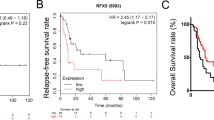
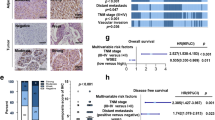
Abstract
FAT10 is a member of the ubiquitin-like modifier family of proteins and has been implicated to play important roles in antigen presentation, cytokine response, apoptosis and mitosis. We have recently demonstrated the upregulation of FAT10 gene expression in 90% of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Here, we identified and characterized the promoter of the FAT10 gene to elucidate the mechanism of FAT10 gene expression. Notably, we found that the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR), from the transcription start site to 15 bases before the translational start site, displays significant promoter activity. Regions upstream of the 5′UTR (from +26 to −1997) do not confer any promoter activity. Curiously, FAT10 promoter activity and expression is significantly repressed in KB3-1 and HepG2 cells, which have wild-type p53, than in p53-negative Hep3B cells. The role of p53 in regulating FAT10 expression was evident by the significant downregulation (P<0.05) of FAT10 mRNA expression and promoter activity when wild-type p53 was transfected into p53-null Hep3B cells. Conversely, inhibiting p53 expression through siRNA against p53 significantly enhanced FAT10 expression and promoter activity. p53 was found to bind in vivo to the 5′ half consensus sequence of p53-binding site located at the FAT10 promoter. Hence, we propose that FAT10 is a downstream target of p53 and dysregulation of FAT10 expression in p53-defective cells could contribute to carcinogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Aguiar J, Santurlidis S, Nowok J, Alexander C, Rudnicki D, Gispert S et al. (1999). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254: 315–318.
Bates EE, Ravel O, Dieu MC, Ho S, Guret C, Bridon JM et al. (1997). Eur J Immunol 27: 2471–2477.
Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC . (1997). Annu Rev Immunol 15: 749–795.
Bressac B, Galvin KM, Liang TJ, Isselbacher KJ, Wands JR, Ozturk M . (1990). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1973–1977.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . (2002). Science 296: 550–553.
Chun AC, Jin DY . (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 37439–37450.
Clark IM, Rowan AD, Edwards DR, Bech-Hansen T, Mann DA, Bahr MJ et al. (1997). Biochem J 324 (Part 2): 611–617.
Dokmanovic M, Chang BD, Fang J, Roninson IB . (2002). Cancer Biol Ther 1: 24–27.
el-Deiry WS . (1998). Semin Cancer Biol 8: 345–357.
Fan W, Cai W, Parimoo S, Schwarz DC, Lennon GG, Weissman SM . (1996). Immunogenetics 44: 97–103.
Farmer G, Colgan J, Nakatani Y, Manley JL, Prives C . (1996). Mol Cell Biol 16: 4295–4304.
Haupt Y, Robles AI, Prives C, Rotter V . (2002). Oncogene 21: 8223–8231.
Hernando E, Nahle Z, Juan G, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Alaminos M, Hemann M et al. (2004). Nature 430: 797–802.
Ho J, Benchimol S . (2003). Cell Death Differ 10: 404–408.
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J, Murphy M . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 3247–3257.
Innocente SA, Abrahamson JL, Cogswell JP, Lee JM . (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 2147–2152.
Jentsch S, Pyrowolakis G . (2000). Trends Cell Biol 10: 335–342.
Jesenberger V, Jentsch S . (2002). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 112–121.
Kumanovics A, Takada T, Lindahl KF . (2003). Annu Rev Immunol 21: 629–657.
Lane DP . (1992). Nature 358: 15–16.
Lee CG, Ramachandra M, Jeang KT, Martin MA, Pastan I, Gottesman MM . (2000). FASEB J 14: 516–522.
Lee CG, Ren J, Cheong IS, Ban KH, Ooi LL, Yong Tan S et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 2592–2603.
Lee KC, Crowe AJ, Barton MC . (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 1279–1288.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell 88: 323–331.
Li GQ, Li H, Zhang HF . (2003). World J Gastroenterol 9: 1972–1975.
Liu YC, Pan J, Zhang C, Fan W, Collinge M, Bender JR et al. (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4313–4318.
Luo X, Tang Z, Rizo J, Yu H . (2002). Mol Cell 9: 59–71.
Maeda Y, Seidel SD, Wei G, Liu X, Sladek FM . (2002). Mol Endocrinol 16: 402–410.
Michel LS, Liberal V, Chatterjee A, Kirchwegger R, Pasche B, Gerald W et al. (2001). Nature 409: 355–359.
Moll UM, Riou G, Levine AJ . (1992). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7262–7266.
Pagano M . (1997). FASEB J 11: 1067–1075.
Pines J . (1994). Nature 371: 742–743.
Raasi S, Schmidtke G, de Giuli R, Groettrup M . (1999). Eur J Immunol 29: 4030–4036.
Stahler F, Roemer K . (1998). Oncogene 17: 3507–3512.
Taylor WR, Schonthal AH, Galante J, Stark GR . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 1998–2006.
Taylor WR, Stark GR . (2001). Oncogene 20: 1803–1815.
van den Elsen PJ, Gobin SJ, van Eggermond MC, Peijnenburg A . (1998). Immunogenetics 48: 208–221.
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ . (2000). Nature 408: 307–310.
Vousden KH, Lu X . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 594–604.
Wang X, Jin DY, Ng RW, Feng H, Wong YC, Cheung AL et al. (2002). Cancer Res 62: 1662–1668.
Zhao R, Gish K, Murphy M, Yin Y, Notterman D, Hoffman WH et al. (2000). Genes Dev 14: 981–993.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Biomedical Research Council (BMRC), National Medical Research Council (NMRC), Singapore and the SingHealth Cluster Research Fund to Caroline GL Lee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Jeang, KT. & Lee, C. p53 negatively regulates the expression of FAT10, a gene upregulated in various cancers. Oncogene 25, 2318–2327 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209220
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209220
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
p53 regulation by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications
Genome Instability & Disease (2022)
-
The expression profile of the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 in immune cells suggests cell type-specific functions
Immunogenetics (2018)
-
As an independent prognostic factor, FAT10 promotes hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression via Akt/GSK3β pathway
Oncogene (2014)
-
Increased Expression of FAT10 is Correlated with Progression and Prognosis of Human Glioma
Pathology & Oncology Research (2012)
-
Ubiquitin D is correlated with colon cancer progression and predicts recurrence for stage II-III disease after curative surgery
British Journal of Cancer (2010)