Summary:
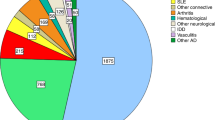
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) can be performed in a variety of refractory autoimmune diseases. A retrospective multicenter analysis is presented to evaluate safety and efficacy of ASCT for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis. In all, 18 of the 34 patients (53%) with a follow-up of 12 to 60 months achieved a drug-free complete remission. There were three cases (9%) of transplant-related mortality and two cases of disease-related mortality (6%). Infectious complications were seen frequently. We propose adjustments in future protocols to reduce this mortality in this high-risk patient group.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Bekkum DW . Stem cell transplantation for autoimmune disorders. Preclinical experiments. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2004; 17: 201–222.
Marmont AM . Stem cell transplantation for autoimmune disorders. Coincidental autoimmune disease in patients transplanted for conventional indications. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2004; 17: 223–232.
Wallace CA, Sherry DD . Trial of intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 1852–1855.
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A et al. Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 763–769.
Yokota S . Interleukin 6 as a therapeutic target in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: 581–586.
Quartier P, Taupin P, Bourdeaut F et al. Efficacy of etanercept for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis according to the onset type. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1093–1101.
Petty RE . Prognosis in children with rheumatic diseases: justification for consideration of new therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999; 38: 739–742.
Spiegel LR, Schneider R, Lang BA et al. Early predictors of poor functional outcome in systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 2402–2409.
Giannini EH, Ruperto N, Ravelli A et al. Preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 1202–1209.
Ruperto N, Ravelli A, Falcini F et al. Performance of the preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile chronic arthritis patients treated with methotrexate. Italian Pediatric Rheumatology Study Group. Ann Rheum Dis 1998; 57: 38–41.
De Kleer IM, Brinkman DM, Ferster A et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis: analysis of clinical efficacy mortality and transplant related morbidity. Ann Rheum Dis 2004; 63: 1318–1326.
Wulffraat NM, Brinkman D, Ferster A et al. Long-term follow-up of autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32 (Suppl. 1): S61–S64.
Ramanan AV, Schneider R . Macrophage activation syndrome – what's in a name!. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: 2513–2516.
Ravelli A, De Benedetti F, Viola S, Martini A . Macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis successfully treated with cyclosporine. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 275–278.
Stephan JL, Kone-Paut I, Galambrun C et al. Reactive haemophagocytic syndrome in children with inflammatory disorders. A retrospective study of 24 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001; 40: 1285–1292.
Silverman ED, Miller III JJ, Bernstein B, Shafai T . Consumption coagulopathy associated with systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Pediatr 1983; 103: 872–876.
Hertzberger-ten Cate R, Cats A . Toxicity of sulfasalazine in systemic juvenile chronic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1991; 9: 85–88.
Prahalad S, Bove KE, Dickens D et al. Etanercept in the treatment of macrophage activation syndrome. J Rheumatol 2001; 28: 2120–2124.
Ravelli A, Caria MC, Buratti S et al. Methotrexate as a possible trigger of macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 2001; 28: 865–867.
Grom AA, Villanueva J, Lee S et al. Natural killer cell dysfunction in patients with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. J Pediatr 2003; 142: 292–296.
Wulffraat NM, Rijkers GT, Elst EF et al. Reduced perforin expression in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is restored by autologous stem cell transplantation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003; 42: 375–379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wulffraat, N., Vastert, B. & Tyndall, A. Treatment of refractory autoimmune diseases with autologous stem cell transplantation: focus on juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Bone Marrow Transplant 35 (Suppl 1), S27–S29 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704840
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704840
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: diagnosis, management, and outcome
Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology (2006)
-
Update on the medical treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Current Rheumatology Reports (2006)