Abstract
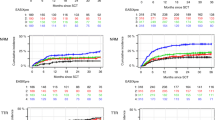
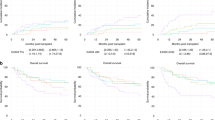
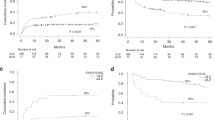
This study investigated whether or not there is a correlation between the changes in the serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT). Eighty-five patients undergoing allo-SCT were prospectively studied. The serum VEGF levels were measured on days 0, +7 and +14 after transplantation. The VEGF levels decreased significantly on day +7 and recovered on day +14. The highest levels from day +7 through day +14 were categorized by cluster analysis, which were then correlated with the nonrelapse mortality (NRM). There was a significant correlation between a low VEGF level and the occurrence of severe acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) including grade III–IV (P=0.029). The 1-year probability of NRM in patients with a low VEGF level was 22.5% compared with 3.5% for those with a high VEGF level (P=0.024). Multivariate analysis revealed clinically defined infections (P=0.011), advanced disease (P=0.014) and a low VEGF cluster (P=0.05) to be significantly associated with the occurrence of NRM in the cohort. In conclusion, low VEGF levels after allo-SCT are associated with NRM with an exacerbated severity of acute GVHD. VEGF monitoring after a transplant might identify those patients at risk of severe transplant-related mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devine SM, Adkins DR, Khoury H, Brown RA, Vij R, Blum W et al. Recent advances in allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. J Lab Clin Med 2003; 141: 7–32.
Wingard JR . Opportunistic infections after blood and marrow transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 1999; 1: 3–20.
Takatsuka H, Takemoto Y, Yamada S, Wada H, Tamura S, Fujimori Y et al. Complications after bone marrow transplantation are manifestations of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 419–426.
Members of the American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference Committee. American college of chest physician/society of critical care medicine consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med 1992; 20: 864–874.
Chen X, Christou NV . Relative contribution of endothelial cell and polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation in their interactions in systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Arch Surg 1996; 131: 1148–1153.
Klagsbrun M, D'Amore PA . Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol 1991; 53: 217–239.
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM . Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 1995; 146: 1029–1039.
Fava RA, Olsen NJ, Spencer-Green G, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Berse B et al. Vascular permeability factor/endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF): accumulation and expression in human synovial fluids and rheumatoid synovial tissue. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 341–346.
Selvaraj SK, Giri RK, Perelman N, Johnson C, Malik P, Kalra VK . Mechanism of monocyte activation and expression of proinflammatory cytochemokines by placenta growth factor. Blood 2003; 102: 1515–1524.
Iyer S, Leonidas DD, Swaminathan GJ, Maglione D, Battisti M, Tucci M et al. The crystal structure of human placenta growth factor-1 (PlGF-1), an angiogenic protein, at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 12153–12161.
Lunn RA, Sumar N, Bansal AS, Treleaven J . Cytokine profiles in stem cell transplantation: Possible use as a predictor of graft-versus-host disease. Hematology 2005; 10: 107–114.
Min CK, Kim DW, Lee JW, Han CW, Min WS, Kim CC . Supplemental peripheral blood stem cells to decrease marrow rejection in adult patients with severe aplastic anemia. Am J Hematol 2002; 69: 15–22.
Nash RA, Antin JH, Karanes C, Fay JW, Avalos BR, Yeager AM et al. Phase 3 study comparing methotrexate and tacrolimus with methotrexate and cyclosporine for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease after marrow transplantation from unrelated donors. Blood 2000; 96: 2062–2068.
Neumann F, Graef T, Tapprich C, Vaupel M, Steidl U, Germing U et al. Cyclosporine A and mycophenolate mofetil vs cyclosporine A and methotrexate for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after stem cell transplantation from HLA-identical siblings. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 1089–1093.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 1980; 69: 204–217.
Yoo JH, Choi SM, Lee DG, Choi JH, Shin WS, Min WS et al. Prognostic factors influencing infection-related mortality in patients with acute leukemia in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 31–35.
McDonald GB, Sharma P, Matthews DE, Shulman HM, Thomas ED . Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology 1984; 4: 116–122.
