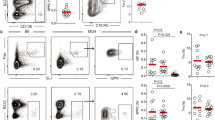
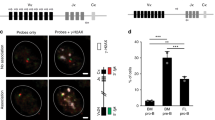
Abstract
B-1 B cells are a self-renewing population of B cells that differ from conventional B cells (B-2 cells) in that they are particularly predisposed to auto-antibody production1,2,3. Although much is known about the signalling pathways that control B-1-cell growth and development (reviewed in ref. 4), less is known about why these cells are prone to produce autoreactive antibodies. Here we show that B-1 cells, like germinal-centre B cells5,6,7,8, can express recombinase-activating genes 1 and 2 (RAG1 and RAG2) and undergo secondary V(D)J recombination of immunoglobulin genes. In addition, B cells from autoimmune-prone NZB mice show high levels of RAG messenger RNA and recombination. We propose that secondary immunoglobulin-gene rearrangements outside organized lymphoid organs may contribute to the development of autoreactive antibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayakawa, K., Hardy, R. R., Parks, D. R. & Herzenberg, L. A. The “Ly-1 B” cell subpopulation in normal immunodefective, and autoimmune mice. J. Exp. Med. 157, 202–218 (1983).
Hayakawa, K. et al. Ly-1 B cells: functionally distinct lymphocytes that secrete IgM autoantibodies. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 81, 2494–2498 (1984).
Hayakawa, K., Hardy, R. R., Herzenberg, L. A. & Herzenberg, L. A. Progenitors for Ly-1 B cells are distinct from progenitors for other B cells. J. Exp. Med. 161, 1554–1568 (1985).
Tarakhovsky, A. Bar Mitzvah for B-1 cells: how will they grow up? J. Exp. Med. 185, 981–984 (1997).
Hikida, M. et al. Reexpression of RAG-1 and RAG-2 genes in activated mature mouse B cells. Science 274, 2092–2094 (1996).
Han, S., Zheng, B., Schatz, D. G., Spanopoulou, E. & Kelsoe, G. Neoteny in lymphocytes: Rag1 and Rag2 expression in germinal center B cells. Science 274, 2094–2097 (1996).
Papavasiliou, F. et al. V(D)J recombination in mature B cells: a new mechanism for diversification of antibody responses. Science 278, 298–301 (1997).
Han, S. et al. V(D)J recombinase activity in a subset of germinal center B lymphocytes. Science 278, 301–305 (1997).
Pelanda, R., Schaal, S., Torres, R. M. & Rajewsky, K. Aprematurely expressed Ig(kappa) transgene, but not V(kappa)J(kappa) gene segment targeted into the Ig(kappa) locus, can rescue B cell development in lambda5-deficient mice. Immunity 5, 229–239 (1996).
Sonoda, E. et al. Bcell development under the condition of allelic inclusion. Immunity 6, 225–233 (1997).
Pelanda, R. et al. Receptor editing in a transgenic mouse model: site efficiency and role in B cell tolerance and antibody diversification. Immunity 7, 765–777 (1997).
Stall, A. M. et al. Rearrangement and expression of endogenous immunoglobulin genes occur in many murine B cells expressing transgenic membrane IgM. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 3546–3550 (1988).
Taki, S., Meiering, M. & Rajewsky, K. Targeted insertion of a variable region gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science 262, 1268–1271 (1993).
Cascalho, M., Wong, J. & Wabl, M. VHgene replacement in hyperselected B cells of the quasimonoclonal mouse. J. Immunol. 159, 5795–5801 (1997).
Spanopoulou, E. et al. Functional immunoglobulin transgenes guide ordered B-cell differentiation in Rag-1-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 8, 1030–1042 (1994).
Taccioli, G. E. et al. Ku80: product of the XRCC5 gene and its role in DNA repair and V(D)J recombination. Science 265, 1442–1445 (1994).
Nussenzweig, A. et al. Requirement for Ku80 in growth and V(D)J recombination. Nature 382, 551–555 (1996).
Murakami, M. et al. Oral administration of lipopolysaccharides activates B-1 cells in the peritoneal cavity and lamina propria of the gut and induces autoimmune symptoms in an autoantibody transgenic mouse. J. Exp. Med. 180, 111–121 (1994).
Arnold, L. W., Pennell, C. A., McCray, S. K. & Clarke, S. H. Development of B-1 cells: segregation of phosphatidyl choline-specific B cells to the B-1 population occurs after immunoglobulin gene expression. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1585–1595 (1994).
Tiegs, S. L., Russell, D. M. & Nemazee, D. Receptor editing in self-reactive bone marrow B cells. J. Exp. Med. 177, 1009–1020 (1993).
Gay, D., Saunders, T., Camper, S. & Weigert, M. Receptor editing: an approach by autoreactive B cells to escape tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 177, 999–1008 (1993).
Nemazee, D. A. & Bürki, K. Clonal deletion of B lymphocytes in a transgenic mouse bearing anti-MHC class I antibody genes. Nature 337, 562–566 (1989).
Goodnow, C. C., Crosbie, J., Jorgensen, H., Brink, R. A. & Basten, A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature 342, 385–391 (1989).
Murakami, M. et al. Antigen-induced apoptotic death of Ly-1 B cells responsible for autoimmune disease in transgenic mice. Nature 357, 77–80 (1992).
Pulendran, B., Kannourakis, G., Nouri, S., Smith, K. G. & Nossal, G. J. Soluble antigen can cause enhanced apoptosis of germinal centre B cells. Nature 375, 331–334 (1995).
Shokat, K. M. & Goodnow, C. C. Antigen-induced B-cell death and elimination during germinal-centre immune responses. Nature 375, 334–338 (1995).
Lalor, P. A., Stall, A. M., Adams, S. & Herzenberg, L. A. Permanent alteration of the murine Ly-1 B repertoire due to selective depletion of Ly-1 B cells in neonatal animals. Eur. J. Immunol. 19, 501–506 (1989).
Tsubata, T., Murakami, M. & Honjo, T. Antigen-receptor cross-linking induces peritoneal B-cell apoptosis in normal but not autoimmunity-prone mice. Curr. Biol. 4, 8–17 (1994).
Murakami, M. et al. Effects of breeding environments on generation and activation of autoreactive B-1 cells in anti-red blood cell autoantibody transgenic mice. J. Exp. Med. 185, 791–794 (1997).
Ehlich, A., Martin, V., Muller, W. & Rajewsky, K. Analysis of the B-cell progenitor compartment at the level of single cells. Curr. Biol. 4, 573–583 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Nussenzweig lab for comments on the manuscript and helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the NIH (to M.C.N.) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (through SFB243) and the EU (to K.R.). X-F.Q. was supported by an RU graduate fellowship and NIH training grant. A.N. was supported in part by a grant from the Arthritis Foundation. M.C.N. is an associate investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, XF., Schwers, S., Yu, W. et al. Secondary V(D)J recombination in B-1 cells. Nature 397, 355–359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/16933
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/16933
This article is cited by
-
Regulating antigen-receptor gene assembly
Nature Reviews Immunology (2003)
-
Marginal-zone B cells
Nature Reviews Immunology (2002)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.