Abstract
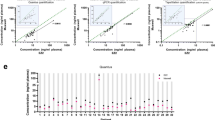
The sensitivity of assays designed to monitor minimal residual disease (MRD) by RT-PCR in leukemia depend on quality and quantity of RNA derived from peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) leukocytes. Shipment of material may lead to RNA degradation resulting in a loss of sensitivity and, potentially, false negative results. Furthermore, degradation may lead to inaccurate estimates of MRD in positive specimens. We sought to determine feasibility and efficacy of a novel blood collection and processing system which is based on integrated RNA stabilization at the time of phlebotomy (PAXgene Blood RNA Kit) by comparison with standard methods of RNA extraction (cesium chloride gradient ultracentrifugation and RNeasy Mini Kit) using unstabilized EDTA anticoagulated PB. In 26 patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) on therapy, PB was processed after a storage time at room temperature of 2 and 72 h according to these protocols. BCR-ABL, total ABL and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) mRNA transcripts of PB samples were quantified as a measure for response to therapy and RNA integrity. RNA yield expressed as the ratio of ABL transcripts after a storage time of 72 h/ABL transcripts after a storage time of 2 h at room temperature was significantly higher with the stabilizing method (median 0.40) compared to the RNeasy method using unstabilized PB (median 0.13, P = 0.01). Furthermore, ratios BCR-ABL/ABL after 72 vs 2 h still correlated well using the PAXgene method (r = 0.99, P < 0.0001) in contrast to the standard method which did not (r = 0.65, P = 0.03). Even investigation of complete cytogenetic responders with very low tumor burden showed a good correlation of ratios BCR-ABL/ABL compared to the reference method. Comparable results were achieved using G6PD transcripts as standard. We conclude that the new PAXgene stabilization method could improve RNA quality and the comparability of molecular monitoring within and between multicenter trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szczepanski T, Orfao A, van der Velden V, San Miguel JF, van Dongen JJ . Minimal residual disease in leukaemia patients Lancet Oncol 2001 2: 409–417
Hochhaus A, Weisser A, La Rosée P, Emig M, Müller MC, Saussele S, Reiter A, Kuhn C, Berger U, Hehlmann R, Cross NC . Detection and quantification of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia Leukemia 2000 14: 998–1005
van Dongen JJ, Macintyre EA, Gabert JA, Delabesse E, Rossi V, Saglio G, Gottardi E, Rambaldi A, Dotti G, Griesinger F, Parreira A, Gameiro P, Diaz MG, Malec M, Langerak AW, San Miguel JF, Biondi A . Standardized RT–PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia Leukemia 1999 13: 1901–1928
Cross NC, Feng L, Bungey J, Goldman JM . Minimal residual disease after bone marrow transplant for chronic myeloid leukaemia detected by the polymerase chain reaction Leuk Lymphoma 1993 11 (Suppl. 1): 39–43
Schoch C, Schnittger S, Bursch S, Gerstner D, Hochhaus A, Berger U, Hehlmann R, Hiddemann W, Haferlach T . Comparison of chromosome banding analysis, interphase- and hypermetaphase-FISH, qualitative and quantitative PCR for diagnosis and for follow-up in chronic myeloid leukemia: a study on 350 cases Leukemia 2002 16: 53–59
Cross NC, Melo JV, Feng L, Goldman JM . An optimized multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of BCR-ABL fusion mRNAs in haematological disorders Leukemia 1994 8: 186–189
Emig M, Saussele S, Wittor H, Weisser A, Reiter A, Willer A, Berger U, Hehlmann R, Cross NC, Hochhaus A . Accurate and rapid analysis of residual disease in patients with CML using specific fluorescent hybridization probes for real time quantitative RT-PCR Leukemia 1999 13: 1825–1832
Mannhalter C, Koizar D, Mitterbauer G . Evaluation of RNA isolation methods and reference genes for RT-PCR analyses of rare target RNA Clin Chem Lab Med 2000 38: 171–177
Burmeister T, Maurer J, Aivado M, Elmaagacli AH, Grunebach F, Held KR, Hess G, Hochhaus A, Hoppner W, Lentes KU, Lubbert M, Schafer KL, Schafhausen P, Schmidt CA, Schuler F, Seeger K, Seelig R, Thiede C, Viehmann S, Weber C, Wilhelm S, Christmann A, Clement JH, Ebener U, Enczmann J, Leo R, Schleuning M, Schoch R, Thiel E . Quality assurance in RT-PCR-based BCR/ABL diagnostics – results of an interlaboratory test and a standardization approach Leukemia 2000 14: 1850–1856
Weisser A, La Rosée P, Burmeister T, Raff T, Kneba M, Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A . Sensitivity, quality and comparability of BCR-ABL quantification by RT-PCR: results of an interlaboratory analysis Blood 2001 98 (Suppl. 1): 320a
Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Niederwieser D, Resta D, Capdeville R, Zoellner U, Talpaz M, Druker B . Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia N Engl J Med 2002 346: 645–652
Cross NC, Feng L, Chase A, Bungey J, Hughes TP, Goldman JM . Competitive polymerase chain reaction to estimate the number of BCR-ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1993 82: 1929–1936
Hochhaus A, Reiter A, Saussele S, Reichert A, Emig M, Kaeda J, Schultheis B, Berger U, Shepherd PC, Allan NC, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NC . Molecular heterogeneity in complete cytogenetic responders after interferon-alpha therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia: low levels of minimal residual disease are associated with continuing remission. German CML Study Group and the UK MRC CML Study Group Blood 2000 95: 62–66
Weisser A, La Rosee P, Paschka P, Kuhn C, Müller MC, Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A . Sample preparation as important factor for detection of minimal residual disease in CML by Real-Time PCR Onkologie 2000 23 (Suppl. 7): 97 (Abstr.)
Pahl A, Brune K . Gene expression changes in blood after phlebotomy: implications for gene expression profiling Blood 2002 100: 1094–1095
Sachs AB . Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes Cell 1993 74: 413–421
Beelman CA, Parker R . Degradation of mRNA in eukaryotes Cell 1995 81: 179–183
Brennan CM, Steitz JA . HuR and mRNA stability Cell Mol Life Sci 2001 58: 266–277
Florell SR, Coffin CM, Holden JA, Zimmermann JW, Gerwels JW, Summers BK, Jones DA, Leachman SA . Preservation of RNA for functional genomic studies: a multidisciplinary tumor bank protocol Mod Pathol 2001 14: 116–128
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by PreAnalytiX GmbH, Hombrechtikon, Switzerland, the Forschungsfonds der Fakultät für Klini- sche Medizin Mannheim der Universität Heidelberg, Germany, and the competence network ‘Acute and chronic leukemias’, sponsored by the German Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Projektträger Gesundheitsforschung; DLR eV).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, M., Merx, K., Weiβer, A. et al. Improvement of molecular monitoring of residual disease in leukemias by bedside RNA stabilization. Leukemia 16, 2395–2399 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402734
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402734
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Profound impact of sample processing delay on gene expression of multiple myeloma plasma cells
BMC Medical Genomics (2015)
-
Human blood RNA stabilization in samples collected and transported for a large biobank
BMC Research Notes (2012)
-
Increased sensitivity of next generation sequencing-based expression profiling after globin reduction in human blood RNA
BMC Genomics (2012)
-
Differential gene expression profiles are dependent upon method of peripheral blood collection and RNA isolation
BMC Genomics (2008)
-
Harmonization of BCR-ABL mRNA quantification using a uniform multifunctional control plasmid in 37 international laboratories
Leukemia (2008)