Fisher DC, Sherrill GB, Hussein A, Rubin P, Vredenburgh JJ, Elkordy M et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy as a complication of high-dose chemotherapy for breast cancer. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 18: 193–198.
Choi SM, Lee DG, Choi JH, Yoo JH, Kim YJ, Park SH et al. Risk-adapted preemptive therapy for cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a single-center experience in Korea. Int J Hematol 2005; 81: 69–74.
Frantz S, Vincent KA, Feron O, Kelly RA . Innate immunity and angiogenesis. Circ Res 2005; 96: 15–26.
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z . Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 1999; 13: 9–22.
Pertovaara L, Kaipainen A, Mustonen T, Orpana A, Ferrara N, Saksela O et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 6271–6274.
Min CK, Lee WY, Min DJ, Lee DG, Kim YJ, Park YH et al. The kinetics of circulating cytokines including IL-6, TNF-α, IL-8 and IL-10 following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 935–940.
Takatsuka H, Takemoto Y, Okamoto T, Fujimori Y, Tamura S, Wada H et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome-like disorders after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1999; 68: 1343–1347.
Takatsuka H, Takemoto Y, Okamoto T, Fujimori Y, Tamura S, Wada H et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 303–306.
Takatsuka H, Takemoto Y, Okamoto T, Fujimori Y, Tamura S, Wada H et al. Predicting the severity of graft-versus-host disease from interleukin-10 levels after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 1005–1007.
Yamada S, Takatsuka H, Takemoto Y, Okamoto T, Fujimori Y, Tamura S et al. Association of cytomegalovirus interstitial pneumonitis with HLA-type following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 861–865.
Kim DH, Sohn SK, Jeon SB, Baek JH, Kim JG, Lee NY et al. Prognostic significance of platelet recovery pattern after allogeneic HLA-identical sibling transplantation and its association with severe acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 101–108.
Wartiovaara U, Salven P, Mikkola H, Lassila R, Kaukonen J, Joukov V et al. Peripheral blood platelets express VEGF-C and VEGF which are released during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 1998; 80: 171–175.
Salgado R, Benoy I, Bogers J, Weytjens R, Vermeulen P, Dirix L et al. Platelets and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a morphological and functional study. Angiogenesis 2001; 4: 37–43.
Kirito K, Kaushansky K . Thrombopoietin stimulates vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) production in hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Cycle 2005; 4: 1729–1731.
Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval S, Bhandari V et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med 2004; 10: 1095–1103.
Teshima T, Ordemann R, Reddy P, Gagin S, Liu C, Cooke KR et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease does not require alloantigen expression on host epithelium. Nat Med 2002; 8: 575–581.
Boissel N, Rousselot P, Raffoux E, Cayuela JM, Maarek O, Charron D et al. Defective blood dendritic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia correlate with high plasmatic VEGF and are not normalized by imatinib mesylate. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1656–1661.
Bae DG, Gho YS, Yoon WH, Chae CB . Arginine-rich anti-vascular endothelial growth factor peptides inhibit tumor growth and metastasis by blocking angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 13588–13596.
Schots R, Van Riet I, Othman TB, Trullemans F, De Waele M, Van Camp B et al. An early increase in serum levels of C-reactive protein is an independent risk factor for the occurrence of major complications and 100-day transplant-related mortality after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 441–446.
Bacigalupo A, Oneto R, Bruno B, Soracco M, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F et al. Early predictors of transplant-related mortality (TRM) after allogeneic bone marrow transplants (BMT): blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and bilirubin. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 653–659.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Bo-Kyung Kim for her excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, CK., Kim, S., Lee, M. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with reduced severity of acute graft-versus-host disease and nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 38, 149–156 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705410
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705410
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Acute graft-versus-host disease increase risk and accuracy in prediction model of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Cytokine levels following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a match-pair analysis of home care versus hospital care
International Journal of Hematology (2021)
-
Biomarkers in Graft-Versus-Host Disease: from Prediction and Diagnosis to Insights into Complex Graft/Host Interactions
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2018)
-
VEGF, ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and MMP-9 expression in the autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and its impact on the time to engraftment
Annals of Hematology (2017)
-
Angiogenic factors are associated with development of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2015)