Abstract
Hematologic relapse remains the greatest obstacle to the cure of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Recent studies have shown that patients with increased risk of relapse can be identified by measuring residual leukemic cells, called minimal residual disease (MRD), during clinical remission. Current PCR methods, however, for measuring MRD are cumbersome and time-consuming. To improve and simplify MRD assessment, we developed a real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) assay for detection of leukemic cells that harbor the TAL-1 deletion. We studied serial dilutions of leukemic DNA and found the assay had a sensitivity of detection of one leukemic cell among 100 000 normal cells. We then investigated 23 samples from eight children with ALL in clinical remission. We quantified residual leukemic cells by using the TAL-1 RQ-PCR assay and by using limiting dilution analysis. In 17 samples, both methods detected MRD levels ⩾0.001%. The percentages of leukemic cells measured by the two methods correlated well (r2 = 0.926). In the remaining six samples, both methods detected fewer than 0.001% leukemic cells. We conclude the TAL-1 RQ-PCR assay can be used for rapid, sensitive and accurate assessment of MRD in T-lineage ALL with the TAL-1 deletion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui CH, Evans WE . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia N Engl J Med 1998 339: 605–615
Pui CH . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children Curr Opin Oncol 2000 12: 3–12
Coustan-Smith E, Behm FG, Sanchez J, Boyett JM, Hancock ML, Raimondi SC, Rubnitz JE, Rivera GK, Sandlund JT, Pui CH, Campana D . Immunological detection of minimal residual disease in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Lancet 1998 351: 550–554
Cave H, van der Werff ten Bosch J, Suciu S, Guidal C, Waterkeyn C, Otten J, Bakkus M, Thielemans K, Grandchamp B, Vilmer E . Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer – Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group N Engl J Med 1998 339: 591–598
van Dongen JJ, Seriu T, Panzer-Grumayer ER, Biondi A, Pongers-Willemse MJ, Corral L, Stolz F, Schrappe M, Masera G, Kamps WA, Gadner H, van Wering ER, Ludwig WD, Basso G, de Bruijn MA, Cazzaniga G, Hettinger K, van der Does-van den Berg A, Hop WC, Riehm H, Bartram CR . Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood Lancet 1998 352: 1731–1738
Foroni L, Harrison CJ, Hoffbrand AV, Potter MN . Investigation of minimal residual disease in childhood and adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by molecular analysis Br J Haematol 1999 105: 7–24
Pui CH, Campana D . New definition of remission in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Leukemia 2000 14: 783–785
Campana D, Pui CH . Detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia: methodologic advances and clinical significance Blood 1995 85: 1416–1434
Brisco MJ, Condon J, Sykes PJ, Neoh SH, Morley AA . Detection and quantitation of neoplastic cells in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, by use of the polymerase chain reaction Br J Haematol 1991 79: 211–217
Sykes PJ, Neoh SH, Brisco MJ, Hughes E, Condon J, Morley AA . Quantitation of targets for PCR by use of limiting dilution Biotechniques 1992 13: 444–449
Ouspenskaia MV, Johnston DA, Roberts WM, Estrov Z, Zipf TF . Accurate quantitation of residual B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia by limiting dilution and a PCR-based detection system: a description of the method and the principles involved Leukemia 1995 9: 321–328
Yokota S, Hansen-Hagge TE, Ludwig WD, Reiter A, Raghavachar A, Kleihauer E, Bartram CR . Use of polymerase chain reactions to monitor minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients Blood 1991 77: 331–339
Biondi A, Yokota S, Hansen-Hagge TE, Rossi V, Giudici G, Maglia O, Basso G, Tell C, Masera G, Bartram CR . Minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of patients in continuous complete remission or with consecutive relapse Leukemia 1992 6: 282–288
Nizet Y, Van Daele S, Lewalle P, Vaerman JL, Philippe M, Vermylen C, Cornu G, Ferrant A, Michaux JL, Martiat P . Long-term follow-up of residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients in complete remission using clonogeneic IgH probes and the polymerase chain reaction Blood 1993 82: 1618–1625
Brown L, Cheng JT, Chen Q, Siciliano MJ, Crist W, Buchanan G, Baer R . Site-specific recombination of the tal-1 gene is a common occurrence in human T cell leukemia EMBO J 1990 9: 3343–3351
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM . Real time quantitative PCR Genome Res 1996 6: 986–994
Bash RO, Crist WM, Shuster JJ, Link MP, Amylon M, Pullen J, Carroll AJ, Buchanan GR, Smith RG, Baer R . Clinical features and outcome of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood with respect to alterations at the TAL1 locus: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Blood 1993 81: 2110–2117
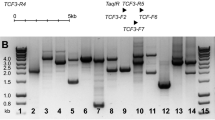
Breit TM, Beishuizen A, Ludwig WD, Mol EJ, Adriaansen HJ, van Wering ER, van Dongen JJ . tal-1 deletions in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia as PCR target for detection of minimal residual disease Leukemia 1993 7: 2004–2011
