Abstract
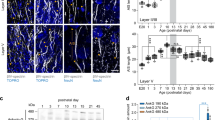
Many representations of sensory stimuli in the neocortex are arranged as topographic maps. These cortical maps are not fixed, but show experience-dependent plasticity1,2. For instance, sensory deprivation causes the cortical area representing the deprived sensory input to shrink, and neighbouring spared representations to enlarge, in somatosensory3, auditory4 or visual cortex5. In adolescent and adult animals, changes in cortical maps are most noticeable in the supragranular layers at the junction of deprived and spared cortex6,7,8,9. However, the cellular mechanisms of this experience-dependent plasticity are unclear. Long-term potentiation and depression have been implicated10,11,12, but have not been proven to be necessary or sufficient for cortical map reorganization. Short-term synaptic dynamics have not been considered. We developed a brain slice preparation involving rat whisker barrel cortex in vitro. Here we report that sensory deprivation alters short-term synaptic dynamics in both vertical and horizontal excitatory pathways within the supragranular cortex. Moreover, modifications of horizontal pathways amplify changes in the vertical inputs. Our findings help to explain the functional cortical reorganization that follows persistent changes of sensory experience.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buonomano, D. V. & Merzenich, M. M. Cortical plasticity: from synapses to maps. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 149–186 (1998).
Gilbert, C. D. Adult cortical dynamics. Physiol. Rev. 78, 467–485 (1998).
Merzenich, M. M.et al. Progression of changes following median nerve section in the cortical representation of the hand in areas 3b and 1 in adult owl and squirrel monkeys. Neuroscience 10, 639–665 (1983).
Robertson, D. & Irvine, D. Plasticity of frequency organization in auditory cortex of guinea pigs with partial unilateral deafness. J. Comp. Neurol. 282, 456–471 (1989).
Kaas, J. H.et al. Reorganization of retinotopic cortical maps in adult mammals after lesions of the retina. Science 248, 229–231 (1990).
Glazewski, S. & Fox, K. Time course of experience-dependent synaptic potentiation and depression in barrel cortex of adolescent rats. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 1714–1729 (1996).
Gilbert, C. D. & Wiesel, T. N. Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex. Nature 356, 150–152 (1992).
Fox, K. Acritical period for experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in rat barrel cortex. J. Neurosci. 12, 1826–1838 (1992).
Diamond, M. E., Huang, W. & Ebner, F. F. Laminar comparison of somatosensory cortical plasticity. Science 265, 1885–1888 (1994).
Kirkwood, A., Rioult, M. C. & Bear, M. F. Experience-dependent modification of synaptic plasticity in visual cortex. Nature 381, 526–528 (1996).
Glazewski, S., Chen, C.-M., Silva, A. & Fox, K. Requirement for α-CaMKII in experience-dependent plasticity of the barrel cortex. Science 272, 421–423 (1996).
Garraghty, P. E. & Muja, N. NMDA receptors and plasticity in adult primate somatosensory cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 367, 319–326 (1996).
Carvell, G. E. & Simons, D. J. Biometric analyses of vibrissal tactile discrimination in the rat. J. Neurosci. 10, 2638–2648 (1990).
Welker, C. & Woolsey, T. A. Structure of layer IV in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat: description and comparison with the mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 158, 437–454 (1974).
Markram, H. & Tsodyks, M. Redistribution of synaptic efficacy between neocortical pyramidal cells. Nature 382, 807–810 (1996).
Abbot, L. F., Varela, J. A., Sen, K. & Nelson, S. B. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science 275, 220–224 (1997).
Tsodyks, M. V. & Markram, H. The neural code between neocortical pyramidal neurons depends on neurotransmitter release probability. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 719–723 (1997).
McCasland, J. S. & Woolsey, T. A. High-resolution 2-deoxyglucose mapping of functional cortical columns in mouse barrel cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 278, 555–569 (1988).
Armstrong-James, M. Diamond, M. E. & Ebner, F. F. An innocuous bias in whisker use in adult rats modifies receptive fields of barrel cortex neurons. J. Neurosci. 14, 6978–6991 (1994).
Darian-Smith, C. & Gilbert, C. D. Axonal sprouting accompanies functional reorganization in adult cat striate cortex. Nature 368, 737–740 (1994).
Florence, S. L., Taub, H. B. & Kaas, J. H. Large-scale sprouting of cortical connections after peripheral injury in adult macaque monkeys. Science 282, 1117–1121 (1998).
Mason, A., Nicoll, A. & Stratford, K. Synaptic transmission between individual pyramidal neurons of the rat visual cortex in vitro. J. Neurosci. 11, 72–84 (1991).
Nicolelis, M. A. L., Baccala, L. A., Lin, R. C. S. & Chapin, J. K. Sensorimotor encoding by synchronous neural ensemble activity at multiple levels of the somatosensory system. Science 268, 1353–1358 (1995).
Stuart, G. & Sakmann, B. Amplification of EPSPs by axosomatic sodium channels in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron 15, 1065–1076 (1995).
Connors, B. W., Malenka, R. C. & Silva, L. R. Two inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and GABAAreceptor-mediated responses in neocortex of rat and cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 406, 443–468 (1988).
Dobrunz, L. E. & Stevens, C. F. Heterogeneity of release probability, facilitation, and depletion at central synapses. Neuron 18, 995–1008 (1997).
Raastad, M., Storm, J. F. & Andersen, P. Putative single quantum and single fibre excitatory postsynaptic currents show similar amplitude range and variability in rat hippocampal slices. Eur. J. Neurosci. 4, 113–117 (1992).
Volgushev, M., Voronin, L. L., Chistiakova, M., Artola, A. & Singer, W. All-or-none excitatory postsynaptic potentials in the rat visual cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 1751–1760 (1995).
Cash, S. & Yuste, R. Input summation by cultured pyramidal neurons is linear and position-independent. J. Neurosci. 18, 10–15 (1998).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Wellcome Trust Advanced Training Fellowship to G.T.F. and a grant to B.W.C. from NIH. We thank S. Patrick for technical assistance with histology; A.Akima for discussions on the optimal slicing angle; D. Pinto for checking the mathematics; and M.Bear, J. Gibson, M. Beierlein and D. Pinto for helpful comments on a earlier version of the manuscript. G.T.F. thanks R. Jones and D. Smith for encouragement with the current project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finnerty, G., Roberts, L. & Connors, B. Sensory experience modifies the short-term dynamics of neocortical synapses. Nature 400, 367–371 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/22553
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/22553
This article is cited by
-
Somatostatin-expressing interneurons modulate neocortical network through GABAb receptors in a synapse-specific manner
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Impact of somatostatin interneurons on interactions between barrels in plasticity induced by whisker deprivation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Defining a critical period for inhibitory circuits within the somatosensory cortex
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Selective corticostriatal plasticity during acquisition of an auditory discrimination task
Nature (2015)
-
A gradual depth-dependent change in connectivity features of supragranular pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex
Brain Structure and Function (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.