Abstract
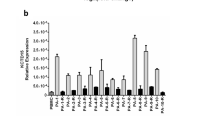
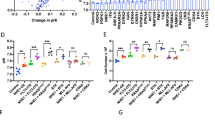
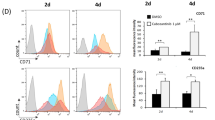
An important target in the understanding of the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemias (AML) relies on deciphering the molecular features of normal and leukemic hemopoietic progenitors. In particular, the analysis of the mechanisms involved in the regulation of cell proliferation is decisive for the establishment of new targeted therapies. To gain further insight into this topic we report herein a novel approach by analyzing the role of HERG K+ channels in the regulation of hemopoietic cell proliferation. These channels, encoded by the human ether-a-gò-gò-related gene (herg), belong to a family of K+ channels, whose role in oncogenesis has been recently demonstrated. We report here that herg is switched off in normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNC) as well as in circulating CD34+ cells, however, it is rapidly turned on in the latter upon induction of the mitotic cycle. Moreover, hergappears to be constitutively activated in leukemic cell lines as well as in the majority of circulating blasts from primary AML. Evidence is also provided that HERG channel activity regulates cell proliferation in stimulated CD34+ as well as in blast cells from AML patients. These results open new perspectives on the pathogenetic role of HERG K+ channels in leukemias.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fialkow PJ, Singer JW, Adamson JW, Vaidya K, Dow LW, Ochs J, Moohr JW . Acute nonlymphocitic leukaemia: heterogeneity of stem cell origin Blood 1981 57: 1068–1073
Blair A, Hogge DE, Sutherland HJ . Most acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo have the phenotype CD34(+)/CD71(−)/HLA-DR Blood 1998 92: 4325–4335
Bonnet D, Dick JE . Human acute myeloid leukaemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell Nat Med 1997 3: 730–737
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B, Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA, Dick JE . A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice Nature 1994 367: 645–648
Blair A, Hogge DE, Ailles LE, Lansdorp PM, Sutherland HJ . Lack of expression of Thy-1(CD90) on acute myeloid leukaemia cells with long term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo Blood 1997 89: 3104–3112
Blair A, Sutherland HJ . Primitive acute myeloid leukaemia cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo lack surface expression of c-kit(CD117) Exp Hematol 2000 28: 660–671
Jordan CT, Upchurch D, Szilvassy SJ, Guzman ML, Howard DS, Pettigrew AL, Meyerrose T, Rossi R, Grimes B, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM, Phillips GL . The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is an unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukaemia stem cells Leukemia 2000 14: 1777–1784
Guzman ML, Upchurch D, Grimes B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM, Phillips GL, Jordan CT . Expression of tumor suppressor genes interferon regulatory factor 1 and death-associated kinase in primitive acute myelogenus leukaemia cells Blood 2001 97: 2177–2179
Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM, Jordan CT . Nuclear factor-KB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenus leukaemia cells Blood 2001 98: 2301–2307
Wonderlin WF, Strobl JS . Potassium channels, proliferation and G1 progression J Membr Biol 1996 154: 91–107
Freedman BD, Price MA, Deutsch CJ . Evidence for voltage modulation of IL-2 production in mitogen-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes J Immunol 1992 149: 3784–3794
Lin CS, Boltz RC, Blake JT, Nguyen M, Talento A, Fischer PA, Springer MS, Sigal NH, Slaughter RS, Garcia ML . Voltage-gated potassium channels regulate calcium-dependent pathways involved in human T lymphocyte activation J Exp Med 1993 177: 637–645
Price M, Lee SC, Deutsch C . Charybdotoxin inhibits proliferation and interleukin 2 production in human peripheral blood lymphocytes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 1017–10175
Wang S, Melkoumian Z, Woodfork KA, Cather C, Davidson AG, Wonderlin WF, Strobl JS . Evidence for an early G1 ionic event necessary for cell cycle progression and survival in the MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell line J Cell Physiol 1998 176: 456–464
Klimatcheva E, Wonderlin WF . An ATP-sensitive K+ current that regulates progression through early G1 phase of the cell cycle in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells J Membr Biol 1999 171: 35–46
Xu B, Wilson BA, Lu L . Induction of human myeloblastic ML-1 cell G1 arrest by suppression of K+ channel activity Am J Physiol 1996 271: C2037–C2044
Wang L, Xu B, White RE, Lu L . Growth factor- mediated K+ channel activity associated with human myeloblastic ML-1 cell proliferation Am J Physiol 1997 273: C1657–1665
Xu D, Wang L, Dai W, Lu L . A requirement for K+ channel activity in growth factor-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in human myeloblastic leukemia ML-1 cells Blood 1999 94: 139–145
