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Sanz GF, Sanz MA, Greenberg PL . Prognostic factors and scoring systems in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 1998; 83: 358–368.
Maes B, Meeus P, Michaux L, Bijnens L, Boogaerts M, Hagemeijer A, De Wolf-Peeters C, Verhoef G . Application of the international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Oncol 1999; 10: 825–829.
Mufti GJ, Stevens JR, Oscier DG, Hamblin TJ, Machin D . Myelodysplastic syndrome: a scoring system with prognostic significance. Br J Haematol 1985; 59: 425–433.
Sanz GF, Sanz MA, Vallespi T, Canizo M . Two regression models and a scoring system for predicting survival and planning treatment in myelodysplastic syndrome: A multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in 370 patients. Blood 1989; 74: 395–408.
Aul C, Gatterman N, Helly A, Germing U . Primary myelodysplastic syndromes: analysis of prognostic factors in 235 patients and proposals for an improved scoring systems. Leukemia 1992; 6: 52–59.
Morel P, Hebbar M, Lai JL, Duhamel A . Cytogenetic analysis has strong prognostic value in de novo myelodysplastic syndromes and can be incorporated in a new scoring system: a report on 408 cases. Leukemia 1993; 7: 1315–1323.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G . International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Goasguen JE, Garand R, Bizet M, Bremond JL, Gardais J, Callat MP, Accard F, Chaperon J . Prognostic factors of myelodysplastic syndromes – a simplified 3-D scoring system. Leukemia Res 1990; 14: 255–262.
Worsley A, Oscier DG, Stevens J, Darlow S, Figes A, Mufti GJ, Hamblin TJ . Prognostic features of chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia: a modified Bournemouth score gives the best prediction of survival. Br J Haematol 1988; 68: 17–21.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, Lister TA, Bloomfield CD . World Health Organization of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting – Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 3835–3849.
Bennett JM . World Health Organization classification of the acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Hematol 2000; 72: 131–133.
Germing U, Gattermann N, Strupp C, Aivado M, Aul C . Validation of the WHO proposals for a new classification of primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a retrospective analysis of 1600 patients. Leukemia Res 2000; 24: 983–992.
Mitelman F (ed.). ISCN. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature, Karger: Basel 1995.
Oguma S, Yoshida Y, Uchino H, Maekawa T, Nomura T, Mizoguchi H . Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a co-operative study based on 838 cases. Anemia Study Group of the Ministry of Health and Welfare. Leukemia Res 1995; 19: 219–225.
Lee JJ, Kim HJ, Chung IJ, Kim JS, Sohn SK, Kim BS, Lee KH, Kwak JY, Park YH, Ahn JS, Park YS . Comparisons of prognostic scoring systems for myelodysplastic syndromes: a Korean multicenter study. Leukemia Res 1999; 23: 425–432.
Tien HF, Wang CH, Chuang SM, Chow JM, Lee FY, Liu MC, Chen YC, Shen MC, Lin DT, Lin KH . Cytogenetic studies, ras mutation, and clinical characteristics in primary myelodysplastic syndrome. A study on 68 Chinese patients in Taiwan. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1994; 74: 40–49.
Intragumtornchai T, Prayoonwiwat W, Swasdikul D, Suwanwela N, Chaimongkol B, Jootar S, Chansung K, Chancharunee S, Leelasiri A, Yoshida Y . Myelodysplastic syndromes in Thailand: a retrospective pathologic and clinical analysis of 117 cases. Leukemia Res 1998; 22: 453–460.
Sole F, Espinet B, Sanz GF, Cervera J, Calasanz MJ, Luno E, Prieto F, Granada I, Hernandez JM, Cigudosa JC, Diez JL, Bureo E, Marques ML, Arranz E, Rios R, Martinez Climent JA, Vallespi T, Florensa L, Woessner S . Incidence, characterization and prognostic significance of chromosomal abnormalities in 640 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Grupo Cooperativo Espanol de Citogenetica Hematologica. Br J Haematol 2000; 108: 346–356.
Balduini CL, Guarnone R, Pecci A, Centenara E, Invernizzi R, Ascari E . The myelodysplastic syndromes: predictive value of eight prognostic systems in 143 cases from a single institution. Haematologica 1999; 84: 12–16.
Vallespi T, Imbert M, Mecucci C, Preudhomme C, Fenaux P . Diagnosis, classification, and cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 1998; 83: 258–275.
Parlier V, van Melle G, Beris P, Schmidt PM, Tobler A, Haller E, Bellomo MJ . Prediction of 18-month survival in patients with primary myelodysplastic syndrome. A regression model and scoring system based on the combination of chromosome findings and the Bournemouth score. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1995; 81: 158–165.
Estey E, Keating M, Pierce S, Beran M . Application of the International Scoring System for myelodysplasia to M.D. Anderson patients. Blood 1997; 90: 2843–2844.
Toyama K, Ohyashiki K, Yoshida Y, Abe T, Asano S, Hirai H, Hirashima K, Hotta T, Kuramoto A, Kuriya S . Clinical implications of chromosomal abnormalities in 401 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a multicentric study in Japan. Leukemia 1993; 7: 499–508.
Nösslinger T, Reisner R, Koller E, Gruner H, Tuchler H, Nowotny H, Pittermann E, Pfeilstocker M . Myelodysplastic syndromes, from French–American–British to World Health Organization: comparison of classifications on 431 unselected patients from a single institution. Blood 2001; 98: 2935–2941.
Onida F, Kantarjian HM, Smith TL, Ball G, Keating MJ, Estey EH, Glassman AB, Albitar M, Kwari MI, Beran M . Prognostic factors and scoring systems in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a retrospective analysis of 213 patients. Blood 2002; 99: 840–849.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Lee, JH., Shin, YR. et al. Application of different prognostic scoring systems and comparison of the FAB and WHO classifications in Korean patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 17, 305–313 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402798
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402798
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multivariate analysis of early surgical management factors affecting posttraumatic penoscrotal avulsion injury: a level I trauma center study
BMC Urology (2021)
-
Clinico-Hematological and cytogenetic spectrum of adult myelodysplastic syndrome: The first retrospective cross-sectional study in Iranian patients
Molecular Cytogenetics (2021)
-
Incorporation of mutations in five genes in the revised International Prognostic Scoring System can improve risk stratification in the patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)
-
Clinicohematological and cytogenetic profile of myelodysplastic syndromes in Pakistan-compare and contrast
Molecular Cytogenetics (2017)
-
The utility of hematopoietic stem cell karyotyping in the diagnosis of de novo myelodysplastic syndromes
Journal of Hematopathology (2016)