Abstract
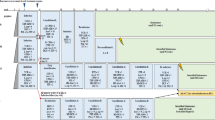
contemporary chemotherapy has significantly improved event-free survival among patients with t cell-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (t-all). unlike b-precursor all, most investigators are still using cranial radiation (crt) and are hesitant to rely solely on intrathecal therapy for t-all. in this study we assessed the effects of crt upon event-free survival and central nervous system (cns) relapses in a cohort of children with high risk features of t cell leukemia. in a series of six consecutive studies (1987–1995) patients were non-randomly assigned their cns prophylaxis per individual protocol. these protocols were based on pog 8704 which relied on rotating drug combinations (cytarabine/cyclophosphamide, teniposide/ ara-c, and vincristine/doxorubicin/6-mp/prednisone) post-induction. modifications such as high-dose cytarabine, intermediate-dose methotrexate, and the addition of g-csf, were designed to give higher cns drug levels (decreasing the need for crt), to eliminate epidophyllotoxin (decreasing the risk of secondary leukemia), and to reduce therapy-related neutropenia (pilot studies pog 9086, 9295, 9296, 9297, 9398). all patients included in this analysis qualified for pog high risk criteria, wbc >50 000/mm3 and/or CNS leukemia. Patients without CNS involvement received 16 doses of age-adjusted triple intra-thecal therapy (TIT = hydrocortisone, MTX, and cytarabine) whereas patients with CNS disease received three more doses of TIT during induction and consolidation. Patients who received CRT were treated with 2400 cGy (POG 8704) or 1800 cGy (POG 9086 and 9295). CNS therapy included CRT in 144 patients while the remaining 78 patients received no radiation by original protocol design. There were 155 males and 57 females with a median age of 8.2 years. The median WBC for the CRT+ and CRT− patients were 186 000/mm3 and 200 000/mm3, respectively. CNS involvement at diagnosis was seen in 16% of the CRT+ and 23% of the CRT− groups. The complete continuous remission rate (CCR) was not significantly different for the irradiated vs non-irradiated groups (P = 0.46). The 3-year event-free survival was 65% (s.e. 6%) and 63% (s.e. 4%) for the non-irradiated vs the radiated group. However, the 3-year CNS relapse rate was significantly higher amongst patients who did not receive CRT; 18% (s.e. 5%) vs 7% (s.e. 3%) in the irradiated group (P = 0.012). Our analysis in a non-randomized setting, suggests that CRT did not significantly correlate with event-free survival but omitting it had an adverse effect on the CNS involvement at the time of relapse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falletta JM, Shuster JJ, Crist WM, Pullen DJ, Borowitz MJ, Wharam M, Patterson R, Foreman E, Vietti TJ . Different patterns of relapse associated with three intensive treatment regimens for pediatric E-rosette positive T cell leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Leukemia 1992 6: 541–546
Amylon MD, Shuster J, Pullen J, Berard C, Link MP, Wharam M, Katz J, Yu A, Laver J, Ravindranath Y, Kurtzberg J, Desai S, Camitta B, Murphy SB . Intensive high dose asparaginase consolidation improves survival for pediatric patients with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and advanced stage lymphoblastic lymphoma: Pediatric Oncology Group study 8704 Leukemia 1999 13: 335–342
Smith M, Arthur D, Camitta B, Carroll AJ, Crist W, Gaynon P, Gelber R, Heerema N, Korn EL, Link M, Murphy S, Pui CH, Pullen J, Reaman G, Sallan SE, Sather H, Shuster J, Simon R, Trigg M, Tubergen D, Uckun F, Ungerleider R . Uniform approach to risk classification and treatment assignment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 18–24
Shuster JJ, Falletta JM, Pullen DJ, Crist WM, Humphrey GB, Dowell BL, Wharam MD, Borowitz M . Prognostic factors in childhood T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group study Blood 1990 75: 166–173
Pullen J, Boyett J, Shuster J, Crist W, Land V, Frankel L, Iyer R, Backstrom L, Van Eys J, Harris M, Ravindranath Y, Sullivan M . Extended triple intrathecal chemotherapy trial for prevention of CNS relapse in good-risk and poor-risk patients with B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group study J Clin Oncol 1993 11: 839–849
Conter V, Schrappe M, Arico’ A, Reiter A, Rizzari C, Dordelmann M, Valsecchi MG, Zimmermann M, Ludwig WD, Basso G, Masera G, Riehm H . Role of cranial radiotherapy for childhood T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with high WBC count and good response to prednisone J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2786–2791
Pui C-H, Behm FG, Singh B, Schell MJ, Williams DL, Rivera GK, Kalwinsky DK, Sandlund JT, Crist WM, Raimondi SC . Heterogeneity of presenting features and their relation to treatment outcome in 120 children with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1990 75: 174–178
Arico M, Basso G, Mandelli F, Rizzari C, Colella R, Barisone E, Zanesco L, Rondelli R, Pession A, Masera G . Good steroid response in vivo predicts a favorable outcome in children with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Cancer 1995 75: 1684–1693
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposals for the classification of the acute leukemias Br J Haematol 1976 33: 451–458
