Abstract
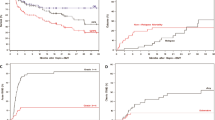
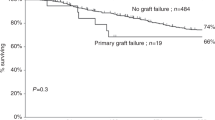
A retrospective, case-matched analysis of the short-term toxicity, risk of GVHD and relapse as well as outcome in pediatric unrelated marrow transplantation was conducted by comparing recipients of T-replete and -depleted grafts in a two-center setting. Both groups contained 30 patients with acute leukemia matched by age at transplant, gender, primary diagnosis and disease status. Acute (90% vs 53%) and chronic (48% vs 0%) GVHD were more common among recipients of T-replete grafts. No significant differences in graft rejection/failure or viral infections were encountered between the two groups. Relapses were more prevalent (37% vs 15%) among recipients of T-depleted grafts. Outcome (EFS) was similar in the two groups. Consequently, in the analysis of transplant outcome, the higher risk of procedure-related, toxic complications among pediatric recipients of T-replete marrow grafts appears to be balanced by an increased risk of relapse among the recipients of T-depleted grafts. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 25, 395–399.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vettenranta K, Hovi L, Saarinen-Pihkala UM . Short-term toxicity in pediatric marrow transplantation using related and unrelated donors Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 23: 459–462
Busca A, Anasetti C, Anderson G et al. Unrelated donor or autologous marrow transplantation for treatment of acute leukemia Blood 1994 83: 3077–3084
Balduzzi A, Gooley T, Anasetti C et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation in children Blood 1995 86: 3247–3256
Casper J, Camitta B, Truitt R et al. Unrelated bone marrow donor transplants for children with leukemia or myelodysplasia Blood 1995 85: 2354–2363
Chown SR, Marks DI, Cornish JM et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation in children and young adults with acute myeloid leukaemia in remission Br J Haematol 1997 99: 36–40
Davies SM, Wagner JE, Shu X-O et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with acute leukemia J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 557–565
Hongeng S, Krance RA, Bowman LC et al. Outcomes of transplantation with matched-sibling and unrelated-donor bone marrow in children with leukaemia Lancet 1997 350: 767–771
Oakhill A, Pamphilon DH, Potter MN et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second complete remission Br J Haematol 1996 94: 574–578
Winiarski J, Ringden O, Remberger M et al. Bone marrow transplantation in children using unrelated donors at Huddinge Hospital Acta Paediatr 1996 85: 327–335
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P et al. Consensus conference on acute GVHD Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 825–828
Vettenranta K, Hovi L, Taskinen M, Saarinen-Pihkala UM . Allograft with unrelated donor accentuates the gastrointestinal toxicity associated with high-dose melphalan and TBI preparative for BMT in children. (submitted for publication)
Margolis D, Camitta B, Pietryga D et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation to treat severe aplastic anemia in children and young adults Br J Haematol 1996 94: 65–72
Green A, Clarke E, Hunt L et al. Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who receive T cell depleted HLA mismatched marrow allo-grafts from unrelated donors have an increased incidence of primary graft failure but a similar overall transplant outcome Blood 1999 94: 2236–2246
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the Nona and Kullervo Väre Foundation, Finland, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vettenranta, K., Saarinen-Pihkala, U., Cornish, J. et al. Pediatric marrow transplantation for acute leukemia using unrelated donors and T-replete or -depleted grafts: a case-matched analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 25, 395–399 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702162
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702162
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Current European practice in pediatric myeloablative conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Alternative donor transplants for adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a comparison of the three major options
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2006)
-
Outcomes of transplantation with partial T-cell depletion of matched or mismatched unrelated or partially matched related donor bone marrow in children and adolescents with leukemias
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)
-
Prompt initiation of immunotherapy in children with an increasing number of autologous cells after allogeneic HCT can induce complete donor-type chimerism: a report of 14 children
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)
-
Influence of transplantation regimen on prognostic significance of high-level minimal residual disease before allogeneic stem cell transplantation in children with ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2001)