Abstract
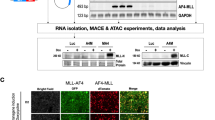
The reciprocal chromosomal translocation t(4;11) is correlated with infant, childhood, adult and therapy-related high-risk acute leukemia. Here, we investigated the biological effects of MLL·AF4, AF4·MLL or the combination of both reciprocal fusion proteins in a conditional in vitro cell culture model system. Several parameters like cell growth, cell cycling capacity, apoptotic behavior and growth transformation were investigated under physiological and stress conditions. Co-transfected cells displayed the highest resistance against apoptotic triggers, cell cycling capacity and loss-of-contact inhibition. These analyses were complemented by gene expression profiling experiments and specific gene signatures were established for each of the three cell lines. Interestingly, co-transfected cells strongly upregulate the homeobox gene Nanog. In combination with Oct4, the Nanog homeoprotein is steering maintenance of pluripotency and self-renewal in embryonic stem cells. Transcription of Nanog and other stem cell factors, like Oct4 and Bmi1, was verified in biopsy material of t(4;11) patient cells which express both reciprocal t(4;11) fusion genes. In conclusion, the presence of both reciprocal MLL fusion proteins confers biological properties known from t(4;11) leukemia, suggesting that each of the two fusion proteins contribute specific properties and, in combination, also synergistic effects to the leukemic phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almstrup K, Hoei-Hansen CE, Wirkner U, Blake J, Schwager C, Ansorge W et al. (2004). Embryonic stem cell-like features of testicular carcinoma in situ revealed by genome-wide gene expression profiling. Cancer Res 64: 4736–4743.
Andersson A, Olofsson T, Lindgren D, Nilsson B, Ritz C, Edén P et al. (2005). Molecular signatures in childhood acute leukemia and their correlations to expression patterns in normal hematopoietic subpopulations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 19069–19074.
Ayton PM, Cleary ML . (2003). Transformation of myeloid progenitors by MLL oncoproteins is dependent on Hoxa7 and Hoxa9. Genes Dev 17: 2298–2307.
Booth HA, Holland PW . (2004). Eleven daughters of NANOG. Genomics 84: 229–238.
Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, Johnstone SE, Levine SS, Zucker JP et al. (2005). Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 122: 947–956.
Bursen A, Moritz S, Gaussmann A, Moritz S, Dingermann T, Marschalek R . (2004). Interaction of AF4 wildtype and AF4·MLL fusion protein with SIAH proteins: indication for t(4;11) pathobiology? Oncogene 23: 6237–6249.
Caslini C, Serna A, Rossi V, Introna M, Biondi A . (2004). Modulation of cell cycle by graded expression of MLL-AF4 fusion oncoprotein. Leukemia 18: 1064–1071.
Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, Nichols J, Lee S, Tweedie S et al. (2003). Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 113: 643–655.
Chen W, Li Q, Hudson WA, Kumar A, Kirchhof N, Kersey JH . (2006). A murine Mll-AF4 knockin model results in lymphoid and myeloid deregulation and hematological malignancy. Blood March 21 (e-pub ahead of print).
Dordelmann M, Reiter A, Borkhardt A, Ludwig WD, Gotz N, Viehmann S et al. (1999). Prednisone response is the strongest predictor of treatment outcome in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 94: 1209–1217.
Downing JR, Head DR, Raimondi SC, Carroll AJ, Curcio-Brint AM, Motroni TA et al. (1994). The der(11)-encoded MLL/AF-4 fusion transcript is consistently detected in t(4;11)(q21;q23)-containing acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 83: 330–335.
Felix CA, Hosler MR, Winick NJ, Masterson M, Wilson AE, Lange BJ . (1995). ALL-1 gene rearrangements in DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor-related leukemia in children. Blood 85: 3250–3256.
Greil J, Gramatzki M, Burger R, Marschalek R, Peltner M, Trautmann U et al. (1994). The acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell line SEM with t(4;11) chromosomal rearrangement is biphenotypic and responsive to interleukin-7. Br J Haematol 86: 275–283.
Guenther MG, Jenner RG, Chevalier B, Nakamura T, Croce CM, Canaani E et al. (2005). Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 8603–8608.
Hoei-Hansen CE, Almstrup K, Nielsen JE, Brask Sonne S, Graem N, Skakkebaek NE et al. (2005). Stem cell pluripotency factor NANOG is expressed in human fetal gonocytes, testicular carcinoma in situ and germ cell tumours. Histopathology 47: 48–56.
Ivanova N, Dobrin R, Lu R, Kotenko I, Levorse J, DeCoste C et al. (2006). Dissecting self-renewal in stem cells with RNA interference. Nature 442: 533–538.
Janssen JW, Ludwig WD, Borkhardt A, Spadinger U, Rieder H, Fonatsch C et al. (1994). Pre-pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia: high frequency of alternatively spliced ALL1-AF4 transcripts and absence of minimal residual disease during complete remission. Blood 84: 3835–3842.
Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M . (2006). Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med 355: 1253–1261.
Kersey JH, Wang D, Oberto M . (1998). Resistance of t(4;11) (MLL-AF4 fusion gene) leukemias to stress-induced cell death: possible mechanism for extensive extramedullary accumulation of cells and poor prognosis. Leukemia 12: 1561–1564.
