Abstract
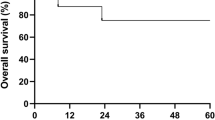
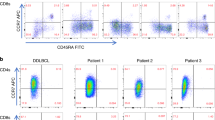
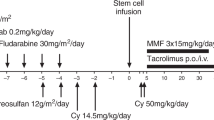
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is uncommonly of T cell origin, especially following BMT. We describe a 13-year-old boy with severe aplastic anemia (SAA) and no evidence of Fanconi’s anemia who underwent BMT at 11 years of age using CY 10 mg/kg once daily i.v. on days −5, −4, antilymphocyte globulin (ALG) 30 mg/kg once daily i.v. on days −5˜−3 and CsA from day −1 as conditioning. The BMT failed and he received a further peripheral blood stem cell transplant (PBSCT) 240 days after BMT. Conditioning was with CY 50 mg/kg once daily i.v. on days −5˜−2, and ALG 15 mg/kg once daily i.v. on days −4˜−2. GVHD prophylaxis included CsA and MTX. Engraftment was later confirmed by cytogenetic studies. Desquamation and ulcers of the oral mucosa and mouth angle developed in the 13th month post PBSCT. A buccal mucosa biopsy on day +524 revealed only plasmacytosis. Immunosuppressants were discontinued at that point. Generalized lymphadenopathy, prolonged fever (waxing and waning) and facial swelling developed in the 18th month post PBSCT. A neck lymph node biopsy on day +601 showed T cell lymphoma of diffuse large cell type with monoclonal TCR γ-chain gene rearrangement. A FISH study showed that the malignant T cells were of recipient origin. EBV in situhybridization was negative. He did not receive further treatment apart from discontinuation of immunosuppressants. He was followed up in our out-patient clinic and showed good performance 1170 days post PBSCT. We speculate that a different mechanism was operating in the pathogenesis of T cell lymphoma in this case. Risk factors include SAA and two transplants, conditioned with CY and ALG, long term use of CsA and treatment with azathioprine. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 26, 893–897.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witherspoon RP, Fisher LD, Thomas ED et al. Secondary cancers after bone marrow transplantation for leukemia or aplastic anemia New Engl J Med 1989 321: 784–789
Deeg HJ, Socie G . Malignancies after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: many questions, some answers Blood 1998 91: 1833–1844
Zutter MM, Durnam DM, Thomas ED et al. Secondary T-cell lymphoproliferation after marrow transplantation Am J Clin Pathol 1990 94: 714–721
Tondo UD, Berloco P, Alfani D . Incidence of tumors in organ transplants Transplant Proc 1997 29: 3623–3624
Hauke RJ, Greiner TC, Bierman PJ et al. Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorder after autologous bone marrow transplantation: report of two cases Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 1271–1274
Gorp JV, Doornewaard H, Tweel JGVD et al. Posttransplant T-cell lymphoma, report of three cases and a review of the literature Cancer 1994 73: 3064–3072
Weissmann DJ, Ferry JA, Spiro I et al. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in solid-organ recipients are predominantly aggressive tumors of host origin Am J Clin Pathol 1995 103: 748–755
Lones MA, Terrada DL, Said JW et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients: disseminated disease of donor origin demonstrated by fluorescence in situ hybridization Arch Pathol Lab Med 1998 122: 708–713
Martin PT, Shulman HM, Thomas ED et al. Fatal Epstein–Barr virus associated proliferation of donor B cells after treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease with a murine anti-T cell antibody Ann Intern Med 1984 101: 310–315
Kingma DW, Weiss WB, Raffeld M et al. Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 oncogene deletions: correlations with malignancy in Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders and malignant lymphomas Blood 1996 88: 242–251
Leblond V, Sutton L, Raphael M et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders after organ transplantation: a report of 24 cases observed in a single center J Clin Oncol 1995 13: 961–968
Su IJ, Wang CH, Chen RL et al. Hemophagocytic syndrome in Epstein–Barr virus-associated T-lymphoproliferative disorders: disease spectrum, pathogenesis, and management Leuk Lymphoma 1995 19: 401–406
Hanson MN, Morrison VA, Lita CE et al. Posttransplant T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders – an aggressive, late complication of solid-organ transplantation Blood 1996 88: 3626–3633
Cohen JI . Epstein–Barr virus lymphoproliferative disease associated with acquired immunodeficiency (review) Medicine 1991 70: 137–160
Armitage JM, Kormos RL, Stuart RS et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in thoracic organ transplant patients: ten years of cyclosporine-based immunosuppression J Heart Lung Transplant 1991 10: 877–887
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Wuh-Liang Hwu for helping with the FISH study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LC., Lu, MY., Yu, J. et al. T cell lymphoproliferative disorder following bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 26, 893–897 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702610
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702610
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
T-cell posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2020)
-
T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following a full haplotype-mismatched haematopoietic stem cell transplant in a patient with acute myeloid leukaemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)