Abstract
Objective: To assess the effects of a comprehensive change in dietary composition on endogenous hormone metabolism. The specific aim was to examine whether this intervention could lead to favourable changes in insulin sensitivity, levels of IGF-I and IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), and total and bioavailable testosterone and estradiol, that would be expected to reduce breast cancer risk.
Design: Randomised dietary intervention study; duration of 5 months.
Subjects: From a total of 99 postmenopausal women, who had elevated baseline plasma testosterone levels, 49 women were randomly assigned to the dietary intervention arm and the other 50 to a control group.
Interventions: Main aspects of the dietary intervention were reductions in the intake of total fat and refined carbohydrates, an increase in the ratio of n-3 over n-6 plus saturated fatty acids, and increased intakes of foods rich in dietary fibre and phytooestrogens.
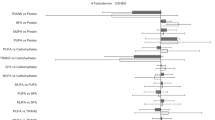
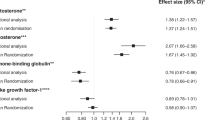
Results: Relative to the control group, women of the intervention group showed a significant reduction of body weight, waist circumference, fasting serum levels of testosterone, C peptide, glucose, and insulin area after glucose tolerance test, and a significant increase of serum levels of sex hormone-binding globulin, IGFBP-1, -2, and growth hormone-binding protein. Serum levels of IGF-I did not change.
Conclusions: This comprehensive dietary intervention strategy proved to be successful in inducing changes in endogenous hormone metabolism that might eventually result in reduced breast cancer risk. Additional studies are needed to show whether the dietary intervention and related hormonal changes can be both maintained over longer periods, of at least several years.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann G (2001): Growth hormone binding protein 2001. J Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 14, 355–375.
Baxter RC & Turtle JR (1978): Regulation of hepatic growth hormone receptors by insulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 84, 350–357.
Berrino F, Muti P, Micheli A, Bolelli G, Krogh V, Sciajno R, Pisani P, Panico S & Secreto G (1996): Serum sex hormone levels after menopause and subsequent breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 88, 291–296.
Berrino F, Bellati C, Secreto G, Camerini E, Pala V, Panico S, Allegro G & Kaaks R (2001a): Reducing bioavailable sex hormones through a comprehensive change in diet: the diet and androgens (DIANA) randomized trial.
Berrino F, Bellati C, Secreto G, Camerini E, Pala V, Panico S, Allegro G & Kaaks R (2001b): Reducing bioavailable sex hormones through a comprehensive change in diet: the diet and androgens (DIANA) randomized trial. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 10, 25–33.
Bondanelli M, Margutti A, Ambrosio M R, Plaino L, Cobellis L, Petraglia F & degli Uberti EC (2001): Blood growth hormone-binding protein levels in premenopausal and postmenopausal women: roles of body weight and estrogen levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1973–1980
Bouchard C, Despres JP & Mauriege P (1993): Genetic and nongenetic determinants of regional fat distribution. Endocr. Rev. 14, 72–93.
Brismar K, Hilding A & Lindgren B (1995): Regulation of IGFBP-1 in humans. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 6, 449–456.
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JM, van Noord PA, Hart AA, de Jong-Bakker M & Nooijen WJ (1992): Insulin resistance and breast–cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 52, 511–516.
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH & Pollak M (1998): Plasma insulin–like growth factor–I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279, 563–566.
Chapman IM, Hartman ML, Pieper KS, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hintz RL & Thorner MO (1998): Recovery of growth hormone release from suppression by exogenous insulin–like growth factor I (IGF–I): evidence for a suppressive action of free rather than bound IGF–I. J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab. 83, 2836–2842.
Chappell J, Leitner JW, Solomon S, Golovchenko I, Goalstone ML & Draznin B (2001): Effect of insulin on cell cycle progression in MCF–7 breast cancer cells. Direct and potentiating influence. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38023–38028.
Crave JC, Lejeune H, Brebant C, Baret C & Pugeat M (1995): Differential effects of insulin and insulin–like growth factor I on the production of plasma steroid–binding globulins by human hepatoblastoma–derived (Hep G2) cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 1283–1289.
Dawson T & Wynford Thomas D (1995): Does autocrine growth factor secretion form part of a mechanism which paradoxically protects against tumour development? Br. J. Cancer 71, 1136–1141.
Del Giudice ME, Fantus IG, Ezzat S, McKeown–Eyssen G, Page D & Goodwin PJ (1998): Insulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk. Breast. Cancer. Res. Treat. 47, 111–120.
Eberhardt MS, Lackland DT, Wheeler FC, German RR & Teutsch SM (1994): Is race related to glycemic control? An assessment of glycosylated hemoglobin in two South Carolina communities. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 47,1181–1189.
Eidson M, Becker TM, Wiggins CL, Key CR & Samet JM (1994): Breast cancer among Hispanics, American Indians and non–Hispanic whites in New Mexico. Int. J. Epidemiol. 23, 231–237.