Lange B, Valtieri M, Santoli D, Caracciolo D, Mavilio F, Gemperlein I et al. (1987). Growth factor requirements of childhood acute leukemia: establishment of GM-CSF-dependent cell lines. Blood 70: 192–199.
Lee TI, Jenner RG, Boyer LA, Guenther MG, Levine SS, Kumar RM et al. (2006). Control of developmental regulators by polycomb in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 21: 301–313 (doi 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.043).
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, Vega VB, Zhang W, Chen X et al. (2006). The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 5: March (e-pub ahead of print).
Metzler M, Forster A, Pannell R, Arends MJ, Daser A, Lobato MN et al. (2006). A conditional model of MLL-AF4 B-cell tumourigenesis using invertor technology. Oncogene 25: 3093–3103.
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K, Murakami M, Takahashi K et al. (2003). The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 113: 631–642.
Mitterbauer-Hohendanner G, Mannhalter C . (2004). The biological and clinical significance of MLL abnormalities in haematological malignancies. Eur J Clin Invest 34: 12–24.
Pui CH, Behm FG, Downing JR, Hancock ML, Shurtleff SA, Ribeiro RC et al. (1994). 11q23/MLL rearrangement confers a poor prognosis in infants with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 12: 909–915.
Reichel M, Gillert E, Angermüller S, Hensel JP, Heidel F, Lode M et al. (2001). Biased distribution of chromosomal breakpoints involving the MLL gene in infants versus children and adults with t(4;11) ALL. Oncogene 20: 2900–2907.
Skotheim RI, Lind GE, Monni O, Nesland JM, Abeler VM, Fossa SD et al. (2005). Differentiation of human embryonal carcinomas in vitro and in vivo reveals expression profiles relevant to normal development. Cancer Res 65: 5588–5598.
So ECW, Wong P, Lin M, Cleary ML . (2004). Disease models and transformation mechanisms mediated by MLL-AF4 family oncoproteins in human leukemia. ASH Abst 467.
Stong RC, Korsmeyer SJ, Parkin JL, Arthur DC, Kersey JH . (1985). Human acute leukemia cell line with the t(4;11) chromosomal rearrangement exhibits B lineage and monocytic characteristics. Blood 65: 21–31.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Bath ML, Cory S . (1990). Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature 348: 331–333.
Takeda S, Chen DY, Westergard TD, Fisher JK, Rubens JA, Sasagawa S et al. (2006). Proteolysis of MLL family proteins is essential for Taspase1-orchestrated cell cycle progression. Genes Dev 29: 2397–2409.
Taranger CK, Noer A, Sorensen AL, Hakelien AM, Boquest AC, Collas P . (2005). Induction of dedifferentiation, genomewide transcriptional programming, and epigenetic reprogramming by extracts of carcinoma and embryonic stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 16: 5719–5735.
Terranova R, Agherbi H, Boned A, Meresse S, Djabali M . (2006). Histone and DNA methylation defects at Hox genes in mice expressing a SET domain-truncated form of Mll. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 6629–6634.
Thomas M, Gessner A, Vornlocher HP, Hadwiger P, Greil J, Heidenreich O . (2005). Targeting MLL-AF4 with short interfering RNAs inhibits clonogenicity and engraftment of t(4;11)-positive human leukemic cells. Blood 106: 3559–3566.
Xia ZB, Popovic R, Chen J, Theisler C, Stuart T, Santillan DA et al. (2005). The MLL fusion gene, MLL-AF4, regulates cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1B (p27kip1) expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 14028–14033.
Yu BD, Hess JL, Horning SE, Brown GA, Korsmeyer SJ . (1995). Altered Hox expression and segmental identity in Mll-mutant mice. Nature 378: 505–508.
Zhang J, Wang X, Li M, Han J, Chen B, Wang B et al. (2006). NANOGP8 is a retrogene expressed in cancers. FEBS J 273: 1723–1730.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Malek Djabali, INSERM Marseille, for providing and sharing yet unpublished data on the MLLΔSET mouse. We are grateful to Richard Young for providing access to his lab, owing to which his Chip-on-CHIP data were publically available. We thank T Burmeister (Berlin) who provided the cDNAs from adult t(4;11) patients, and André Schrauder (Kiel) who provided the cDNAs from infant t(4;11) patients. This study was supported by grants MA 1876/8-1 from the DFG, N1KR-S12T13 from the BMBF, and 2001.061.2 from the Wilhelm-Sander-Foundation to RM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaussmann, A., Wenger, T., Eberle, I. et al. Combined effects of the two reciprocal t(4;11) fusion proteins MLL·AF4 and AF4·MLL confer resistance to apoptosis, cell cycling capacity and growth transformation. Oncogene 26, 3352–3363 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210125
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210125
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of class I HDACs abrogates the dominant effect of MLL-AF4 by activation of wild-type MLL
Oncogenesis (2014)
-
OCT4 pseudogenes present in human leukemia cells
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2012)
-
The leukemogenic AF4–MLL fusion protein causes P-TEFb kinase activation and altered epigenetic signatures
Leukemia (2011)
-
Insights into the cellular origin and etiology of the infant pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with MLL-AF4 rearrangement
Leukemia (2011)
-
The heterodimerization domains of MLL—FYRN and FYRC—are potential target structures in t(4;11) leukemia
Leukemia (2011)