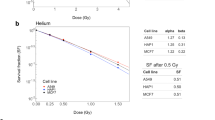
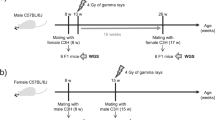
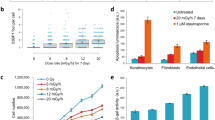
Abstract
MAMMALIAN radiation genetics has been largely concerned with the effects of X- and γ-irradiation, about which much has been learned in recent years. Surprisingly little work has been done with neutrons, although it is known that fast neutrons of modal energy around 1 MeV are about six times as effective as acute X-irradiation for the induction of dominant lethal mutations in mouse spermatozoa, whether the neutron dose is administered at high or at low intensity1,2. For the assessment of human hazards from high linear energy transfer radiation, it is particularly important to investigate the effectiveness of chronic neutron exposures with respect to the induction of point mutations in immature germ-cells of mammals. An experiment of this type, using the specific locus method, is now in progress and has revealed a surprisingly high yield of mutations following fast neutron irradiation of mouse spermatogonia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell, W. L., Russell, L. B., and Oakberg, E. F., in Radiation Biology and Medicine, edit. by Claus, 189 (Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass., 1958).
Searle, A. G., and Phillips, R. J. S., in Biological Effects of Neutrons, I.A.E.A. Symp. (in the press).
Neary, G. J., Munson, R. J., and Mole, R. H., Chronic Radiation Hazards (Pergamon Press, London, 1957).
Russell, W. L., and Russell, L. B., Rad. Res., Supp. 1, 296 (1959).
Phillips, R. J. S., Brit. J. Radiol., 34, 261 (1961).
Russell, W. L., Russell, L. B., and Kelly, E. M., Science, 128, 1546 (1958).
Carter, T. C., Lyon, M. F., and Phillips, R. J. S., Nature, 183, 409 (1958).
Russell, L. B., Prog. Med. Genet., 2, 230 (1962).
Edington, C. W., and Randolph, M. L., Genetics, 43, 715 (1958).
RBE Committee, Health Physics, 9, 357 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BATCHELOR, A., PHILLIPS, R. & SEARLE, A. High Effectiveness of Chronic Neutron Exposures for the Induction of Specific Locus Mutations in Mice. Nature 201, 207–208 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/201207a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/201207a0
This article is cited by
-
Natural and Artificial Radionuclides in Seafoods and Marine Protein Concentrates
Nature (1969)
-
Effects of Fast Neutrons on Eye Colour Mutations in Dahlbominus
Nature (1966)
-
Polonium-210 in Man
Nature (1965)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.