Pui C-H, Behm FG, Crist WM . Clinical and biologic relevance of immunologic marker studies in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1993 82: 343–362
Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P, Breslow NE, Cox DR, Howard SV, Mantel N, McPherson K, Peto J, Smith PG . Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. Analysis and examples Br J Cancer 1977 35: 1–39
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 1958 35: 457–481
Rivera GK, Pinkel D, Simone JV, Hancock ML, Crist WM . Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 30 years’ experience at St Jude Children's Research Hospital New Engl J Med 1993 329: 1289–1295
Rimm IJ, Li FC, Tarbell NJ, Winston DR, Sallan SE . Brain tumors after cranial irradiation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A 13-year experience from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and The Children's Hospital Cancer 1987 59: 1506–1508
Brouwers P, Poplack D . Memory and learning sequelae in long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: association with attention deficits Am J Ped Hematol/Oncol 1990 12: 174–181
Nachman J, Sather HN, Cherlow JM, Sensel MG, Gaynon PS, Lukens JN, Wolff L, Trigg ME . Response of children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with and without cranial irradiation: a report from the Children's Cancer Group J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 920–930
Pui C-H, Mahmoud HH, Rivera GK, Hancock ML, Sandlund JT, Behm FG, Head DR, Relling MV, Ribeiro PC, Rubnitz JE, Kun LE, Evans WE . Early intensification of intrathecal chemotherapy virtually eliminates central nervous system relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1999 92: 411–415
Uckun FM, Sensel MG, Sun L, Steinherz PG, Trigg ME, Heerema NA, Sather HN, Reaman GH, Gaynon PS . Biology and treatment of childhood T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1998 91: 735–746
Early AP, Preisler HD, Slocum H, Rustum YM . A pilot study of high-dose 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine for acute leukemia and refractory lymphoma: clinical response and pharmacology Cancer Res 1982 42: 1587–1594
Shapiro WR, Young DG, Mehta BM . Methotrexate distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular, and lumbar injections New Engl J Med 1975 293: 161–166
Freeman AI, Weinberg V, Brecher ML, Jones B, Glicksman AS, Sinks LF, Weil M, Pleuss H, Hananian J, Burgert EO, Gilchrist GS, Necheles T, Harris M, Kung F, Patterson RB, Maurer H, Leventhal B, Chevalier L, Forman E, Holland JF . Comparison of intermediate-dose methotrexate with cranial irradiation for the post-induction treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia in children New Engl J Med 1983 308: 477–484
Ritchey AK, Pollock BH, Lauer SJ, Andejeski Y, Barredo J, Buchanan GR . Improved survival of children with isolated CNS relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A Pediatric Oncology Group study J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 3745–3752
Thompson CB, Sanders JE, Flournoy N, Buckner CD, Thomas ED . The risks of central nervous system relapse and leukoencephalopathy in patients receiving marrow transplants for acute leukemia Blood 1986 67: 195–199
Pullen DJ, Sullivan MP, Falletta JM, Boyett JM, Humphrey GB, Starling KA, Land VJ, Dyment PG, Vats T, Duncan MH . Modified LSA2-L2 treatment in 53 children with E-rosette-positive T cell leukemia: results and prognostic factors (a Pediatric Oncology Group study) Blood 1982 60: 1159–1168
Nachman JB, Sather HN, Sensel MG, Trigg ME, Cherlow JM, Lukens JN, Wolff L, Uckun FM, Ganynon PS . Augmented post-induction therapy for children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia and a slow response to initial therapy New Engl J Med 1998 338: 1663–1671
Reiter A, Schrappe M, Ludwig WD, Hiddenmann W, Sauter S, Henze G, Zimmerman M, Lampert F, Havers W, Niethammer D et al. Chemotherapy in 998 unselected childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Results and conclusions of the multicenter trial ALL-BFM 86 Blood 1994 84: 3122–3133
Shuster JJ . Publishing clinical trials and dealing with external comparisons Control Clin Trials 1998 19: 269–270
Shuster JJ, Gieser PW . Meta-analysis and prospective meta-analysis in childhood leukemia: clinical research Ann Oncol 1996 7: 1009–1014
Valsecchi MG, Masera G . A new challenge in clinical research in childhood ALL: the prospective meta-analysis strategy for inter-group collaboration Ann Oncol 1996 7: 1005–1008
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants: CA-69177, CA-33603, CA-15525, CA-30969, CA-15989, CA-29139, and CA-39139 from the National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laver, J., Barredo, J., Amylon, M. et al. Effects of cranial radiation in children with high risk T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group report. Leukemia 14, 369–373 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401693
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401693
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biology and Treatment Paradigms in T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Older Adolescents and Adults
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2020)