Abstract
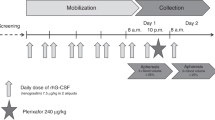
Granulocyte transfusions have been advocated by some for the treatment of severe, progressive infections in neutropenic patients who fail to respond to antimicrobial agents and recombinant hematopoietic growth factors. We conducted the current study to determine an appropriate method of granulocyte mobilization in healthy donors, and to evaluate the safety and efficacy of granulocyte transfusion therapy in patients with neutropenia-related infections. To mobilize granulocytes (n = 55), healthy normal donors were stimulated in one of the following ways: (1) dexamethasone, 3 mg/m2 intravenously 15 min prior to leukapheresis (n = 5); (2) granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), 5 μg/kg subcutaneously 12 to 14 h prior to collection (n = 37); or (3) G-CSF and dexamethasone (n = 13). The mean granulocyte yield from stimulation with G-CSF plus dexamethasone was significantly higher than from stimulation with dexamethasone or G-CSF alone. Twenty-five patients with severe neutropenia-related infections unresponsive to appropriate antimicrobial agents received a total of 55 granulocyte transfusions. The patients from whom fungi or Gram-negative organisms were isolated showed a more favorable response than those infected with Gram-positive organisms. However, the responses to the granulocyte transfusion therapy could not be correlated with the transfused dose, mobilization agents, or the 1 h or 24 h post-transfusion absolute neutrophil counts. We conclude that granulocyte transfusion therapy may be clinically useful for neutropenia-related infections by fungi or Gram-negative organisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pizzo PA . Management of fever in patients with cancer and treatment-induced neutropenia N Engl J Med 1993 328: 1323–1332
Chanock SJ, Pizzo PA . Infectious complications of patients undergoing therapy for acute leukemia: current status and future prospects Semin Oncol 1997 24: 132–140
Kim SK, Demetri GD . Chemotherapy and neutropenia Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1996 10: 377–395
Groopman JE, Molina JM, Scadden DT . Hematopoietic growth factors. Biology and clinical applications N Engl J Med 1989 321: 1449–1459
Dale DC, Liles WC, Summer WR, Nelson S . Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-role and relationships in infectious diseases J Infect Dis 1995 172: 1061–1075
Strauss RG . Therapeutic granulocyte transfusions in 1993 Blood 1993 81: 1675–1678
Klein HG, Strauss RG, Schiffer CA . Granulocyte transfusion therapy Semin Hematol 1996 33: 359–368
Dale DC, Liles WC, Price TH . Renewed interest in granulocyte transfusion therapy Br J Haematol 1997 98: 497–501
Price TH . Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized granulocyte concentrate transfusions Curr Opin Hematol 1998 5: 391–395
Schiffer CA . Granulocyte transfusion therapy Curr Opin Hematol 1999 6: 3–7
Bensinger WI, Price TH, Dale DC, Appelbaum FR, Clift R, Lilleby K, Williams B, Storb R, Thomas ED, Buckner CD . The effects of daily recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration on normal granulocyte donors undergoing leukapheresis Blood 1993 81: 1883–1888
Dignani MC, Anaissie EJ, Hester JP, O'Brien S, Vartivarian SE, Rex JH, Kantarjian H, Jendiroba DB, Lichtiger B, Andersson BS, Freireich EJ . Treatment of neutropenia-related fungal infections with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-elicited white blood cell transfusions: a pilot study Leukemia 1997 11: 1621–1630
Peters C, Minkov M, Matthes-Martin S, Potschger U, Witt V, Mann G, Hocker P, Worel N, Stary J, Klingebiel T, Gadner H . Leucocyte transfusions from rhG-CSF or prednisolone stimulated donors for treatment of severe infections in immunocompromised neutropenic patients Br J Haematol 1999 106: 689–696
Lee JJ, Chung IJ, Kim HJ, Park MR, Shin DH, Byun JR, Kwon SY, Yang DH, Kim CJ, Kook H, Hwang TJ, Kim JP, Ryang DW . Clinical effect of granulocyte transfusion therapy in neutropenia-related infection Kor J Hematol 1999 34: 326–333
Caspar CB, Seger RA, Burger J, Gmur J . Effective stimulation of donors for granulocyte transfusions with recombinant methionyl granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Blood 1993 81: 2866–2871
