Abstract
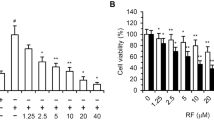
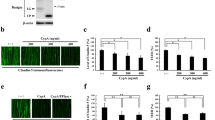
A second generation genetically-engineered cell-based drug delivery system, referred to as apoptotic-induced drug delivery (AIDD), was developed using endothelial cells (ECs) that undergo apoptosis upon binding of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to a Flk-1:Fas fusion protein (FF). This new AIDD was redesigned using mouse brain derived ECs, bEnd3 cells, and an adenovirus vector in order to enhance and control the expression of FF. The FF was tagged with a HA epitope (FFHA) and designed to be coexpressed with green fluorescence protein (GFP) by the regulation of cytomegalovirus promoters in the adenovirus vector. bEnd3 cells showed favorable coexpression of FFHA and GFP consistent with the multiplicity of infection of the adenovirus. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that FFHA was localized at the plasma membrane, whereas GFP was predominantly located in the cytoplasm of ECs. Cell death was induced by VEGF, but not by platelet derived growth factor or fibroblast growth factor in a dose-dependent manner (range 2–20 ng/ml), and revealed caspase-dependent apoptotic profiles. The FFHA expressing bEnd3 cells underwent apoptosis when cocultured with a glioma cell (SF188V+) line able to overexpress VEGF. The combined data indicated that the FFHA adenovirus system can induce apoptotic signaling in ECs in response to VEGF, and thus, is an instrumental modification to the development of AIDD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkman RA, Merrill MJ, Reinhold WC, Monacci WT, Saxena A, Clark WC et al. (1993). J Clin Invest 91: 153–159.
Carpenito C, Davis PD, Dougherty ST, Dougherty GJ . (2002). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54: 1473–1478.
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM . (1995). Cell 81: 505–512.
Dass CR . (2002). J Pharm Pharmacol 54: 3–27.
Dejana E . (2004). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 261–270.
Hallmann R, Savigni DL, Morgan EH, Baker E . (2000). Endothelium 7: 135–147.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (1998). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 2509–2514.
Itoh N, Nagata S . (1993). J Biol Chem 268: 10932–10937.
Le Ricousse-Roussanne S, Barateau V, Contreres JO, Boval B, Kraus-Berthier L, Tobelem G . (2004). Cardiovasc Res 62: 176–184.
Ma J, Gallo JM . (1998a). Apoptosis 3: 195–202.
Ma J, Reed KA, Gallo JM . (2002). Cancer Res 62: 1382–1387.
Ma J, Zhou-Li F, Klein-Szanto A, Gallo JM . (1998b). Clin Exp Metastasis 16: 559–568.
Mitsuuchi Y, Johnson SW, Moonblatt S, Testa JR . (1998). J Cell Biochem 70: 433–441.
Ni R, Tomita Y, Matsuda K, Ichihara A, Ishimura K, Ogasawara J et al. (1994). Exp Cell Res 215: 332–337.
Pereboeva L, Komarova S, Mikheeva G, Krasnykh V, Curiel DT . (2003). Stem Cells 21: 389–404.
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Mennel HD, Risau W . (1994). Int J Cancer 59: 520–529.
Quinn TP, Soifer SJ, Ramer K, Williams LT, Nakamura MC . (2001). Cancer Res 61: 8629–8637.
Scappaticci FA . (2002). J Clin Oncol 20: 3906–3927.
Soga N, Connolly JO, Chellaiah M, Kawamura J, Hruska KA . (2001). Cell Commun Adhes 8: 1–13.
ten Tije AJ, Verweij J, Loos WJ, Sparreboom A . (2003). Clin Pharmacokinet 42: 665–685.
Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP . (1999). Annu Rev Immunol 17: 331–367.
Wrede CE, Dickson LM, Lingohr MK, Briaud I, Rhodes CJ . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 49676–49684.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs P Guo, F Zhou and J Ma for technical advice and assistance. This work was supported by NIH Grant CA085577.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsuuchi, Y., Powell, D. & Gallo, J. Adenoviral modification of mouse brain derived endothelial cells, bEnd3, to induce apoptosis by vascular endothelial growth factor. Oncogene 25, 954–958 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209142