Abstract
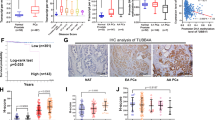
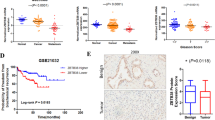
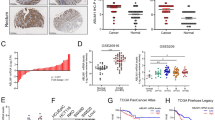
We have recently identified ZNF185 as a gene that is downregulated in prostate cancer (PCa), in part via epigenetic alteration, and maybe associated with disease progression. In this study, we cloned the ZNF185 cDNA from normal human prostate tissues and investigated its biological function. We show that ZNF185 is a novel actin–cytoskeleton-associated Lin-l 1, Isl-1 and Mec-3 (LIM) domain-containing protein that localizes to F-actin structures, and is enriched at focal adhesions. We find that the NH2-terminal region, which we designate the actin-targeting domain, facilitates ZNF185 binding to actin in vitro and is both necessary and sufficient to mediate actin–cytoskeleton targeting of ZNF185, whereas the LIM domain, which is localized in the COOH-terminus is dispensable for this phenomenon. Interestingly, ectopic expression of full-length ZNF185, but not a mutant lacking the actin-targeting domain, could suppress proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of PCa cells. Together, our data suggest that ZNF185 may function as a tumor-suppressor protein by associating with the actin–cytoskeleton.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach I . (2000). Mech Dev 91: 5–17.
Dawid IB, Breen JJ, Toyama R . (1998). Trends Genet 14: 156–162.
Dhanasekaran SM, Barrette TR, Ghosh D, Shah R, Varambally S, Kurachi K et al. (2001). Nature 412: 822–826.
Freyd G, Kim SK, Horvitz HR . (1990). Nature 344: 876–879.
Garvalov BK, Higgins TE, Sutherland JD, Zettl M, Scaplehorn N, Kocher T et al. (2003). J Cell Biol 161: 33–39.
Gonzalez HE, Gujrati M, Frederick M, Henderson Y, Arumugam J, Spring PW et al. (2003). Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129: 754–759.
Heiss NS, Gloeckner G, Bachner D, Kioschis P, Klauck SM, Hinzmann B et al. (1997). Genomics 43: 329–338.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C et al. (2006). CA Cancer J Clin 56: 106–130.
Kadrmas JL, Beckerle MC . (2004). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 920–931.
Karlsson O, Thor S, Norberg T, Ohlsson H, Edlund T . (1990). Nature 344: 879–882.
Labouesse M, Georges-Labouesse E . (2003). Curr Biol 13: 528–530.
Luo J, Duggan DJ, Chen Y, Sauvageot J, Ewing CM, Bittner ML et al. (2001). Cancer Res 61: 4683–4688.
Magee JA, Araki T, Patil S, Ehrig T, True L, Humphrey PA et al. (2001). Cancer Res 61: 5692–5696.
Maul RS, Chang DD . (1999). Oncogene 18: 7838–7841.
Medina PP, Carretero J, Ballestar E, Angulo B, Lopez-Rios F, Esteller M et al. (2005). Hum Mol Genet 14: 973–982.
Pan Y, Zhang JS, Gazi MH, Young CY . (2003). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 8: 769–774.
Rogers S, Wells R, Rechsteiner M . (1986). Science 234: 364–368.
Rubin MA, Zhou M, Dhanasekaran SM, Varambally S, Barrette TR, Sanda MG et al. (2002). JAMA 287: 1662–1670.
Song Y, Maul RS, Gerbin CS, Chang DD . (2002). Mol Biol Cell 13: 1408–1416.
Sum EY, Peng B, Yu X, Chen J, Byrne J, Lindeman GJ et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 7849–7856.
Tatarelli C, Linnenbach A, Mimori K, Croce CM . (2000). Genomics 68: 1–12.
Tobias ES, Hurlstone AF, MacKenzie E, McFarlane R, Black DM . (2001). Oncogene 20: 2844–2853.
Vanaja DK, Cheville JC, Iturria SJ, Young CY . (2003). Cancer Res 63: 3877–3882.
Visvader JE, Venter D, Hahm K, Santamaria M, Sum EY, O’Reilly L et al. (2001). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 14452–14457.
Way JC, Chalfie M . (1988). Cell 54: 5–16.
Welsh JB, Sapinoso LM, Su AI, Kern SG, Wang-Rodriguez J, Moskaluk CA et al. (2001). Cancer Res 61: 5974–5978.
Wong N, Chan KY, Macgregor PF, Lai PB, Squire JA, Beheshti B et al. (2005). Clin Cancer Res 11: 1319–1326.
Xu J, Meyers D, Freije D, Isaacs S, Wiley K, Nusskern D et al. (1998). Nat Genet 20: 175–179.
Zhang JS, Gong A, Cheville JC, Smith DI, Young CY . (2005). Genes Chromosome Cancer 43: 249–259.
Zhang JS, Moncrieffe MC, Kaczynski J, Ellenrieder V, Prendergast FG, Urrutia R . (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 5041–5049.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Daniel D Billadeau for enlightening discussions and critically reading this article, and Dr Hong Cao and Dr McNiven's laboratory for providing the FR cells. This work was supported in part by NIH Grants CA70892 and CA91956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JS., Gong, A. & Young, C. ZNF185, an actin–cytoskeleton-associated growth inhibitory LIM protein in prostate cancer. Oncogene 26, 111–122 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209769
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209769
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ZNF185 prevents stress fiber formation through the inhibition of RhoA in endothelial cells
Communications Biology (2023)
-
ZNF185 is a p63 target gene critical for epidermal differentiation and squamous cell carcinoma development
Oncogene (2019)
-
Distinct prostate cancer-related mRNA cargo in extracellular vesicle subsets from prostate cell lines
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease
Cell Death Discovery (2017)
-
Bending Maxwell's rule
Nature Physics (2011)