Erfurth EM, Hagmar LE, Saaf M & Hall K (1996): Serum levels of insulin–like growth factor I and insulin–like growth factor–binding protein 1 correlate with serum free testosterone and sex hormone binding globulin levels in healthy young and middle–aged men. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 44, 659–664.
Frystyk J, Vestbo E, Skjaerbaek C, Mogensen CE & Orskov H (1995): Free insulin–like growth factors in human obesity. Metabolism 44, 37–44.
Giovannucci E, Pollak MN, Plate EA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Majeed N, Colditz GA, Speizer FE & Hankinson SE (2000): A prospective study of plasma insulin–like growth factor–1 and binding protein–3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer. Epidemiol. Biomarkers. Prev. 9, 345–349.
Goldin BR, Adlercreutz H, Gorbach SL, Warram JH, Dwyer JT, Swenson L & Woods MN (1982): Estrogen excretion patterns and plasma levels in vegetarian and omnivorous women. N. Engl. J. Med. 307, 1542–1547.
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Madamas Y, Hartwick W, Hoffman B & Hood N (2002): Fasting insulin and outcome in early–stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 42–51.
Hanaire-Broutin H, Sallerin-Caute B, Poncet MF, Tauber M, Bastide R, Rosenfeld R & Tauber JP (1998): Insulin therapy and GH–IGF–I axis disorders in diabetes: impact of glycaemic control and hepatic insulinization. Diabetes Metab. 22: 245–250.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE & Pollak M (1998): Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor, I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 351, 1393–1396.
Jones JI & Clemmons DR (1995): Insulin–like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr. Rev. 16, 3–34.
Kaaks R (1996): Nutrition, hormones, and breast cancer: is insulin the missing link? Cancer Causes Control 7, 605–625.
Kaaks R & Lukanova A (2001): Energy balance and cancer the role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 60: 91–106.
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A & Friend KE (2000): The effects of insulin–like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr. Rev. 21, 215–244.
Lai A, Sarcevic B, Prall OW & Sutherland RL (2001): Insulin/insulin–like growth factor–I and estrogen cooperate to stimulate cyclin E–Cdk2 activation and cell cycle progression in MCF–7 breast cancer cells through differential regulation of cyclin E and p21(WAFl/Cipl). J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25823–25833.
Li BD, Khosravi MJ, Berkel HJ, Diamandi A, Dayton MA, Smith M & Yu H (2001): Free insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer. 91, 736–739.
Lovejoy JC (1999): Dietary fatty acids and insulin resistance. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 1, 215–220
Ludwig DS (2002): The glycemic index: physiological mechanisms relating to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. JAMA 287, 2414–2423.
Lukanova A, Soederberg S, Stattin P, Palmquist R, Lundin E, Biessy C, Rinaldi S, Riboli E, Hallmans G & Kaaks R (2002): Non–linear relationship of insulin-like growth factor(IGF-I) and IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 ratio with indices of adiposity and plasma insulin. Cancer Causes Control. 13, 509–516.
Mazur W & Adlercreutz H (1988): Naturally occurring oestrogens in food. Pure. Appl. Chem. 70, 1759–1776.
Mercado M & Baumann G (1995): Characteristics of the somatotropic axis in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Res. 26, 101–109.
Muti P, Trevisan M, Micheli A, Krogh V, Bolelli G, Sciajno R & Berrino F (1996): Reliability of serum hormones in premenopausal and postmenopausal women over a one-year period. Cancer. Epidemiol. Biomarkers. Prev. 5, 917–922.
Nam SY, Lee EJ, Kim KR, Cha BS, Song YD, Lim SK, Lee HC & Huh KB (1997): Effect of obesity on total and free insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and their relationship to IGF–binding protein (BP)-l, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, insulin, and growth hormone. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 21, 355–359.
Nesbitt PD & Thompson LU (1997): Lignans in homemade and commercial products containing flax seed. Nutr. Cancer. 29, 222–227.
Nyomba BL, Berard L & Murphy LJ (1997): Free insulin–like growth factor I (IGF–I) in healthy subjects: relationship with IGF–binding proteins and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 2177–2181.
Palmqvist R, Hallmans G, Rinaldi S, Biessy C, Stenling E, Riboli E & Kaaks R (2002): Plasma IGF-I, IGF-binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study in Northern Sweden. Gut. 50, 642–646.
Papa V & Belfiore A (1996): Insulin receptors in breast cancer: biological and clinical role. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 19, 324–333.
Pfeilschifter J, Scheidt–Nave C, Leidig–Brackner G, Woitge HW, Blum WF, Wuster C, Haack D & Ziegler R (1996): Relationship between circulating insulin–like growth factor components and sex hormones in a population–based sample of 50- to 80-year-old men and women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 2534–2540.
Pisani P, Faggiano F, Krogh V, Palli D, Vineis P & Berrino F (1997): Relative validity and reproducibility of a food frequency dietary questionnaire for use in the Italian EPIC centres. Int. J. Epidemiol. 26(Suppl 1), S152–S160.
Polonsky K, Frank B, Pugh W, Addis A, Karrison T, Meier P, Tager H & Rubenstein A (1986): The limitations to and valid use of C-peptide as a marker of the secretion of insulin. Diabetes 35, 379–386.
