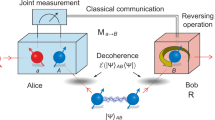
Abstract
Quantum-mechanical systems have information processing capabilities1,2 that are not possible with classical devices. One example is quantum teleportation3, in which the quantum state of a system is transported from one location to another without moving through the intervening space. But although partial implementations4,5 of quantum teleportation over macroscopic distances have been achieved using optical systems, the final stage of the teleportation procedure — which allows the complete recovery of the original state — was omitted. Here we report an experimental implementation of full quantum teleportation over interatomic distances using liquid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. We achieve teleportation of the quantum state of a carbon nucleus to a hydrogen nucleus in molecules of trichloroethylene, by exploiting natural phase decoherence of the carbon nuclei. Such a teleportation scheme may be used as a subroutine in larger quantum computations, or for quantum communication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C. H. Quantum information and computation. Phys. Today 48, 24–30 (1995).
Preskill, J. Quantum computing: pro and con. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454, 469–486 (1998).
Bennett, C. H.et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and EPR channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993).
Bouwmeester, D.et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997).
Boschi, D., Branca, S., De Martini, F., Hardy, L. & Popescu, S. Experimental realization of teleporting an unknown pure quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolski-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1121–1125 (1998).
Sakurai, J. J. Modern Quantum Mechanics(Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, (1995)).
Bennett, C. H., DiVencenzo, D. P., Smolin, J. A. & Wootters, W. K. Mixed state entanglement and quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. A 54, 3824–3851 (1996).
Cirac, J. I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H. J. & Mabuchi, H. Quantum state transfer and entanglement distribution among distant nodes in a quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221–3224 (1997).
Cory, D. G., Fahmy, A. F. & Havel, T. F. Ensemble quantum computing by NMR spectroscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1634–1639 (1997).
Ernst, R., Bodenhausen, G. & Wokaun, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions(Oxford Univ. Press, (1990)).
Grant, D. M. & Harris, R. K. (eds) Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(Wiley, New York, (1996)).
Gershenfeld, N. & Chuang, I. L. Bulk spin resonance quantum computation. Science 275, 350–356 (1997).
Cory, D. G., Price, M. D. & Havel, T. F. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: An experimentally accessible paradigm for quantum computing. Physica D 120, 82–101 (1998).
Laflamme, R., Knill, E., Zurek, W. H., Catasti, P. & Mariappan, S. V. S. NMR Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 356, 1941–1947 (1998).
Cory, D. G.et al. Experimental quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2152–2155 (1998).
Chuang, I. L., Gershenfeld, N. & Kubinec, M. Experimental implementation of fast quantum searching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 18, 3408–3411 (1998).
Jones, J. A. & Mosca, M. Implementation of a quantum algorithm on a nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computer. J. Chem. Phys. 109, 1648–1653 (1998).
Chuang, I. L., Vandersypen, L. M. K., Zhou, X. L., Leung, D. W. & Lloyd, S. Experimental realization of a quantum algorithm. Nature 393, 143–146 (1998).
Jones, J. A., Mosca, M. & Hansen, R. H. Implementation of a quantum search algorithm on a nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computer. Nature 393, 344–346 (1998).
Brassard, G., Braunstein, S. & Cleve, R. Teleportation as a quantum computation. Physica D 120, 43–47 (1998).
Zurek, W. H. Decoherence and the transition from quantum to classical. Phys. Today 44, 36–44 (1991).
Schumacher, B. W. Sending entanglement through noisy quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 54, 2614–2628 (1996).
Barnum, H., Nielsen, M. A. & Schumacher, B. W. Information transmission through a noisy quantum channel. Phys. Res. A 57, 4153–4175 (1998).
Poyatos, J. F., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Complete characterization of a quantum process: the two-bit quantum gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 390–393 (1997).
Chuang, I. L. & Nielsen, M. A. Prescription for experimental determination of the dynamics of a quantum black box. J. Mod. Opt. 44, 2455–2467 (1997).
Nielsen, M. A. & Caves, C. M. Reversible quantum operations and their application to teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 55, 2547–2556 (1997).
Furusawa, A.et al. Unconditional quantum teleportation. Science(in the press).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Cory, C. Jarzynski, J. Ye and W. Zurek for discussions, the Stable Isotope Laboratory at Los Alamos for use of their facility, and the National Security Agency and Office of Naval Research for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, M., Knill, E. & Laflamme, R. Complete quantum teleportation using nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 396, 52–55 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/23891
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/23891
This article is cited by
-
Enhancing quantum teleportation efficacy with noiseless linear amplification
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Hertz-rate metropolitan quantum teleportation
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Teleportation goes to Hertz rate
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Experimental quantum state transfer of an arbitrary single-qubit state on a cycle with four vertices using a coined quantum random walk
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Enhancing quantum teleportation: an enable-based protocol exploiting distributed quantum gates
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.