Abstract
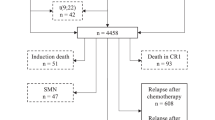
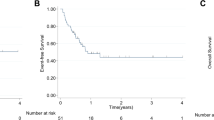
The rapidity of response to induction therapy is emerging as an important prognostic factor in children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). We studied the relationship between rapidity of reduction in peripheral blood blast count and treatment outcome in children with T cell ALL (T-ALL). Initial systemic chemotherapy included prednisone, vincristine, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. A Cox analysis evaluated the correlation between the length of time that the peripheral blood absolute blast count (ABC) remained above 1000/mm3 following the start of treatment and event-free survival (efs). data were available for 281 patients. patients for whom the abc remained >1000/mm3 for 3 or more days following administration of intensive therapy had an estimated 5-year EFS of 34.2% (s.e. = 7.2) vs 58.3% (3.5) for those whose ABC was <1000/mm3 within 0–2 days, with a hazard ratio (HR) of failure of 2.03 (95% CI = 1.35–3.06, P < 0.001) for the slower responding patients. pre-treatment of some type (usually with prednisone) occurred in 128 patients (average duration 1.7 days). when this was accounted for, patients with an abc >1000/mm3 for 5 or more days following the start of treatment of any kind had a HR for failure of 2.27 (95% CI = 1.38–3.72, P < 0.001) compared to those responding within 0–4 days. inclusion of other clinical and biological factors in a multivariate analysis did not alter the prognostic importance of slower blast clearance. pediatric patients with t-all who have a circulating blast count >1000/mm3 at diagnosis and a relatively slower response to initial treatment are at increased risk of treatment failure. Rapidity of response may therefore be a clinically useful prognostic factor for patients with T-ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui C-H . Childhood leukemias New Engl J Med 1995 332: 1618–1630
Pui C-H, Behm FG, Crist WM . Clinical and biologic relevance of immunological marker studies in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1993 82: 343–362
Pui C-H, Crist WM, Look AT . Biological and clinical significance of cytogenetic abnormalities in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1990 76: 1449–1463
Miller DR, Coccia PF, Bleyer WA, Lukens JN, Siegel SE, Sather HN, Hammond GD . Early response to induction therapy as a predictor of disease-free survival and late recurrence of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A report from the Children's Cancer Study Group J Clin Oncol 1989 7: 1807–1815
Gaynon PS, Bleyer WA, Steinherz PG, Finklestein JZ, Littman P, Miller DR, Reaman G, Sather H, Hammond GD . Day 7 marrow response and outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and unfavorable presenting features Med Pediatr Oncol 1990 18: 273–279
Hutchinson R, Bertolone S, Cooper H, Roskos K, Wells L, Heerema N, Tannous R, Neerhout R, Sather H, Sailer S, Hummell D, Trigg M, Hammond G . Early marrow response predicts outcome for patients with low-risk ALL: results of CCG-1881 Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1994 13: 319 (Abstr. 1051)
Steinherz PG, Gaynon PS, Breneman JC, Cherlow JM, Grossman NJ, Kersey JH, Johnstone HS, Sather HN, Trigg ME, Chappell R, Hammond D, Bleyer WA . Cytoreduction and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia – the importance of early marrow response: report from the Children's Cancer Group J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 389–398
Nachman J, Sather HN, Gaynon PS, Lukens JN, Wolff L, Trigg ME . Augmented Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster therapy abrogates the adverse prognostic significance of slow early response to induction therapy for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and unfavorable presenting features: a report from the Children's Cancer Group J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2222–2230
Riehm H, Gadner H, Henze G, Kornhuber B, Lampert F, Niethammer D, Reiter A, Schellong G . Results and significance of six randomized trials in four consecutive ALL-BFM studies Hematol Bluttransfus 1990 33: 439–450
Reiter A, Schrappe M, Ludwig W-D, Hiddeman W, Sauter S, Henze G, Zimmermann M, Lampert F, Havers W, Niethammer D, Odenwald E, Ritter J, Mann G, Welte K, Gadner H, Riehm H . Chemotherapy in 998 unselected childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Results and conclusions of the multi-center trial ALL-BFM 86 Blood 1994 84: 3122–3133
Arico M, Basso G, Mandelli F, Rizzari C, Colella R, Barisone E, Zanesco L, Rondelli R, Pession A, Masera G . Good steroid response in vivo predicts a favorable outcome in children with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Cancer 1995 75: 1684–1693