Nilius B, Wohlrab W . Potassium channels and regulation of proliferation in human melanoma cells J Physiol (Lond) 1992 445: 537–548
Skryma RN, Prevarskaya NB, Dufy-Barbe L, Odessa MF, Audin J, Dufy B . Potassium conductance in the androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP: involvement in cell proliferation Prostate 1997 33: 112–122
Rybalchenko V, Prevarskaya N, Van Coppenolle F, Legrand G, Lemonnier L, Le Bourhis X, Skryma R . Verapamil inhibits proliferation of LNCaP human prostate cancer cells influencing channel gating Mol Pharmacol 2001 59: 1376–1387
Yao X, Kwan HY . Activity of voltage-gated K+ channels is associated with cell proliferation and Ca2+ influx in carcinoma cells of colon cancer Life Sci 1999 65: 55–62
Shieh CC, Coghlan M, Sullivan JP, Gopalakrishnan M . Potassium channels: molecular defects, diseases and therapeutic opportunities Pharmacol Rev 2000 52: 557–593
Pardo LA, del Camino D, Sanchez A, Alves F, Bruggemann A, Beckh S, Stuhmer W . Oncogenic potential of EAG K+channels EMBO J 1999 18: 5540–5547
Binggeli R, Weinstein RC . Membrane potentials and sodium channels: hypotheses for growth regulation and cancer formation based on changes in sodium channels and gap junctions J Theor Biol 1986 123: 377–401
Warmke JW, Ganetzky B . A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 3438–3442
Sanguinetti MC, Jang C, Curran ME, Keating MT . A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel Cell 1995 81: 299–307
Arcangeli A, Bianchi L, Becchetti A, Faravelli L, Coronnello M, Mini E, Olivotto M, Wanke E . A novel inward-rectifying K+current with a cell-cycle dependence governs the resting potential of mammalian neuroblastoma cells J Physiol (London) 1995 489: 455–471
Bianchi L, Wible B, Arcangeli A, Taglialatela M, Morra F, Castaldo P, Crociani O, Rosati B, Faravelli L, Olivotto M, Wanke E . herg encodes a K+current highly conserved in tumors of different histogenesis: a selective advantage for cancer cells? Cancer Res 1998 58: 815–822
Cherubini A, Taddei GL, Crociani O, Paglierani M, Buccoliero AM, Fontana L, Noci I, Borri P, Borrani E, Giachi M, Becchetti A, Rosati B, Wanke E, Olivotto M, Arcangeli A . HERG potassium channels are more frequently expressed in human endometrial cancer as compared to non-cancerous endometrium Br J Cancer 2000 83: 1722–1729
Arcangeli A, Rosati B, Cherubini A, Crociani O, Fontana L, Ziller C, Wanke E, Olivotto M . HERG and IRK-like inward rectifier currents are sequentially expressed during neuronal development of neural crest cells and their derivatives Eur J Neurosci 1997 9: 2596–2604
Crociani O, Cherubini A, Piccini E, Polvani S, Costa L, Fontana L, Hofmann G, Rosati B, Wanke E, Olivotto M, Arcangeli A . erg gene(s) expression during development of the nervous and muscular system of quail embryos Mech Dev 2000 95: 239–243
Faravelli L, Arcangeli A, Olivotto M, Wanke E . A HERG like K+ channel in rat F11 Drg cell line: pharmacological identification and biophysical characterization J Physiol 1996 496: 13–23
Overholt JL, Ficker E, Yang T, Shams H, Bright GR, Prabhakar NR . HERG-like potassium current regulates the resting membrane potential in glomus cells of the rabbit carotid body J Neurophysiol 2000 83: 1150–1157
Bennet JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French–American–British (FAB) co-operative group Br J Haematol 1976 33: 451–458
Gattei V, Bernabei PA, Pinto A, Bezzini R, Ringressi A, Formigli L, Tanini A, Attadia V, Brandi ML . Phorbol ester induced osteoclast-like differentiation of a novel human leukemic cell line (FLG 29.1) J Cell Biol 1992 116: 437–447
Schönherr R, Rosati B, Hehl S, Rao VG, Arcangeli A, Olivotto M, Heinemann SH, Wanke E . Functional role of the slow activation property of ERG K+ channels Eur J Neurosci 1999 11: 753–760
Hofmann G, Bernabei PA, Crociani O, Cherubini A, Guasti L, Pillozzi S, Lastraioli E, Polvani S, Bartolozzi B, Solazzo V, Gragnani L, Defilippi P, Rosati B, Wanke E, Olivotto M, Arcangeli A . HERG K+channels activation during β1 integrin-mediated adhesion to fibronectin induces an up-regulation of αvβ3 integrin in the preosteoclastic leukemia cell line FLG 29.1 J Biol Chem 2001 276: 4923–4931
Lemoli RM, Tafuri A, Fortuna A, Petrucci MT, Ricciardi MR, Catani L, Rondelli D, Fogli M, Leopardi G, Ariola C, Tura S . Cycling status of CD34+ mobilized into peripheral blood of healthy donors by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Blood 1997 89: 1189–1196
Traycoff CM, Abboud MR, Laver J, Clapp DW, Hoffman R, Law P, Srour EF . Human umbilical cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cells: are they the same as their adult bone marrow counterparts? Blood Cells 1994 20: 382–390
Leitner A, Stroble H, Fischmeister G, Kurz M, Romanakis K, Haas OA, Printz D, Buchinger P, Bauer S, Gadner H . Lack of DNA synthesis among CD34+ cells in cord blood and in cytokine-mobilized blood Br J Haematol 1996 92: 255–262
Vindelov LL, Christensen IJ . A review of techniques and results obtained in one laboratory by an integrated system of methods designed for routine clinical flow cytometric DNA analysis Cytometry 1990 11: 753–770
