Abstract
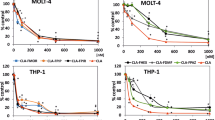
The rate of ara-cytosine triphosphate (ara-CTP) accumulation and its retention has been correlated with 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C)-mediated toxicity and clinical outcome in childhood and adult leukemia. We tested to what extent preincubation with the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors fludarabine (F-ara-A) and hydroxyurea (HU) enhanced ara-CTP levels in two human myeloid (HL-60, CMK) and two lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines (MOLT-4, BLIN-1) and also in blasts from 28 children with acute leukemia (AML: 14, ALL: 14). Incubation experiments carried out with cell lines showed F-ara-A and HU to be equipotent in increasing ara-CTP levels. The highest increase was observed in HL-60 cells whereas preincubation had no modulatory effect in MOLT-4 cells. Accordingly, modulation of intracellular ara-CTP levels differed between the subtypes of childhood acute leukemia: whereas in T-ALL (five) preincubation with F-ara-A and HU had no effect on intracellular ara-C metabolism, increased ara-CTP levels were seen in some cases of pre-B-ALL (seven). In myelogenous blasts (12) clinically relevant enhancement of ara-C toxification was regularly obtained with both, F-ara-A (1.9-fold) and HU (1.5-fold). In conclusion, our data suggest that combinations of ara-C and ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors are apt to increase ara-CTP levels depending on the individual cell type and its sensitivity towards ara-C modulators.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capizzi RL, White JC, Powell BL, Perrino F . Effect of dose on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of cytarabine Semin Hematol 1991 28: (Suppl. 4) 54–69
Kufe DW, Spriggs DR . Biochemical and cellular pharmacology of cytosine arabinoside Semin Oncol 1985 12: (Suppl. 3) 34–48
Pourquier P, Takebayashi Y, Urasaki Y, Gioffre C, Kohlhagen G, Pommier Y . Induction of topoisomerase I cleavage complexes by 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C) in vitro and in ara-C-treated cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 1885–1890
Boos J, Hohenlochter B, Schulze-Westhoff P, Schiller M, Zimmermann M, Creutzig U, Ritter J, Jurgens H . Intracellular retention of cytosine arabinoside triphosphate in blast cells from children with acute myelogenous and lymphoblastic leukemia Med Pediatr Oncol 1996 26: 397–404
Kufe D, Spriggs D, Egan EM, Munroe D . Relationships among Ara-CTP pools, formation of (Ara-C)DNA, and cytotoxicity of human leukemic cells Blood 1984 64: 54–58
Plunkett W, Iacoboni S, Keating MJ . Cellular pharmacology and optimal therapeutic concentrations of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate in leukemic blasts during treatment of refractory leukemia with high-dose 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine Scand J Haematol Suppl 1986 44: 51–59
Zuhlsdorf M, Vormoor J, Boos J . Cytosine arabinoside in childhood leukemia Int J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol 1997 4: 565–581
Coleman CN, Stoller RG, Drake JC, Chabner BA . Deoxycytidine kinase: properties of the enzyme from human leukemic granulocytes Blood 1975 46: 791–803
Colly LP, Peters WG, Richel D, Arentsen-Honders MW, Starrenburg CW, Willemze R . Deoxycytidine kinase and deoxycytidine deaminase values correspond closely to clinical response to cytosine arabinoside remission induction therapy in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia Semin Oncol 1987 14: (Suppl. 1) 257–261
Kees UR, Ford J, Dawson VM, Piall E, Aherne GW . Development of resistance to 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine after high-dose treatment in childhood lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of resistance mechanism in established cells lines Cancer Res 1989 49: 3015–3019
Donehower RC . An overview of the clinical experience with hydroxyurea Semin Oncol 1992 19: (Suppl. 9) 11–19
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Biochemical modulation of arabinosylcytosine for therapy of leukemias Leuk Lymphoma 1993 10: (Suppl) 109–114
Plunkett W, Huang P, Gandhi V . Metabolism and action of fludarabine phosphate Semin Oncol 1990 17: (Suppl. 8) 3–17
Plunkett W, Gandhi V, Huang P, Robertson LE, Yang LY, Gregoire V, Estey E, Keating MJ . Fludarabine: pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, and rationales for combination therapies Semin Oncol 1993 20: (Suppl. 7) 2–12
Walsh CT, Craig RW, Agarwal RP . Increased activation of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine by hydroxyurea in L1210 cells Cancer Res 1980 40: 3286–3292
Gandhi V, Nowak B, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Modulation of arabinosylcytosine metabolism by arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine in lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implications for combination therapy Blood 1989 74: 2070–2075
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Fludarabine potentiates metabolism of cytarabine in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia during therapy J Clin Oncol 1993 11: 116–124
Avramis VI, Wiersma S, Krailo MD, Ramilo-Torno LV, Sharpe A, Liu-Mares W, Kowck R, Reaman GH, Sato JK . Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of fludarabine and cytosine arabinoside administered as loading boluses followed by continuous infusions after a phase I/II study in pediatric patients with relapsed leukemias. The Children's Cancer Group Clin Cancer Res 1998 4: 45–52