Jendiroba DB, Lichtiger B, Anaissie E, Reddy V, O'Brien S, Kantarjian H, Freireich EJ . Evaluation and comparison of three mobilization methods for the collection of granulocytes Transfusion 1998 38: 722–728
Hester JP, Dignani MC, Anaissie EJ, Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Freireich EJ . Collection and transfusion of granulocyte concentrates from donors primed with granulocyte stimulating factor and response of myelosuppressed patients with established infection J Clin Apheresis 1995 10: 188–193
Leitman SF, Yu M, Lekstrom J . Pair-controlled study of granulocyte colony stimulating factor plus dexamethasone for granulocytapheresis donors Transfusion 1995 35: 53S
Liles WC, Huang JE, Llewellyn C, SenGupta D, Price TH, Dale DC . A comparative trial of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and dexamethasone, separately and in combination, for the mobilization of neutrophils in the peripheral blood of normal volunteers Transfusion 1997 37: 182–187
Clarke K, Szer J, Shelton M, Coghlan D, Grigg A . Multiple granulocyte transfusions facilitating successful unrelated bone marrow transplantation in a patient with very severe aplastic anemia complicated by suspected fungal infection Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 16: 723–726
Grigg A, Lusk J, Szer J . G-CSF stimulated donor granulocyte collections for neutropenic sepsis Leuk Lymphoma 1995 18: 329–334
Adkins D, Spitzer G, Johnston M, Velasquez W, Dunphy F, Petruska P . Transfusions of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor-mobilized granulocyte components to allogeneic transplant recipients: analysis of kinetics and factors determining posttransfusion neutrophil and platelet counts Transfusion 1997 37: 737–748
Vamvakas EC, Pineda AA . Determinants of the efficacy of prophylactic granulocyte transfusions: a meta-analysis J Clin Apheresis 1997 12: 74–81
Strauss RG, Connett JE, Gale RP, Bloomfield CD, Herzig GP, McCullough J, Maguire LC, Winston DJ, Ho W, Stump DC, Miller WV, Koepke JA . A controlled trial of prophylactic granulocyte transfusions during initial induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia N Engl J Med 1981 305: 597–603
Lee JJ, Chung IJ, Kim HJ, Park MR, Yang DH, Cho SH, Kook H, Hwang TJ, Ryang DW, Song HC, Min JJ, Bom HS . Technetium-99m-HMPAO granulocyte scintigraphy as the predictor of response to granulocyte transfusion Kor J Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant 1999 4: 346a
Stroncek DF, Leonard K, Eiber G, Malech HL, Gallin JI, Leitman SF . Alloimmunization after granulocyte transfusions Transfusion 1996 36: 1009–1015
Wright DG, Robichaud KJ, Pizzo PA, Deisseroth AB . Lethal pulmonary reactions associated with the combined use of amphotericin B and leukocyte transfusions N Engl J Med 1981 304: 1185–1189
Lee JJ, Chung IJ, Ahn YK, Park MR, Shin DH, Cho JG, Kim HJ . Life-threatening paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia developed during granulocyte transfusion therapy for neutropenia-related infection Leukemia 2000 14: 1324–1325
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr TF Tisdale, NHLBI, NIH, USA and Dr Y Takaue, Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Japan for critical review during the preparation of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JJ., Chung, IJ., Park, MR. et al. Clinical efficacy of granulocyte transfusion therapy in patients with neutropenia-related infections. Leukemia 15, 203–207 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402007
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402007
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Granulocyte transfusions in children and adults with hematological malignancies: benefits and controversies
Journal of Translational Medicine (2015)
-
Randomized phase III study of granulocyte transfusions in neutropenic patients
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
G-CSF mobilised granulocyte transfusions in 32 paediatric patients with neutropenic sepsis
Supportive Care in Cancer (2006)
-
Prophylactic and interventional granulocyte transfusions in patients with haematological malignancies and life-threatening infections during neutropenia
Annals of Hematology (2005)
-
Granulocyte transfusions in the G-CSF era. Where do we stand?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)