Abstract
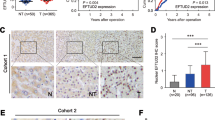
A significant challenge in the post-genomic era is how to prioritize differentially expressed and uncharacterized novel genes found in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) microarray profiling. One such category is cell cycle regulated genes that have only evolved in higher organisms but not in lower eukaryotic cells. Characterization of these genes may reveal some novel human cancer-specific abnormalities. A novel transcript, FLJ10540 was identified. FLJ10540 is overexpressed in HCC as examined by quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. The patients with higher FLJ10540 expression had a poor survival than those with lower FLJ10540 expression. Functional characterization indicates that FLJ10540 displays a number of characteristics associated with an oncogene, including anchorage-independent growth, enhanced cell growth at low serum levels and induction of tumorigenesis in nude mice. FLJ10540-elicited cell transformation is mediated by activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. Moreover, FLJ10540 forms a complex with PI3K and can activate PI3K activity, which provides a mechanistic basis for FLJ10540-mediated oncogenesis. Together, using a combination of bioinformatics searches and empirical data, we have identified a novel oncogene, FLJ10540, which is conserved only in higher organisms. The finding raises the possibility that FLJ10540 is a potential new therapeutic target for HCC treatment. These findings may contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies that are able to block the PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D et al. (1998). Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17: 313–325.
Cantley LC . (2002). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296: 1655–1657.
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, Fan ST, Barry C, Higgins J et al. (2002). Gene expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell 13: 1929–1939.
Chen YL, Law PY, Loh HH . (2004). Inhibition of akt/protein kinase B signaling by naltrindole in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 64: 8723–8730.
Fabbro M, Zhou BB, Takahashi M, Sarcevic B, Lal P, Graham ME et al. (2005). Cdk1/Erk2- and Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of a centrosome protein, Cep55, is required for its recruitment to midbody and cytokinesis. Dev Cell 9: 477–488.
Foster KW, Ren S, Louro ID, Lobo-Ruppert SM, McKie-Bell P, Grizzle W et al. (1999). Oncogene expression cloning by retroviral transduction of adenovirus E1A-immortalized rat kidney RK3E cells: transformation of a host with epithelial features by c-MYC and the zinc finger protein GKLF. Cell Growth Differ 10: 423–434.
Fu SL, Huang YJ, Liang FP, Huang YF, Chuang CF, Wang SW et al. (2005). Malignant transformation of an epithelial cell by v-Src via tv-a-mediated retroviral infection: a new cell model for studying carcinogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338: 830–838.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Hsu JM, Lee YC, Yu CT, Huang CY . (2004). Fbx7 functions in the SCF complex regulating Cdk1-cyclin B-phosphorylated hepatoma up-regulated protein (HURP) proteolysis by a proline-rich region. J Biol Chem 279: 32592–32602.
Kim SA, Kim HW, Kim DK, Kim SG, Park JC, Kang DW et al. (2006). Rapid induction of malignant tumor in Sprague–Dawley rats by injection of RK3E-ras cells. Cancer Lett 235: 53–59.
Kobayashi N, Saeki K, Yuo A . (2003). Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 induce cell cycle progression through the synthesis of c-Myc protein by internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in human factor-dependent leukemic cells. Blood 102: 3186–3195.
Kolligs FT, Kolligs B, Hajra KM, Hu G, Tani M, Cho KR et al. (2000). Gamma-catenin is regulated by the APC tumor suppressor and its oncogenic activity is distinct from that of beta-catenin. Genes Dev 14: 1319–1331.
Liang J, Slingerland JM . (2003). Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2: 339–345.
Ma XJ, Salunga R, Tuggle JT, Gaudet J, Enright E, McQuary P et al. (2003). Gene expression profiles of human breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5974–5979.
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yamasaki S, Todo S, Hirohashi S . (2005). Akt phosphorylation is a risk factor for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 103: 307–312.
Nicholson KM, Streuli CH, Anderson NG . (2003). Autocrine signalling through erbB receptors promotes constitutive activation of protein kinase B/Akt in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 81: 117–128.