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Seriu T, Stolz F, d'Aniello E, Gameiro P, Pisa P, Gonzalez M, Bartram CR, Panzer-Grumayer ER, Biondi A, San Miguel JF, van Dongen JJ . Primers and protocols for standardized detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene rearrangements and TAL1 deletions as PCR targets: report of the BIOMED-1 CONCERTED ACTION: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia Leukemia 1999 13: 110–118
Taswell C . Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis J Immunol 1981 126: 1614–1619
Aplan PD, Lombardi DP, Reaman GH, Sather HN, Hammond GD, Kirsch IR . Involvement of the putative hematopoietic transcription factor SCL in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1992 79: 1327–1333
Delabesse E, Bernard M, Landman-Parker J, Davi F, Leboeuf D, Varet B, Valensi F, Macintyre EA . Simultaneous SIL-TAL1 RT-PCR detection of all tal(d) deletions and identification of novel tal(d) variants Br J Haematol 1997 99: 901–907
Hosler GA, Bash RO, Bai X, Jain V, Scheuermann RH . Development and validation of a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay to evaluate minimal residual disease for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and follicular lymphoma Am J Pathol 1999 154: 1023–1035
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Verhagen OJ, Tibbe GJ, Wijkhuijs AJ, de Haas V, Roovers E, van der Schoot CE, van Dongen JJ . Real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using junctional region specific TaqMan probes Leukemia 1998 12: 2006–2014
Eckert C, Landt O, Taube T, Seeger K, Beyermann B, Proba J, Henze G . Potential of LightCycler technology for quantification of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Leukemia 2000 14: 316–323
Donovan JW, Ladetto M, Zou G, Neuberg D, Poor C, Bowers D, Gribben JG . Immunoglobulin heavy-chain consensus probes for real-time PCR quantification of residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 2000 95: 2651–2658
Kwan E, Norris MD, Zhu L, Ferrara D, Marshall GM, Haber M . Simultaneous detection and quantification of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia using real-time polymerase chain reaction Br J Haematol 2000 109: 430–434
Mensink E, van de Locht A, Schattenberg A, Linders E, Schaap N, Geurts van Kessel A, De Witte T . Quantitation of minimal residual disease in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using real-time quantitative RT-PCR Br J Haematol 1998 102: 768–774
Eder M, Battmer K, Kafert S, Stucki A, Ganser A, Hertenstein B . Monitoring of BCR-ABL expression using real-time RT-PCR in CML after bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation Leukemia 1999 13: 1383–1389
Marcucci G, Livak KJ, Bi W, Strout MP, Bloomfield CD, Caligiuri MA . Detection of minimal residual disease in patients with AML1/ETO-associated acute myeloid leukemia using a novel quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay Leukemia 1998 12: 1482–1489
Sugimoto T, Das H, Imoto S, Murayama T, Gomyo H, Chakraborty S, Taniguchi R, Isobe T, Nakagawa T, Nishimura R, Koizumi T . Quantitation of minimal residual disease in t(8;21)-positive acute myelogenous leukemia patients using real-time quantitative RT-PCR Am J Hematol 2000 64: 101–106
Fujimaki S, Funato T, Harigae H, Imaizumi M, Suzuki H, Kaneko Y, Miura Y, Sasaki T . A quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction method for the detection of leukaemic cells with t(8;21) in peripheral blood Eur J Haematol 2000 64: 252–258
Cassinat B, Zassadowski F, Balitrand N, Barbey C, Rain JD, Fenaux P, Degos L, Vidaud M, Chomienne C . Quantitation of minimal residual disease in acute promyelocytic leukemia patients with t(15;17) translocation using real-time RT-PCR Leukemia 2000 14: 324–328
Luthra R, McBride JA, Cabanillas F, Sarris A . Novel 5′ exonuclease-based real-time PCR assay for the detection of t(14;18)(q32;q21) in patients with follicular lymphoma Am J Pathol 1998 153: 63–68
Olsson K, Gerard CJ, Zehnder J, Jones C, Ramanathan R, Reading C, Hanania EG . Real-time t(11;14) and t(14;18) PCR assays provide sensitive and quantitative assessments of minimal residual disease (MRD) Leukemia 1999 13: 1833–1842
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the following NIH grants: R01 CA52259, R01 CA43237 and P30 CA21765; by a Center of Excellence grant from the State of Tennessee, and by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC). We thank Ms Sharon Naron for editorial assistance with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Pan, Q., Stow, P. et al. Quantification of minimal residual disease in T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the TAL-1 deletion using a standardized real-time PCR assay. Leukemia 15, 166–170 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402000
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402000
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways to leukemia
Leukemia (2008)
-
Comparative analysis of flow cytometry and polymerase chain reaction for the detection of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2004)
-
Detection of minimal residual disease in hematologic malignancies by real-time quantitative PCR: principles, approaches, and laboratory aspects
Leukemia (2003)
-
Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia – A Europe Against Cancer Program
Leukemia (2003)
-
Quantitative Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Childhood Lymphoid Malignancies Using an Allele-Specific Oligonucleotide Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
International Journal of Hematology (2002)