Abstract
Objective: To examine total energy expenditure (TEE) in relation to occupation and reported leisure time activities in free-living Chinese adults, and to determine whether measured TEE values differ from current international dietary energy recommendations.
Setting and subjects: Seventy three weight-maintaining adults aged 35–49 y, leading unrestricted lives in urban Beijing, with a wide variety of occupations.
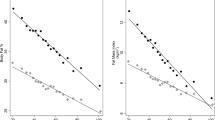
Design and methods: A cross-sectional study in which TEE was determined by doubly labeled water, body composition by deuterium oxide (2H2O) dilution, resting energy expenditure (pREE) by prediction equations, and occupational and leisure time activities by questionnaire.
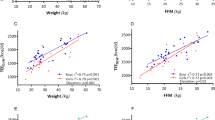
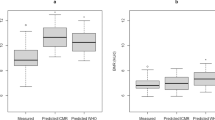
Results: For men and women respectively, TEE averaged 12.10±0.32 and 9.53±0.23 MJ/day (P<0.001), and physical activity level (PAL=TEE/pREE) was 1.77±0.04 and 1.66±0.02 (P<0.05). Fat-free mass (FFM) was the single best predictor of TEE (adjusted r2=0.71, P<0.001). Occupational category (light, moderate and heavy) further predicted TEE, independent of FFM (adjusted multiple r2=0.82, P<0.001). Both TEE adjusted for weight and PAL increased with occupational category. Measured TEE was slightly but significantly higher than the 1985 FAO/WHO/UNU estimates for women with light occupations, but did not differ from estimates for men with light occupations, or for adults with moderate or heavy occupations.
Conclusion: Level of occupational activity, but not duration or type of leisure activity, significantly predicted TEE in free-living urban Chinese adults. Current energy requirement recommendations slightly underestimated the energy needs of women with light occupations but were accurate for men and women with moderate and heavy occupations.
Sponsorship: NIH grants DK53404 and F32-DK09747.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baecke JAH, Burema J, Frijters JER . 1982 A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 36: 936–942
Black AE . 2000 The sensitivity and specificity of the Goldberg cut-off for EI:BMI for identifying diet reports of poor validity Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 54: 395–404
Black AE, Coward WA, Cole TJ, Prentice AM . 1996 Human energy expenditure in affluent societies: an analysis of 574 doubly-labeled water measurements Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50: 72–92
Block G . 1982 A review of validations of dietary assessment methods Am. J. Epidemiol. 115: 492–505
Calazel CM, Young VR, Evans WJ, Roberts SB . 1993 Effect of fasting and feeding on measurement of carbon dioxide production using doubly labeled water J. Appl. Physiol. 74: 1824–1829
Carpenter WH, Poehlman ET, O'Connell M, Goran MI . 1995 Influence of body composition and resting metabolic rate on variation in total energy expenditure: a meta-analysis Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 61: 4–10
Case KO, Brahler CJ, Heiss C . 1997 Resting energy expenditures in Asian women measured by indirect calorimetry are lower than expenditures calculated from prediction equations J. Am. Diet Assoc. 11: 1288–1292
Chinese Nutrition Expert Panel. 2000 Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes Beijing: Chinese Light Industry Publishing House
Coward WA . 1988 The doubly-labeled-water (2H218O) method: principles and practice Proc. Nutr. Soc. 47: 209–218
Coward WA . 1998 Contributions of the doubly labeled water method to studies of energy balance in the Third World Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: (Suppl): S962–S969
Dallal GE, Roberts SB . 1991 DLW: a computer program for the calculation of total energy expenditure in doubly labeled water (2H218O) studies Comp. Biomed. Res. 24: 143–151
de Weir J . 1949 New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein J. Physiol. 109: 1–9
Diaz E, Goldberg GR, Taylor M, Savage JM, Sellen D, Coward WA, Prentice AM . 1991 Effects of dietary supplementation on work performance in Gambian laborers Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 53: 803–811
Durnin JVGA . 1990a Is satisfactory energy balance possible on low energy intakes? Bull. Nutr. Found. India 11: 1–4
