Abstract
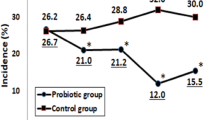
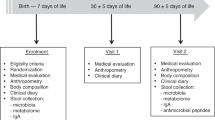
For several years cytokine production has been associated with infections but it was not suspected that some types of food could also induce cytokines, even in a state of non-infection. Lactic bacteria can induce interferon (IFN) production in human healthy subjects, thus, a better protection against infections would be expected. Therefore, we planned to evaluate the effect of two diets including yoghurt or milk on IFN-γ production during nutritional recovery in two different situations of malnutrition: (1) children with diarrhoea; and (2) patients with anorexia nervosa (AN). Both the diet including yoghurt of that including milk seemed to increase IFN-γ production at the end of nutritional recovery in the malnourished children with diarrhoea. The significance of interferon production and the lymphocyte subset increase should be explored to know if a better resistance against pathogens is related to them. Regulation of intestinal absorption and moderate stimulation of interferon production make the yoghurt-based diet a good choice in the nutritional care of children. In the same way, an increase in the IFN-γ production was observed in AN patients consuming yoghurt. This increase of IFN-γ production could be considered a biological marker to detect the effect of probiotics on the immune response, especially in the improvement of a deficient nutritional status.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solis, B., Nova, E., Gómez, S. et al. The effect of fermented milk on interferon production in malnourished children and in anorexia nervosa patients undergoing nutritional care. Eur J Clin Nutr 56 (Suppl 4), S27–S33 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601659
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601659
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Psychobiotics: the Influence of Gut Microbiota on the Gut-Brain Axis in Neurological Disorders
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2022)
-
Effects of a nutritional intervention with yogurt on lymphocyte subsets and cytokine production capacity in anorexia nervosa patients
European Journal of Nutrition (2006)
-
The effect of milk fermented by yogurt cultures plus Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on the immune response of subjects under academic examination stress
European Journal of Nutrition (2004)