Abstract
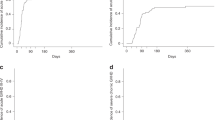
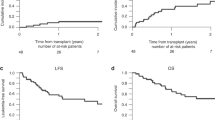
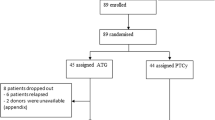
Reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) for allogeneic stem cell transplantation allows stable donor cell engraftment with the maintenance of a graft versus malignancy effect. Many different regimens exist employing various combinations of chemotherapy, radiotherapy and T-cell depletion. We examined the role of non-T-cell depleted RIC regimens in 56 patients with haematological malignancies. Patients received fludarabine phosphate for 5 days (30 mg/m2 in 35 patients, 25 mg/m2 in 21 patients) and melphalan for 1 day (140 mg/m2 in 36 patients, 100 mg/m2 in 20 patients). Immunosuppression was with CyA alone in 33 patients and CyA/MTX in 23 patients. Twenty-four of the 26 patients with chimerism data showed >95% donor chimerism at 3 months post transplant. aGVHD occurred in 18% of patients receiving CyA/MTX compared to 53% of patients receiving CyA. The 100-day mortality rate was 0.16 (95%CI 0.08–0.28) and 1-year nonrelapse mortality was 0.24 (95%CI 0.13–0.38). Thirty-three patients remained alive and in CR at a median of 19 months post transplant (range 3–38 months). We have shown that patients transplanted with fludarabine phosphate, melphalan 100 mg/m2 and with CyA/MTX as post transplant immunosuppression can achieve good disease control with an acceptable level of toxicity. Further studies are required to confirm these findings.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giralt S, Estey E, Albitar M, van Besien K, Rondón G, Anderlini P et al. Engraftment of allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cells with purine analog-containing chemotherapy: harnessing graft-versus-leukemia without myeloablative therapy. Blood 1997; 89: 4531–4536.
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik Y, Aker M, Cividalli G et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
McSweeney PA, Niederwieser D, Shizuru JA, Sandmaier BM, Molina AJ, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with hematologic malignancies: replacing high-dose cytotoxic therapy with graft-versus-tumor effects. Blood 2001; 97: 3390–3400.
Massenkeil G, Nagy M, Neuburger S, Tamm I, Lutz C, le Coutre P et al. Survival after reduced-intensity conditioning is not inferior to standard high-dose conditioning before allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation in acute leukaemias. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 683–689.
Robinson SP, Goldstone AH, Mackinnon S, Carella A, Russell N, de Elvira CR et al. Chemoresistant or aggressive lymphoma predicts for a poor outcome following reduced-intensity allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation: an analysis from the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2002; 100: 4310–4316.
Kassim AA, Chinratanalab W, Ferrara JLM, Mineishi S . Reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute leukemias: ‘what is the best recipe?’. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 565–574.
Anderlini P, Saliba R, Acholonu S, Okoroji G-J, Donato M, Giralt S et al. Reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's disease: low transplant-related mortality and impact of intensity of conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 943–951.
Valcárcel D, Martino R, Caballero D, Mateos MV, Pérez-Simón JA, Canals C et al. Chimerism analysis following allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 387–392.
Mohr B, Koch R, Thiede C, Kroschinsky F, Ehninger G, Bornhäuser M . CD34+ cell dose, conditioning regimen and prior chemotherapy: factors with significant impact on the early kinetics of donor chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 949–954.
Pérez-Simón JA, Caballero D, Diez-Campelo M, Lopez-Pérez R, Mateos G, Cañizo C et al. Chimerism and minimal residual disease monitoring after reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) allogeneic transplantation. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1423–1431.
Baron F, Baker JE, Storb R, Gooley TA, Sandmaier BM, Maris MB et al. Kinetics of engraftment in patients with hematologic malignancies given allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Blood 2004; 104: 2254–2262.
de Lima M, Anagnostopoulos A, Munsell M, Shahjahan M, Ueno N, Ippoliti C et al. Nonablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: dose is relevant for long-term disease control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 865–872.
Devine SM, Sanborn R, Jessop E, Stock W, Huml M, Peace D et al. Fludarabine and melphalan-based conditioning for patients with advanced hematological malignancies relapsing after a previous hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 557–562.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X, Braunschweig I, Ippolitti C et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 631–637.