Durnin JVGA . 1990b Low energy expenditures in free-living populations Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 44: 95–102
FAO/WHO/UNU. 1985 Energy and protein requirements Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation. Technical Report Series, 724 Geneva: World Health Organization
Ge KY (ed.). 1992 The Dietary and Nutritional Status of Chinese Population Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House
Goran MI, Poehlman ET . 1992 Total energy expenditure and energy requirements in healthy elderly persons Metabolism 41: 744–753
Goran MI, Beer WH, Wolfe RR, Poehlman ET, Young VR . 1993 Variation in total energy expenditure in young healthy free-living men Metabolism 42: 487–496
Haggarty P, Valencia ME, McNeil G . 1997 Energy expenditure during heavy work and its interaction with body weight Br. J. Nutr. 77: 359–373
Heini A, Mingelli G, Diaz E, Prentice A . 1996 Free-living energy expenditure assessed by two different methods in rural Gambian men Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50: 284–289
Huss-Ashmore R, Goodman JL, Sibiya TE, Stein TP . 1989 Energy expenditure of young Swazi women as measured by the doubly labelled water method Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 43: 737–748
Jia H, Meng Q, Shan C . 1999 Study on energy expenditure in Healthy Adults Chin. J. Clin. Nutr. 7: 70–73
Kashiwazaki H, Dejima Y, Orias-Rivera J, Coward WA . 1995 Energy expenditure determined by the doubly labeled water method in Bolivian Aymara living in a high altitude agropastoral community Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62: 901–910
Kuang AK (ed.). 1990 Internal Medicine Manual Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press
Leung R, Woo J, Chan D, Tang N . 2000 Validation of prediction equations for basal metabolic rate in Chinese subjects Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 54: 551–554
Liu HY, Lu YF, Chen WJ . 1995 Predictive equations for basal metabolic rate in Chinese adults: a cross-validation study J. Am. Diet Assoc. 95: 1403–1408
Lohman TAR, Martorell R . (1988) Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics
Montoye HJ, Kemper HCG, Saris WHM, Washburn RA . 1996 Measuring Physical Activity and Energy Expenditure Champaign, IL; Human Kinetics
Pace N, Rathburn EN . 1945 Studies on body composition. III. The body water and chemically combined nitrogen content in relation to fat content J. Biol. Chem. 158: 685–691
Prentice AM, Black AE, Coward WA, Davies AL, Goldberg GR . 1986 High levels of energy expenditure in obese women Br. Med. J. 292: 983–987
Prosser SJ, Scrimgeour CM . 1995 High-precision determination of 2H/1H in H2 and H2O by continuous-flow isotope ratio mass-spectrometry Anal. Chem. 67: 1992–1997
Racette SB, Schoeller DA, Luke AH, Shay KHHJ, Kushner RF . 1994 Relative dilution spaces of 2H and 18O labeled water in humans Am. J. Physiol. 267: E585–E590
Reilly JJ, Lord A, Bunker VW, Prentice AM, Coward WA, Thomas AJ, Briggs RS . 1993 Energy balance in healthy elderly women Br. J. Nutr. 69: 21–27
Roberts SB . 1989 A review of the doubly labeled water method for measurement of total energy expenditure, total body water, water intake and metabolizable energy intake in humans and small animals Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac. 67: 1190–1198
Roberts SB, Young VR, Fuss P, Fiatarone MA, Richard B, Rasmussen H, Wagner D, Joseph L, Holehouse E, Evans WJ . 1990 Energy expenditure and subsequent nutrient intakes in overfed young men Am. J. Physiol. 259: R461–R469
Roberts SB, Heyman MB, Evans WJ, Fuss P, Tsay R, Young VR . 1991 Dietary energy requirements of young adult men, determined by using the doubly labeled water method Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54: 499–505
Roberts SB, Young VR, Fuss P . 1992 What are the dietary energy needs of elderly adults? Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 16: 969–976
Roeykens J, Rogers R, Meeusen R, Magnus L, Borms J, de Meieleir K . 1998 Validity and reliability in a Flemish population of the WHO-MONICA Optional Study of Physical Activity Questionnaire Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 30: 1071–1075
Rush EC, Plank LD, Coward WA . 1999 Energy expenditure of young Polynesian and European women in New Zealand and relations to body composition Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 69: 43–48