Rautonen J, Hovi L, Siimes MA . Slow disappearance of peripheral blast cells: an independent risk factor indicating poor prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1998 71: 989–991
Gajjar A, Ribero R, Hancock ML, Rivera GK, Mahmoud H, Sandlund JT, Crist WM, Pui C-H . Persistence of circulating blasts after 1 week of multi-agent chemotherapy confers a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1995 86: 1292–1295
Legrand O, Marie JP, Cadiou M, Blanc C, Ramon S, Zittoun R . Early cytoreduction: a major prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia Leuk Lymphoma 1994 15: 433–438
Uckun FM, Sensel MG, Sun L, Steinherz PG, Trigg ME, Heerema NA, Sather HN, Reaman GH, Gaynon PS . Biology and treatment of childhood T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1998 91: 735–746
Crist WM, Shuster JJ, Faletta J, Pullen DJ, Berard CW, Vietti TJ, Alvarado CS, Roper MA, Prasthofer E, Grossi CE . Clinical features and outcome in childhood T-cell leukemia–lymphoma according to stage of thymocyte differentiation: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Blood 1998 72: 1891–1897
Shuster JJ, Faletta JM, Pullen DJ, Crist WM, Humphrey GB, Dowell BL, Wharam MD, Borowitz M . Prognostic factors in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Blood 1990 75: 166–173
Uckun F, Steinherz P, Sather H, Trigg M, Arthur D, Tubergen D, Gaynon P, Reaman G . CD2 antigen expression on leukemia cells as a predictor of event-free survival after chemotherapy of T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children's Cancer Group study Blood 1996 88: 4288–4295
Uckun FM, Gaynon P, Sensel M, Nachman J, Trigg ME, Steinherz PG, Hutchinson R, Bostrom BC, Sather HN, Reaman GH . Clinical features and treatment outcome of childhood T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia according to the apparent maturational stage of T-lineage leukemic blasts: a Children's Cancer Group study J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2214–2221
Amylon MD, Shuster J, Pullen J, Berard C, Link MP, Wharam M, Katz J, Yu A, Laver J, Ravindranath Y, Kurtzberg J, Desai S, Camitta B, Murphy SB . Intensive high dose asparaginase consolidation improves survival for pediatric patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Leukemia 1999 13: 335–342
Cox DR . Regression models and life tables J R Stat Soc (B) 1972 34: 187–220
Bartolucci AA, Fraser MD . Comparative step-up and composite tests for selecting prognostic indicators associated with survival Biometrical J 1977 19: 437–448
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 1958 53: 457–481
Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P, Breslow NE, Cox DR, Howard SV, Mantel N, McPherson K, Peto J, Smith PG . Design and analysis of clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. Analysis and examples Br J Cancer 1977 35: 1–39
Wasserman R, Galili N, Ito Y, Silber JH, Reichard BA, Shane S, Womer RB, Lange B, Rovera G . Residual disease at the end of induction therapy as a predictor of relapse during therapy in childhood B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1992 10: 1879–1888
Gruhn B, Hongeng S, Yi H, Hancock ML, Rubnitz JE, Neale GAM, Kitchingman GR . Minimal residual disease after intensive induction therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia predicts outcome Leukemia 1998 12: 675–681
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffin, T., Shuster, J., Buchanan, G. et al. Slow disappearance of peripheral blood blasts is an adverse prognostic factor in childhood T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. Leukemia 14, 792–795 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401768
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401768
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Glucocorticoids attenuate the sensitivity of glucocorticoid-resistant lymphoid cells to doxorubicin via reduction in OCTN2
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2019)
-
Prediction of outcomes by early treatment responses in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study in China
BMC Pediatrics (2015)
-
Outcome of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) following induction therapy with a modified (pulsed dexamethasone rather than continuous prednisone) UKALL XII/ECOG E2993 protocol at Tawam Hospital, United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Medical Oncology (2013)
-
Having a higher blast percentage in circulation than bone marrow: clinical implications in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute lymphoid and myeloid leukemias
Leukemia (2005)
-
Immunologic monitoring in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Current Oncology Reports (2003)