Dinndorf PA, Avramis VI, Wiersma S, Krailo MD, Liu-Mares W, Seibel NL, Sato JK, Mosher RB, Kelleher JF, Reaman GH . Phase I/II study of idarubicin given with continuous infusion fludarabine followed by continuous infusion cytarabine in children with acute leukemia: a report from the Children's Cancer Group J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2780–2785
Estey E, Plunkett W, Gandhi V, Rios MB, Kantarjian H, Keating MJ . Fludarabine and arabinosylcytosine therapy of refractory and relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia Leuk Lymphoma 1993 9: 343–350
Fleischhack G, Hasan C, Graf N, Mann G, Bode U . IDA-FLAG (idarubicin, fludarabine, cytarabine, G-CSF), an effective remission-induction therapy for poor-prognosis AML of childhood prior to allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplantation: experiences of a phase II trial Br J Haematol 1998 102: 647–655
Suki S, Kantarjian H, Gandhi V, Estey E, O'Brien S, Beran M, Rios MB, Plunkett W, Keating M . Fludarabine and cytosine arabinoside in the treatment of refractory or relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia Cancer 1993 72: 2155–2160
Visani G, Tosi P, Zinzani PL, Manfroi S, Ottaviani E, Testoni N, Clavio M, Cenacchi A, Gamberi B, Carrara P . FLAG (fludarabine + high-dose cytarabine + G-CSF): an effective and tolerable protocol for the treatment of ‘poor risk’ acute myeloid leukemias Leukemia 1994 8: 1842–1846
Donehower RC, Karp JE, Burke PJ . Pharmacology and toxicity of high-dose cytarabine by 72-hour continuous infusion Cancer Treat Rep 1986 70: 1059–1065
Kubota M, Takimoto T, Tanizawa A, Akiyama Y, Mikawa H . Differential modulation of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine metabolism by hydroxyurea in human leukemic cell lines Biochem Pharmacol 1988 37: 1745–1749
Plagemann PG, Marz R, Wohlhueter RM . Transport and metabolism of deoxycytidine and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine into cultured Novikoff rat hepatoma cells, relationship to phosphorylation, and regulation of triphosphate synthesis Cancer Res 1978 38: 978–989
Rauscher F, Cadman E . Biochemical and cytokinetic modulation of L1210 and HL-60 cells by hydroxyurea and effect on 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine metabolism and cytotoxicity Cancer Res 1983 43: 2688–2693
Schilsky RL, Ratain MJ, Vokes EE, Vogelzang NJ, Anderson J, Peterson BA . Laboratory and clinical studies of biochemical modulation by hydroxyurea Semin Oncol 1992 19: (Suppl. 9) 84–89
Streifel JA, Howell SB . Synergisticinteraction between 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine, thymidine, and hydroxyurea against human B cells and leukemic blasts in vitro Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1981 78: 5132–5136
Gallagher R, Collins S, Trujillo J, McCredie K, Ahearn M, Tsai S, Metzgar R, Aulakh G, Ting R, Ruscetti F et al. Characterization of the continuous, differentiating myeloid cell line (HL-60) from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1979 54: 713–733
Minowada J, Onuma T, Moore GE . Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes J Natl Cancer Inst 1972 49: 891–895
Sato T, Fuse A, Eguchi M, Hayashi Y, Ryo R, Adachi M, Kishimoto Y, Teramura M, Mizoguchi H, Shima Y . Establishment of a human leukaemic cell line (CMK) with megakaryocytic characteristics from a Down's syndrome patient with acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia Br J Haematol 1989 72: 184–190
Wormann B, Anderson JM, Liberty JA, Gajl-Peczalska K, Brunning RD, Silberman TL, Arthur DC, LeBien TW . Establishment of a leukemic cell model for studying human pre-B to B cell differentiation J Immunol 1989 142: 110–117
Gandhi V, Kemena A, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Fludarabine infusion potentiates arabinosylcytosine metabolism in lymphocytes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia Cancer Res 1992 52: 897–903
Rossig C, Freund A, Mayer G, Hohenlochter B, Gescher A, Jurgens H, Boos J . Comparison of hydroxyurea, fludarabine and cladarabine in modulating ara-C pharmacology in the ara-C sensitive and resistant HL-60 and HL-60/Ara-C cell lines. In: Hiddemann W (ed) Acute Leukemias VII^Experimental Approaches and Novel Therapies Springer Verlag: Berlin, Heidelberg 1998 pp 645–650
Gandhi V, Plunkett W . Modulation of arabinosylnucleoside metabolism by arabinosylnucleotides in human leukemia cells Cancer Res 1988 48: 329–334
Boos J . A simple isocratic ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate for intracellular drug-monitoring and in vitro incubation assays J Pharm Biomed Anal 1991 9: 47–52
Avramis VI, Wiersma S, Krailo MD, Ramilo-Torno LV, Sharpe A, Liu-Mares W, Kowck R, Reaman GH, Sato JK . Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of fludarabine and cytosine arabinoside administered as loading boluses followed by continuous infusions after a phase I/II study in pediatric patients with relapsed leukemias. The Children's Cancer Group Clin Cancer Res 1998 4: 45–52
Rayappa C, McCulloch EA . A cell culture model for the treatment of acute myeloblastic leukemia with fludarabine and cytosine arabinoside Leukemia 1993 7: 992–999
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Federal Department of Research and Technology (No. 01EC9401). We thank Mrs G Braun-Munzinger for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlmann, M., Lanvers, C., Lümkemann, K. et al. Modulation of ara-CTP levels by fludarabine and hydroxyurea in leukemic cells. Leukemia 15, 69–73 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401992
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401992