Schoeller DA . 1988 Measurement of energy expenditure in free-living humans by using doubly labeled water J. Nutr. 118: 1278–1289
Schoeller DA, Ravussin E, Schutz Y, Acheson KJ, Baertschi P, Jequier E . 1986 Validation in humans and proposed calculation Am. J. Physiol. 250: (5 Pt 2) R823–R830
Schoeller DA, Bandini LG, Dietz WH . 1990 Inaccuracies in self-reported intake identified by comparison with the doubly labelled water method Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac. 68: 941–949
Schofield WN . 1985 Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr 39C: (Suppl 1): 5–41
Schulz LO, Schoeller DA . 1994 A compilation of total daily energy expenditures and body weights in healthy adults Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60: 676–681
Shetty PS, Henry CJK, Black AE, Prentice AM . 1996 Energy requirements of adults: an update on basal metabolic rates (BMRs) and physical activity levels (PALs) Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50: (Suppl 1): S11–S23
Singh J, Prentice AM, Diaz E, Coward WA, Ashford J, Sawyer M, Whitehead RG . 1989 Energy expenditure of Gambian women during peak agricultural activity measured by the doubly-labelled water method Br. J. Nutr. 62: 315–329
Southgate DA . 1973 Fiber and other unavailable carbohydrates and their effects on the energy value of the diet Proc. Nutr. Soc. 32: 131–136
Stein TP, Johnston FE, Greiner L . 1988 Energy expenditure and socioeconomic status in Guatemala as measured by the doubly labelled water method Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 47: 196–200
Surrao J, Sawaya AL, Dallal GE, Tsay R, Roberts SB . 1998 Use of food quotients in human doubly labeled water studies: comparable results obtained with four widely used food intake methods J. Am. Diet Assoc. 98: 1015–1020
van Assema P, Brug J, Kok G, Brants H . 1992 The reliability and validity of a Dutch questionnaire on fat consumption as a means to rank subjects according to individual fat intake Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 1: 375–380
van Loan MD . 1997 Multicompartment model of body composition assessment in Chinese-American adults Am. J. Hum. Biol. 9: 21–27
WHO. 1997 The MONICA Optional Study of Physical Activity (MOSPA) Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 25: S162–S169
Yao M, Roberts SB, Ma GS, Pan H, McCrory MA . 2002 Field methods for body composition assessment are valid in healthy Chinese adults J. Nutr. (in press)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank BM Popkin at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, KY Ge at the Institute of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, and F Zheng at the Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Academy of Preventive Medicine, for discussions about the protocol; H Pan, J Song and SJ Gao for their technical assistance; I Ellis for performing isotopic analyses; Dr GE Dallal for statistical advice; P Fuss for assistance with the manuscript, and the subjects and their families for participating in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, M., McCrory, M., Ma, G. et al. Energy requirements of urban Chinese adults with manual or sedentary occupations, determined using the doubly labeled water method. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 575–584 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601361
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601361
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Physical activity modifies the association between CYBA gene polymorphisms and small artery elasticity in a Chinese population
Hypertension Research (2012)
-
Location of breakfast consumption predicts body mass index change in young Hong Kong children
International Journal of Obesity (2012)
-
Physical activity energy expenditure has not declined since the 1980s and matches energy expenditures of wild mammals
International Journal of Obesity (2008)
-
Use of body mass index to identify obesity-related metabolic disorders in the Chinese population
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2006)
-
Relative influence of diet and physical activity on cardiovascular risk factors in urban Chinese adults
International Journal of Obesity (2003)