Abstract
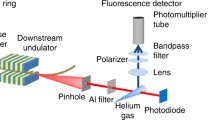
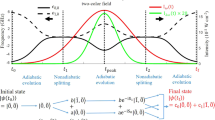
The ability to control the shape and motion of quantum states1,2 may lead to methods for bond-selective chemistry and novel quantum technologies, such as quantum computing. The classical coherence of laser light has been used to guide quantum systems into desired target states through interfering pathways3,4,5. These experiments used the control of target properties — such as fluorescence from a dye solution6, the current in a semiconductor7,8 or the dissociation fraction of an excited molecule9 — to infer control over the quantum state. Here we report a direct approach to coherent quantum control that allows us to actively manipulate the shape of an atomic electron's radial wavefunction. We use a computer-controlled laser to excite a coherent state in atomic caesium. The shape of the wavefunction is then measured10 and the information fed back into the laser control system, which reprograms the optical field. The process is iterated until the measured shape of the wavefunction matches that of a target wavepacket, established at the start of the experiment. We find that, using a variation of quantum holography11 to reconstruct the measured wavefunction, the quantum state can be reshaped to match the target within two iterations of the feedback loop.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warren, W. S., Rabitz, H. & Dahleh, M. Coherent control of quantum dynamics: the dream is alive. Science 259, 1581–1589 (1993).
Gordon, R. J. & Rice, S. A. Active control of the dynamics of atoms and molecules. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 48, 601–641 (1997).
Tannor, D. J. & Rice, S. A. Coherent pulse sequence control of product formation in chemical-reactions. Adv. Chem. Phys. 70, 441–523 (1998).
Shapiro, M. & Brumer, P. Coherent and incoherent laser control of photochemical-reactions. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 13, 187–229 (1994).
Judson, R. S. & Rabitz, H. Teaching lasers to control molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1500–1503 (1992).
Bardeen, C. J. et al. Feedback quantum control of molecular electronic population transfer. Chem. Phys. Lett. 280, 151–158 (1997).
Dupont, E., Corkum, P. B., Liu, H. C., Buchanan, M. & Wasilewski, Z. R. Phase-controlled currents in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3596–2599 (1995).
Hache, A. et al. Observation of coherently controlled photocurrent in unbiased, bulk GaAs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 306–309 (1997).
Kleiman, V., Zhu, L., Li, X. & Gordon, R. J. Coherent phase control of the photoionization of H2S. J.Chem. Phys. 102, 5863–5866 (1995).
Weinacht, T. C., Ahn, J. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Measurement of the amplitude and phase of a sculpted Rydberg wave packet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 5508–5511 (1998).
Leichtle, C., Schleich, W. P., Averbukh, I. S. & Shapiro, M. Quantum state holography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1418–1421 (1998).
Xin, C. & Yeazell, J. A. Analytical wave-packet design scheme: control of dynamics and creation of exotic wave packets. Phys. Rev. A 56, R2274–R2277 (1997).
Fittinghoff, D. N. et al. Measurement of the intensity and phase of ultraweak, ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 21, 884–886 (1996).
Gallagher, T. F., Humphrey, L. M., Cooke, W. E., Hill, R. M. & Edelstein, S. A. Field ionization of highly excited states of sodium. Phys. Rev. A 16, 1098–1108 (1977).
Kinrot, O., Averbukh, I. S. & Prior, Y. Measuring coherence while observing noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3822–3825 (1995).
Hanbury-Brown, R. & Twiss, R. Q. Correlation between photons in two coherent beams of light. Nature 175, 27–29 (1956).
Schleich, W. & Raymer, M. Quantum state preparation and measurement. J. Mod. Opt. 44, 2021–2022 (1997).
Freyberger, M., Bardroff, P., Leichtle, C., Schrade, G. & Schleich, W. The art of measuring quantum states. Phys. World 10, 41–45 (1997).
Leibfried, D., Pfau, T. & Monroe, C. Shadows and mirrors: reconstructing quantum states of atom motion. Phys. Today 51, 22–28 (1998).
Leonhardt, U. Measuring the Quantum State of Light(Cambridge Univ. Press, (1997)).
Strickland, D. & Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 55, 447–449 (1985).
Tull, J. X., Dugan, M. A. & Warren, W. S. High resolution, ultrafast laser pulse shaping and its applications. Adv. Opt. Magn. Reson. 20, 1–51 (1996).
Raman, C., Conover, C. W. S., Sukenik, C. I. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Ionization of Rydberg wave packets by subpicosecond, half-cycle electromagnetic pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 2436–2439 (1996).
Krause, J. L., Schafer, K. J., Ben-Nun, M. & Wilson, K. R. Creating and detecting shaped Rydberg wave packets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 4978–4981 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Tannor, J. Krause and J. Cohen for discussions. This work was supported by the NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinacht, T., Ahn, J. & Bucksbaum, P. Controlling the shape of a quantum wavefunction. Nature 397, 233–235 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/16654
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/16654
This article is cited by
-
How Distorting the Trajectories of Quantum Particles Shapes the Statistical Properties of their Ensemble
International Journal of Theoretical Physics (2023)
-
Ultrafast beam pattern modulation by superposition of chirped optical vortex pulses
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
All-optical temporal differentiation in hot standing-wave-dressed atoms
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2019)
-
Coherent control theory and experiment of optical phonons in diamond
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Derivation and Numerical analysis of an Attenuation Operator for non-relativistic waves
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.