Okano J, Shiota G, Matsumoto K, Yasui S, Kurimasa A, Hisatome I et al. (2003). Hepatocyte growth factor exerts a proliferative effect on oval cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309: 298–304.
Ruppert JM, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . (1991). The zinc finger protein GLI transforms primary cells in cooperation with adenovirus E1A. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1724–1728.
Sakai M, Shimokawa T, Kobayashi T, Matsushima S, Yamada Y, Nakamura Y et al. (2006). Elevated expression of C10orf3 (chromosome 10 open reading frame 3) is involved in the growth of human colon tumor. Oncogene 25: 480–486.
Su LJ, Hsu SL, Yang JS, Tseng HH, Huang SF, Huang CY . (2006). Global gene expression profiling of dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis: from pathological and biochemical data to microarray analysis. Gene Expr 13: 107–132.
Tsou AP, Chuang YC, Su JY, Yang CW, Liao YL, Liu WK et al. (2003). Overexpression of a novel imprinted gene, PEG10, in human hepatocellular carcinoma and in regenerating mouse livers. J Biomed Sci 10: 625–635.
Ueki K, Algenstaedt P, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Kahn CR . (2000). Positive and negative regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathways by three different gene products of the p85alpha regulatory subunit. Mol Cell Biol 20: 8035–8046.
Weng Z, Xin M, Pablo L, Grueneberg D, Hagel M, Bain G et al. (2002). Protection against anoikis and down-regulation of cadherin expression by a regulatable beta-catenin protein. J Biol Chem 277: 18677–18686.
Whitfield ML, Sherlock G, Saldanha AJ, Murray JI, Ball CA, Alexander KE et al. (2002). Identification of genes periodically expressed in the human cell cycle and their expression in tumors. Mol Biol Cell 13: 1977–2000.
Wu JC, Chen TY, Yu CT, Tsai SJ, Hsu JM, Tang MJ et al. (2005). Identification of V23RalA-Ser194 as a critical mediator for Aurora-A-induced cellular motility and transformation by small pool expression screening. J Biol Chem 280: 9013–9022.
Xu X, Sakon M, Nagano H, Hiraoka N, Yamamoto H, Hayashi N et al. (2004). Akt2 expression correlates with prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 11: 25–32.
Yang CW, Su JY, Tsou AP, Chau GY, Liu HL, Chen CH et al. (2005). Integrative genomics based identification of potential human hepatocarcinogenesis-associated cell cycle regulators: RHAMM as an example. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330: 489–497.
Yu CT, Hsu JM, Lee YC, Tsou AP, Chou CK, Huang CY . (2005). Phosphorylation and stabilization of HURP by Aurora-A: implication of HURP as a transforming target of Aurora-A. Mol Cell Biol 25: 5789–5800.
Zhao WM, Seki A, Fang G . (2006). Cep55, a microtubule-bundling protein, associates with centralspindlin to control the midbody integrity and cell abscission during cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell 17: 3881–3896.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Chang Gung Hospital (CMRPD33100) and NSC (94–2752-B-010–002-PAE) to Chen-Kung Chou, and NSC (95–2320-B-400–009-MY3) and NHRI to Chi-Ying F. Huang. We thank Pei-Fen Yen, Yu-Lien Wu and Jia-Je Li for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CH., Lu, PJ., Chen, YC. et al. FLJ10540-elicited cell transformation is through the activation of PI3-kinase/AKT pathway. Oncogene 26, 4272–4283 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210207
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of CEP55, SERPINE1 and SMPD3 genes and proteins as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in gastric carcinoma in Egyptian patients
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences (2022)
-
CEP55 3’-UTR promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and enhances tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA regulating miR-497-5p
Cellular Oncology (2022)
-
Cep55 overexpression promotes genomic instability and tumorigenesis in mice
Communications Biology (2020)
-
Cep55 promotes cytokinesis of neural progenitors but is dispensable for most mammalian cell divisions
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Genes CEP55, FOXD3, FOXF2, GNAO1, GRIA4, and KCNA5 as potential diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer
BMC Medical Genomics (2019)