Lozzio CB, Lozzio BB . Human chronic myelogenous leukemiacell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome Blood 1975 45: 321–334
Collins SJ, Ruscetti FW, Gallagher RE, Gallo RC . Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1978 75: 2458–2462
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J . Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor 1989
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann F, Sigworth FJ . Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches Pfluegers Arch 1981 391: 85–100
Faravelli L, Arcangeli A, Olivotto M, Wanke E . A HERG-like channel in rat F-11 DRG cell line: pharmacological identification and biophysical characterization J Physiol 1996 496: 13–23
Oh I-H, Lau A, Eaves CJ . During ontogeny primitive (CD34+CD38−) hematopoietic cells show altered expression of a subset of genes associated with early cytokine and differentiation responses of their adult counterparts Blood 2000 96: 4160–4168
Shirihai O, Merchav S, Attali B, Dagan D . K+ channel antisense oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit cytokine-induced expansion of human haemopoietic progenitors Eur J Physiol 1996 431: 632–638
Shirihai O, Attali B, Dagan D, Merchav S . Expression of two inward rectifier potassium channels is essential for differentiation of primitive human hematopoietic progenitor cells J Cell Physiol 1998 177: 197–205
Gabutti V, Pileri A, Tarocco RP, Gavosto F, Cooper EH . Proliferative potential of out of cycle leukaemic cells Nature 1969 224: 375–376
Weber-Nordt RM, Egen C, Wehinger J, Ludwig W, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Mertelsmann R, Finke J . Constitutive activation of STAT proteins in primary lymphoid and myeloid leukemia cells and in Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-related lymphoma cell lines Blood 1996 88: 809–816
Preisler HD, Perambakam S, Li B, Hsu WT, Venugopal P, Creech S, Sivaraman S, Tanaka N . Alterations in IRF1/IRF2 expression in acute myelogenous leukemia Am J Hematol 2001 68: 23–31
Vandenberg JI, Walker BD, Campbell TJ . HERG K+ channels: friend and foe Trends Pharmacol Sci 2001 22: 240–246
Wang L, Zhou P, Craig RW, Lu L . Protection from cell death by mcl-1 is mediated by membrane hyperpolarization induced by K+ channel activation J Membr Biol 1999 172: 113–120
Yu SP, Canzoniero L, Choi DW . Ion homeostasis and apoptosis Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001 13: 405–411
Olivotto M, Arcangeli A, Carlà M, Wanke E . Electric fields at the plasma membrane level: a neglected element in the mechanism of cell signalling Bioessays 1996 18: 495–504
Arcangeli A, Carlà M, Del Bene MR, Becchetti A, Wanke E, Olivotto M . Polar/apolar compounds induce leukemia cell differentiation by modulating cell surface potential Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 90: 5858–5862
Arcangeli A, Fontana L, Crociani O, Cherubini A, Hofmann G, Piccini E, Polvani S, D'Amico M, Carlà M, Olivotto M . A transient dephosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK2 characterises the early phase response of murine erytroleukemia cells to the differentiation inducer hexamethylenebisacetamide Leukemia 2000 14: 2112–2117
Hille B . Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, 2nd edn Sinauer: USA 1992
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Associazione Italiana Contro le Leucemie (AIL, Firenze) to AA and AIL Comitato 30 ore to AA, from the Ministero dell'Università e Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (MURST, Cofin ‘99) to AA, from the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) to MO and to MFB and from Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze (CARIFI). Thanks are due to D. Laura Gragnani (for performing some immunocytochemical experiments) and to Dr Roberto Bezzini (for providing normal peripheral blood buffy coats).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pillozzi, S., Brizzi, M., Balzi, M. et al. HERG potassium channels are constitutively expressed in primary human acute myeloid leukemias and regulate cell proliferation of normal and leukemic hemopoietic progenitors. Leukemia 16, 1791–1798 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402572
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402572
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Influence of Kv11.1 (hERG1) K+ channel expression on DNA damage induced by the genotoxic agent methyl methanesulfonate
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2021)
-
Memantine potentiates cytarabine-induced cell death of acute leukemia correlating with inhibition of Kv1.3 potassium channels, AKT and ERK1/2 signaling
Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
The ion channels and transporters gene expression profile indicates a shift in excitability and metabolisms during malignant progression of Follicular Lymphoma
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Macrolide antibiotics exert antileukemic effects by modulating the autophagic flux through inhibition of hERG1 potassium channels
Blood Cancer Journal (2016)
-
hERG1 potassium channel in cancer cells: a tool to reprogram immortality
European Biophysics Journal (2016)