Abstract
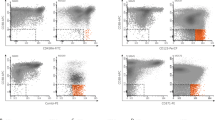
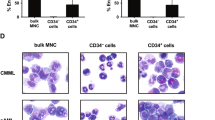
Acute myeloid leukemia arises from the clonal expansion of a malignant transformed progenitor cell. Despite intensive chemotherapy, final disease eradication is achieved by a small proportion of cases only and 50–70% of adults with AML will ultimately relapse and die from their disease. Hence residual disease below the level of morphological detectability must be assumed in clinical and morphological complete remission. CD34+/CD38− and CD34+/CD38+ subpopulations of seven patients in morphological complete remission were isolated by FACS (purity >98%) and were analyzed by conventional cytogenetics or FISH for chromosomal aberrations. In five of seven patients, clonal chromosomal abnormalities were detected in the CD34+/CD38+ subpopulation and in one patient with AML M2 (add (2)(q37)) in the most immature CD34+/CD38− stem cell compartment. One patient with AML M4Eo (inv(16),+8), showed a normal karyotype by conventional cytogenetic analysis, whereas four of 15 metaphases of the sorted CD34+/CD38+ subpopulation revealed the inversion 16. These observations underline that leukemic cells can survive intensive chemotherapy in the niche of the stem cell compartment. In some patients the sensitivity for the detection of persistent leukemic cells seems to be higher in FACS-sorted subpopulations than conventional cytogenetic analysis of the unseparated bone marrow. Immunophenotyping revealed minimal residual disease in four of the patients. Functional analysis has to be performed to investigate the leukemogenic potential of these residual cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feuring-Buske, M., Haase, D., Buske, C. et al. Clonal chromosomal abnormalities in the stem cell compartment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia in morphological complete remission. Leukemia 13, 386–392 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401300
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401300
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of chromosomal aberrations in clonal diversity and progression of acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2015)
-
Sensitive detection of tumour cells in effusions by combining cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH)
British Journal of Cancer (2004)
-
Characteristics and analysis of normal and leukemic stem cells: current concepts and future directions
Leukemia (2000)