Poretsky L, Cataldo NA, Rosenwaks Z & Giudice LC (1999): The insulin-related ovarian regulatory system in health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 20, 535–582.
Pugeat M, Crave JC, Elmidani M, Nicolas MH, Garoscio Cholet M, Lejeune H, Dechaud H & Tourniaire J (1991): Pathophysiology of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). relation to insulin. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40, 841–849.
Rasmussen MH, Ho KK, Kjems L & Hilsted J (1996): Serum growth hormone-binding protein in obesity: effect of a short-term, very low calorie diet and diet-induced weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 1519–1524.
Reinli K & Block G (1996): Phytoestrogen content of foods—a compendium of literature values. Nutr. Cancer. 26, 123–148.
Rinaldi S, Geay A, Dechaud H, Biessy C, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Akhmedkhanov A, Snore RE, Riboli E, Toniolo P, Kaaks R (2002): Validity of free testosterone and free estradiol determinations in serum samples from postmenopausal women by theoretical calculations. Cancer Epidemol Biomarkers Prev. 11, 1065–1071.
Salvini S, Parpinel M, Gnagnarella P, Maisonneuve P & Turrini A (1998): Banca dati di composizione degli alimenti per studi epidemiologici in Italia. Milano, Itália.
Singh A, Hamilton Fairley D, Koistinen R, Seppala M, James VH, Franks S & Reed MJ (1990): Effect of insulin–like growth factor-type I (IGF-I) and insulin on secretion of sex hormone binding globulin and IGF-I binding protein (IBP-I) by human hepatoma cells. J. Endocrinol 124, R1–3.
Slimani N, Ferrari P, Ocke M, Welch A, Boeing H, Liere M, Pala V, Amiano P, Lagiou A, Mattisson I, Stripp C, Engeset D, Charrondiere R, Buzzard M, Staveren W & Riboli E (2000): Standardization of the 24-hour diet recall calibration method used in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC): general concepts and preliminary results. Eur J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 900–917.
Stattin P, Bylund A, Rinaldi S, Biessy C, Dechaud H, Stenman UH, Egevad L, Riboli E, Hallmans G & Kaaks R (2000): Plasma insulin–like growth factor I, insulin like growth factor–binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 92, 1910–1917.
Tannenbaum GS, Guyda HJ & Posner BI (1983): Insulin–like growth factors: a role in growth hormone negative feedback and body weight regulation via brain. Science 220, 77–79.
The Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group (2002): Endogenous sex hormones and breast cancer in postmenopausal women: reanalysis of nine prospective studies. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 94, 606–616.
Thissen JP, Ketelslegers JM & Underwood LE (1994): Nutritional regulation of the insulin like growth factors. Endocr. Rev. 15, 80–101.
Thompson LU, Robb P Serraino M & Cheung F (1991): Mammalian lignan production from various foods. Nutr. Cancer. 16, 43–52.
Tollet P, Enberg B & Mode A (1990): Growth hormone (GH) regulation of cytochrome P-450IIC12, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and GH receptor messenger RNA expression in primary rat hepatocytes: a hormonal interplay with insulin, IGF-I, and thyroid hormone. Mol. Endocrinol. 4, 1934–1942.
Toniolo P, Bruning PF, Akhmedkhanov A, Bonfrer JM, Koenig KL, Lukanova A, Shore RE & Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A (2000): Serum insulin-like growth factor–I and breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 88, 828–832.
Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM (1999): A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 3666–3672.
Wakai K, Egami I, Kato K, Kawamura T, Tamakoshi A, Lin Y, Nakayama T, Wada M & Ohno Y (1999): Dietary intake and sources of isoflavones among Japanese. Nutr. Cancer 33, 139–145.
Whelan EA, Sandier DP, Root JL, Smith KR & Weinberg CR (1994): Menstrual cycle patterns and risk of breast cancer. Am. J. Epidemiol. 140, 1081–1090.
Yang G, Lu G, Jin F, Dai Q, Best R, Shu XO, Chen JR, Pan XY, Shrubsole M & Zheng W (2001): Population-based, case–control study of blood C-peptide level and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers. Prev. 10, 1207–1211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaaks, R., Bellati, C., Venturelli, E. et al. Effects of dietary intervention on IGF-I and IGF-binding proteins, and related alterations in sex steroid metabolism: the Diet and Androgens (DIANA) Randomised Trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 57, 1079–1088 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601647
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601647
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dietary patterns in relation to glioma: a case–control study
Cancer & Metabolism (2024)
-
How the COVID-19 pandemic has affected eating habits and physical activity in breast cancer survivors: the DianaWeb study
Journal of Cancer Survivorship (2022)
-
Adherence to plant-based dietary patterns in relation to glioma: a case–control study
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A randomized controlled trial of diet and physical activity in BRCA mutation carriers
Familial Cancer (2014)
-
Serum levels of IGF-I and BRCA penetrance: a case control study in breast cancer families
Familial Cancer (2011)