Abstract
Objective: To evaluate plasma total, free (FL) and protein-bound (BL) leptin in children with Down's syndrome (DS) and different degrees of adiposity and its relationship with thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and free triiodothyronine (FT3).
Subjects: A total of 24 prepubertal clinically euthyroid DS children.
Methods: Plasma leptin, TSH, FT4, and FT3 concentrations were determined by immunometric/radioimmunologic assays. FL and BL were evaluated by fast protein liquid chromatography.
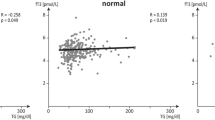
Results: In DS children, leptin circulates in two fractions, corresponding to BL and FL. The amount of BL and FL is negatively and positively correlated to body mass index (BMI), respectively. Plasma leptin concentrations correlate with BMI, but not with TSH, FT4, and FT3.
Conclusions: In prepubertal DS children, leptin circulates as both BL and FL, correlates with adiposity and its concentration appears independent of thyroid function.
Sponsorship: MIUR, Università degli Studi di Milano, Banca Popolare di Milano Foundation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahima RS, Saper CB, Flier JS & Elmquist JK (2000): Leptin regulation of neuroendocrine systems. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 21, 263–307.
Asami T, Ciomarten T & Uchiyama M (2000): Relationship between serum leptin and thyroid hormones in children. Pediatr. Int. 42, 293–295.
Ballauff A, Ziegler A, Emons G, Sturm G, Blum WF, Remschmidt H & Hebebrand J (1999): Serum leptin and gonadotropin levels in patients with anorexia nervosa during weight gain. Mol. Psychiatr. 4, 71–75.
Brabant G, Horn R, Muhlen AVZ, Mayr B, Wurster U, Heidenreich F, Schnabel D, Gruters-Kieslich A, Zimmermann-Belsing T & Feldt-Rasmussen U (2000): Free and protein bound leptin are distinct and independently controlled factors in energy regulation. Diabetologia 43, 438–442.
Cento RM, Proto C, Spada RS, Ragusa L, Reitano S, Napolitano V & Lanzone A (1999): Serum leptin concentrations in obese women with Down syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 13, 36–41.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM & Dietz WH (2000): Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ. 320, 1240–1243.
Corbetta S, Englaro P, Giambona S, Persani L, Blum WF & Beck-Peccoz P (1997): Lack of effects of circulating thyroid hormone levels on serum leptin concentrations. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 137, 659–663.
Garcia-Mayor R, Andrade M, Rios M, Lage M, Dieguez C & Casanueva F (1997): Serum leptin levels in normal children: relationship to age, gender, body mass index, pituitary–gonadal hormones and pubertal stage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 2849–2855.
Ghizzoni L, Mastorakos G, Ziveri M, Furlini M, Solazzi A, Vottero A & Bernasconi S (2001): Interactions of leptin and thyrotropin 24-hour secretory profiles in short normal children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 2065–2072.
Korbonits M (1998): Leptin and the thyroid—a puzzle with missing pieces. Clin. Endocrinol. 49, 569–572.
Kratzsch J, Lammert A, Bottner A, Seidel B, Mueller G, Thiery J, Hebebrand J & Kiess W (2002): Circulating soluble leptin receptor and free leptin index during childhood, puberty, and adolescence. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 4587–4594.
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pretley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, Kern PA & Friedman JM (1995): Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1, 1155–1161.
Magni P, Motta M & Martini L (2000): Leptin: a possible link between food intake, energy expenditure, and reproductive function. Regul. Pept. 92, 51–56.
Reinehr T & Andler W (2002): Thyroid hormones before and after weight loss in obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 87, 320–323.
Sharav T & Bowman T (1992): Dietary practices, physical activity, and body-mass index in a selected population of Down syndrome children and their siblings. Clin. Pediatr. 31, 341–344.
Sinha MK, Opentanova I, Ohannesian JP, Kolaczwnski JW, Heiman ML, Hale J, Becker GW, Bowsher RR, Stephens TW & Caro JF (1996): Evidence of free and bound leptin in human circulation. Studies in lean and obese subjects and during short-term fasting. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1277–1282.
Valcavi R, Zini M, Peino R, Casanueva FF & Dieguez C (1997): Influence of thyroid status on serum immunoreactive leptin levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 1632–1634.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Paola Assi and Giovanna Miccichè for expert technical collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: P Magni.
Contributors: PM and MMC were responsible for the study concept and writing of the manuscript. MR and ED were responsible of the biochemical studies and the literature search. FL was responsible for the clinical management. ER and MM were responsible for the critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magni, P., Ruscica, M., Dozio, E. et al. Free and bound leptin in prepubertal children with Down's syndrome and different degrees of adiposity. Eur J Clin Nutr 58, 1547–1549 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602000
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602000
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Meta-analysis of metabolites involved in bioenergetic pathways reveals a pseudohypoxic state in Down syndrome
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Free and bound plasma leptin in anorexia nervosa patients during a refeeding program
Endocrine (2016)
-
Resting energy expenditure and adiposity accretion among children with Down syndrome: a 3-year prospective study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013)