Abstract
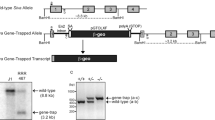
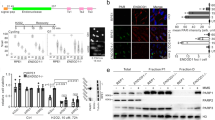
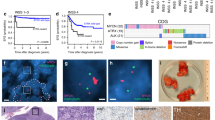
AMID is an apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)-homologous and mitochondria-associated protein that has been implicated in caspase-independent apoptosis. Transcription of human AMID gene is upregulated by p53 and downregulated in tumors in comparison to their matched normal tissues, suggesting the possibility that AMID is involved in the downstream effects of p53. To investigate the physiological functions of AMID, we generated AMID-deficient mice by gene targeting. AMID-deficient mice are viable and fertile, develop normally and lack obvious phenotypic changes compared to wild-type mice up to 1 year old. AMID−/− mice up to 1 year old have no spontaneous tumors and show similar fibrosarcoma incidence after MCA inoculation compared to wild-type mice. AMID−/− embryonic fibroblasts exhibit normal proliferation but slightly increased resistance to genotoxin-induced growth arrest. These findings suggest that AMID is not required for normal development and p53-mediated tumor suppression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarante-Mendes GP, Finucane DM, Martin SJ, Cotter TG, Salvesen GS, Green DR . (1998). Cell Death Differ 5: 298–306.
Bidere N, Senik A . (2001). Apoptosis 6: 371–375.
Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Larochette N, Zamzami N et al. (2002). Biochimie 84: 215–222.
Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI, Roth KA, Gruss P . (1998). Cell 94: 727–737.
Daugas E, Nochy D, Ravagnan L, Loeffler M, Susin SA, Zamzami N et al. (2000). FEBS Lett 476: 118–123.
Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, McArthur MJ, Montgomery Jr CA, Butel JS et al. (1992). Nature 356: 215–221.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X . (2000). Cell 102: 33–42.
Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB . (1998). Genes Dev 12: 2973–2983.
Green DR, Reed JC . (1998). Science 281: 1309–1312.
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS et al. (1998). Cell 94: 339–352.
Hansen R, Oren M . (1997). Curr Opin Genet Dev 7: 46–51.
Hengartner MO . (2000). Nature 407: 770–776.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY et al. (2001). Nature 410: 549–554.
Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D, Karasuyama H et al. (1996). Nature 384: 368–372.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell 88: 323–331.
Li K, Li Y, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Spencer E, Chen ZJ et al. (2000). Cell 101: 389–399.
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X . (1996). Cell 86: 147–157.
Miramar MD, Costantini P, Ravagnan L, Saraiva LM, Haouzi D, Brothers G et al. (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 16391–16398.
Mosmann T . (1983). J Immunol Methods 65: 55–63.
Ohiro Y, Garkavtsev I, Kobayashi S, Sreekumar KR, Nantz R, Higashikubo BT et al. (2002). FEBS Lett 524: 163–171.
Prives C, Hall PA . (1999). J Pathol 187: 112–126.
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM et al. (1999). Nature 397: 441–446.
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE et al. (2000). Cell 102: 43–53.
Wang X . (2001). Genes Dev 15: 2922–2933.
Wu M, Xu LG, Li X, Zhai Z, Shu HB . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 25617–25623.
Wu M, Xu LG, Su T, Tian Y, Zhai Z, Shu HB . (2004). Oncogene 23: 6815–6819.
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A, Hakem R et al. (1998). Cell 94: 739–750.
Zhang P, Li MZ, Elledge SJ . (2002). Nat Genet 30: 31–39.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Raul Torres for help with gene knockout studies, Dr Gwinevere Murphy for providing us anti-p53 antibody and Dr Stephen J Elledge for providing the Recombination Cloning System.This work was supported by a grant from the NIH (CA108771).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, J., Webb, S., Zhang, B. et al. The p53-inducible apoptotic protein AMID is not required for normal development and tumor suppression. Oncogene 25, 849–856 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A targetable CoQ-FSP1 axis drives ferroptosis- and radiation-resistance in KEAP1 inactive lung cancers
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2021)
-
A new checkpoint against ferroptosis
Cell Research (2020)
-
AMID: new insights on its intracellular localization and expression at apoptosis
Apoptosis (2008)
-
Bioinformatic and image analyses of the cellular localization of the apoptotic proteins endonuclease G, AIF, and AMID during apoptosis in human cells
Apoptosis (2007)