Abstract
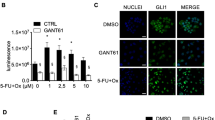
A major obstacle to successful chemotherapy is intrinsic or acquired multi-drug resistance (MDR). The most common cause of MDR involves increased drug efflux from cancer cells mediated by members of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family. The regulation of ABC transporters in the context of cancer is poorly understood, and clinical efforts to inhibit their function have not been fruitful. Constitutive activation of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway has been shown to contribute to the growth and maintenance of various cancers. Here, we show that inhibition of Hh signaling increases the response of cancer cells to multiple structurally unrelated chemotherapies. We further show that Hh pathway activation induces chemoresistance in part by increasing drug efflux in an ABC transporter-dependent manner. We found that Hh signaling regulates the expression of the ABC transporter proteins multi-drug resistance protein-1 (MDR1, ABCB1, P-glycoprotein) and (BCRP, ABCG2), and that targeted knockdown of MDR1 and BCRP expression by small interfering RNA partially reverses Hh-induced chemoresistance. These results suggest that the Hh pathway may be a target to overcome MDR and increase chemotherapeutic response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K et al. (2003). Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature 425: 846–851.
Bigelow RL, Chari NS, Unden AB, Spurgers KB, Lee S, Roop DR et al. (2004). Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 mediated by the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway through gli-1. J Biol Chem 279: 1197–1205.
Bunting KD, Zhou S, Lu T, Sorrentino BP . (2000). Enforced P-glycoprotein pump function in murine bone marrow cells results in expansion of side population stem cells in vitro and repopulating cells in vivo. Blood 96: 902–909.
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, Beachy PA . (2002). Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev 16: 2743–2748.
Chintamani, Singh JP, Mittal MK, Saxena S, Bansal A, Bhatia A et al. (2005). Role of p-glycoprotein expression in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer – a prospective clinical study. World J Surg Oncol 3: 61.
Doyle LA, Ross DD . (2003). Multidrug resistance mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2). Oncogene 22: 7340–7358.
Ingham PW, McMahon AP . (2001). Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev 15: 3059–3087.
Kubo A, Corley DA . (2004). Marked multi-ethnic variation of esophageal and gastric cardia carcinomas within the United States. Am J Gastroenterol 99: 582–588.
Lindstrom E, Shimokawa T, Toftgard R, Zaphiropoulos PG . (2006). PTCH mutations: distribution and analyses. Hum Mutat 27: 215–219.
Okano-Uchida T, Himi T, Komiya Y, Ishizaki Y . (2004). Cerebellar granule cell precursors can differentiate into astroglial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 1211–1216.
Perez-Tomas R . (2006). Multidrug resistance: retrospect and prospects in anti-cancer drug treatment. Curr Med Chem 13: 1859–1876.
Reifenberger J, Wolter M, Knobbe CB, Kohler B, Schonicke A, Scharwachter C et al. (2005). Somatic mutations in the PTCH, SMOH, SUFUH and TP53 genes in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol 152: 43–51.
Ruel L, Rodriguez R, Gallet A, Lavenant-Staccini L, Therond PP . (2003). Stability and association of Smoothened, Costal2 and Fused with Cubitus interruptus are regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol 5: 907–913.
Sims-Mourtada J, Izzo JG, Apisarnthanarax S, Wu T-T, Malhotra U, Luthra R et al. (2006). Hedgehog: an attribute to tumor regrowth after chemoradiotherapy and a target to improve radiation response. Clinical Cancer Research 12: 6565–6572.
Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM . (2006). Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 219–234.
Takara K, Sakaeda T, Okumura K . (2006). An update on overcoming MDR1-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Curr Pharm Des 12: 273–286.
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ et al. (2001). The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med 7: 1028–1034.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants CA89198, CA121551 and P50 CA97007 from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute; the MD Anderson Cancer Center Esophageal Multidisciplinary Research Project Grant; and grants from the Rivercreek Foundation and the Dallas, Cantu, Smith and Park families. Department of Defence grant PC050508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sims-Mourtada, J., Izzo, J., Ajani, J. et al. Sonic Hedgehog promotes multiple drug resistance by regulation of drug transport. Oncogene 26, 5674–5679 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210356
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210356
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance in lung tumor cells
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
Aberrant activation of the Hedgehog signalling pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva as a potential target for cancer therapy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Up-regulation of GLI1 in vincristine-resistant rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Down-regulation of MDR1 by Ad-DKK3 via Akt/NFκB pathways augments the anti-tumor effect of temozolomide in glioblastoma cells and a murine xenograft model
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2018)
-
Targeting the hedgehog transcription factors GLI1 and GLI2 restores sensitivity to vemurafenib-resistant human melanoma cells
Oncogene (2017)