Abstract
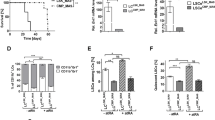
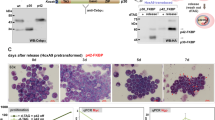
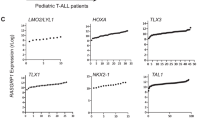
All-trans retinoic acid (RA) induces granulocytic differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells both in vivo and in vitro. In the HL-60 wild-type (WT) early promyelocytic leukemia cell line, granulocytic differentiation appears to be directly mediated by the nuclear receptor RARα. An HL-60 subline resistant to RA (HL-60 R) contains a point mutation which results in a truncation of 52 amino acids at the COOH end of RARα. Cross-talk between differentiation, clonal inhibition of growth and apoptosis was studied using HL-60 WT, HL-60 R, and HL-60 R infected by a retroviral vector containing RARα (LX) as targets, which were cultured with various retinoids, vitamin D3 analogs, HMBA, or DMSO. None of these compounds induced significant differentiation of HL-60 R and HL-60 LX, but they did induce differentiation of HL-60 WT. In contrast, retinoids inhibited the clonal proliferation of HL-60 WT, HL-60 R, and HL-60 LX. Vitamin D3 analogs including KH1060 stimulated the clonal growth of HL-60 R; but they inhibited clonal growth of HL-60 WT and LX. Levels of Bcl-2 strongly decreased in HL-60 WT and LX after treatment by retinoids, while no change in expression occurred in HL-60 R. Neither KH 1060 nor 9-cis RA induced apoptosis of HL-60 R, but these agents did induce apoptosis in HL-60 LX WT. Taken together, we showed that HL-60 R has a global defect in its ability to be induced to differentiate by a variety of pathways, not merely the retinoid pathway. Furthermore, our HL-60 models showed that inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis and differentiation can be dissociated. Clinically, these results suggest that several putative differentiation agents may have anti-cancer (antiproliferative) activities, even though they do not induce differentiation of the cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grillier, I., Umiel, T., Elstner, E. et al. Alterations of differentiation, clonal proliferation, cell cycle progression and bcl-2 expression in RARα-altered sublines of HL-60. Leukemia 11, 393–400 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400575
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400575
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enasidenib-induced differentiation promotes sensitivity to venetoclax in IDH2-mutated acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2022)
-
The pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor obatoclax promotes differentiation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells
Investigational New Drugs (2020)
-
Retinoic acid resistance in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2002)
-
Ectopic expression of Bcl-2 switches over nuclear signalling for cAMP-induced apoptosis to granulocytic differentiation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2000)