Giralt S, Aleman A, Anagnostopoulos A, Weber D, Khouri I, Anderlini P et al. Fludarabine/melphalan conditioning for allogeneic transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 367–373.
Wong R, Giralt SA, Martin T, Couriel DR, Anagnostopoulos A, Hosing C et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning for unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as treatment for myeloid malignancies in patients older than 55 years. Blood 2003; 102: 3052–3059.
van Besien K, Devine S, Wickrema A, Jessop E, Amin K, Yassine M et al. Regimen-related toxicity after fludarabine-melphalan conditioning: a prospective study of 31 patients with hematologic malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 471–476.
de Lima M, Bonamino M, Vasconcelos Z, Colares M, Diamond H, Zalcberg I et al. Prophylactic donor lymphocyte infusions after moderately ablative chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies: high remission rate among poor prognosis patients at the expense of graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 73–78.
Gómez-Núñez M, Martino R, Caballero MD, Pérez-Simón JA, Canals C, Mateos MV et al. Elderly age and prior autologous transplantation have a deleterious effect on survival following allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning: results from the Spanish multicenter prospective trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 477–482.
Ueno NT, Cheng YC, Rondón G, Tannir NM, Gajewski JL, Couriel DR et al. Rapid induction of complete donor chimerism by the use of a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen composed of fludarabine and melphalan in allogeneic stem cell transplantation for metastatic solid tumors. Blood 2003; 102: 3829–3836.
Ritchie DS, Morton J, Szer J, Roberts AW, Durrant S, Shuttleworth P et al. Graft-versus-host disease, donor chimerism, and organ toxicity in stem cell transplantation after conditioning with fludarabine and melphalan. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2003; 9: 435–442.
Khouri IF, Lee MS, Saliba RM, Jun G, Fayad L, Younes A et al. Nonablative stem-cell transplantation for advanced/recurrent mantle-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 4407–4412.
Kottaridis PD, Milligan DW, Chopra R, Chakraverty RK, Chakrabarti S, Robinson S et al. In vivo CAMPATH-1H prevents graft-versus-host disease following nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation. Blood 2000; 96: 2419–2425.
Bacigalupo A . Third EBMT/AMGEN Workshop on reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplants (RIC-HSCT), and panel consensus. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 691–696.
Hartwig UF, Winkelmann N, Wehler T, Kreiter S, Schneider PM, Meyer RG et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by allografting of CD34-selected stem cells and <106/kg T cells may have an adverse effect on transplant-related mortality. Ann Hematol 2005; 84: 331–338.
Perez-Simon JA, Kottaridis PD, Martino R, Craddock C, Caballero D, Chopra R et al. Nonmyeloablative transplantation with or without alemtuzumab: comparison between 2 prospective studies in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2002; 100: 3121–3127.
Glass B, Nickelsen M, Dreger P, Claviez A, Hasenkamp J, Wulf G et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning prior to allogeneic transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells: the need for T cells early after transplantation to induce a graft-versus-lymphoma effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 391–397.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Ralph Bloomfield, Senior Statistician at Schering Health Care Limited. This work was supported by Schering Germany. Professor GJ Morgan is supported by the Leukaemia Research Fund. Three of the authors were employed by a company (Schering Health Care Limited) whose product was studied in the present work, and these authors were involved in the management of the company-sponsored clinical trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dasgupta, R., Rule, S., Johnson, P. et al. Fludarabine phosphate and melphalan: a reduced intensity conditioning regimen suitable for allogeneic transplantation that maintains the graft versus malignancy effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 37, 455–461 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705271
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705271
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of reduced conditionings combining fludarabine with melphalan or 3-day busulfan in patients allografted for myeloid neoplasms
International Journal of Hematology (2014)
-
Indications and outcomes of reduced-toxicity hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with hematological malignancies
International Journal of Hematology (2013)
-
Phase II prospective study of treosulfan-based reduced-intensity conditioning in allogeneic HSCT for hematological malignancies from 10/10 HLA-identical unrelated donor
Annals of Hematology (2012)
-
Promising Role of Reduced-Toxicity Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (PART-I)
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2012)
-
CD34+ cell dose and establishment of full donor chimerism at day +100 are important factors for survival with reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and melphalan before allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for hematologic malignancies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)