Abstract
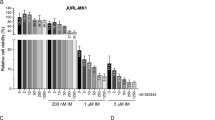
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is caused by Bcr-Abl, an activated tyrosine kinase. The amounts of Bcr-Abl mRNA and protein in cells from patients in blast crisis (BC) are higher than in those chronic phase (CP), indicating that their expression rises with disease progression. In order to study this phenomenon on cells with the same genetic background, we transfected the 32D cell line with the BCR-ABL transgene and selected clones with graded expression of Bcr-Abl within the range found in cells from CP to BC. In vitro, we found that Bcr-Abl exerted dose-dependent effects upon growth factor dependence, clonogenicity and migration. However, the relationship between Bcr-Abl expression and cellular adhesion to fibronectin was more complex: rather than a direct positive correlation, clones that expressed low, but not high, levels of Bcr-Abl were less adhesive than growth factor stimulated, parental BCR-ABL-negative 32D cells. This finding parallels the situation with normal and CML-CP progenitors where the latter exhibit defective adhesion to fibronectin. Treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate reversed the adhesion deficient phenotype of clones expressing low levels of Bcr-Abl. When injected subcutaneously into syngeneic mice, cell lines expressing high levels of Bcr-Abl rapidly induced tumors, whereas low-expressing clones led to tumor formation only after a prolonged latency. These findings suggest that the level of Bcr-Abl may be essential in determining the phenotype of the leukemic clone at different stages of the disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos TA, Lewis JL, Grand FH, Gooding RP, Goldman JM and Gordon MY . (1995). Br. J. Haematol., 91, 387–393.
Bazzoni G, Carlesso N, Griffin JD and Hemler ME . (1996). J. Clin. Invest., 98, 521–528.
Bhatia R, Munthe HA and Forman SJ . (2001). Br. J. Haematol., 115, 845–853.
Bhatia R, Munthe HA and Verfaillie CM . (1998). Leukemia, 12, 1708–1717.
Bhatia R and Verfaillie CM . (1998). Blood, 91, 3414–3422.
Cambier N, Chopra R, Strasser A, Metcalf D and Elefanty AG . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 335–348.
Dazzi F, Capelli D, Hasserjian R, Cotter F, Corbo M, Poletti A, Chinswangwatanakul W, Goldman JM and Gordon MY . (1998). Blood, 92, 1390–1396.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM and Melo JV . (2000). Blood, 96, 3343–3356.
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J and Lydon NB . (1996). Nat. Med., 2, 561–566.
Elmaagacli AH, Beelen DW, Opalka B, Seeber S and Schaefer UW . (2000). Ann. Hematol., 79, 424–431.
Gaiger A, Henn T, Horth E, Geissler K, Mitterbauer G, Maier-Dobersberger T, Greinix H, Mannhalter C, Haas OA and Lechner K . (1995). Blood, 86, 2371–2378.
Gordon MY, Dowding CR, Riley GP, Goldman JM and Greaves MF . (1987). Nature, 328, 342–344.
Guo JQ, Wang JY and Arlinghaus RB . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 3048–3051.
Hurley RW, McCarthy JB and Verfaillie CM . (1995). J. Clin. Invest., 96, 511–519.
Issaad C, Ahmed M, Novault S, Bonnet ML, Bennardo T, Varet B, Vainchenker W and Turhan AG . (2000). Leukemia, 14, 662–670.
Kabarowski JH, Allen PB and Wiedemann LM . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 5887–5895.
Kramer A, Horner S, Willer A, Fruehauf S, Hochhaus A, Hallek M and Hehlmann R . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 96, 2087–2092.
Laemmli UK . (1970). Nature, 227, 680–685.
Laneuville P, Heisterkamp N and Groffen J . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 275–282.
Levesque JP, Leavesley DI, Niutta S, Vadas M and Simmons PJ . (1995). J. Exp. Med., 181, 1805–1815.
Lewis ID, McDiarmid LA, Samels LM, To LB and Hughes TP . (1998). Blood, 91, 630–640.
Lin F, van Rhee F, Goldman JM and Cross NC . (1996). Blood, 87, 4473–4478.
Morgenstern JP and Land H . (1990). Nucleic. Acids. Res., 18, 3587–3596.
Pear WS, Miller JP, Xu L, Pui JC, Soffer B, Quackenbush RC, Pendergast AM, Bronson R, Aster JC, Scott ML and Baltimore D . (1998). Blood, 92, 3780–3792.
Ramaraj P, Singh H, Niu N, Chu S, Holtz M, Yee JK and Bhatia R . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 5322–5331.
Salgia R, Li JL, Ewaniuk DS, Pear W, Pisick E, Burky SA, Ernst T, Sattler M, Chen LB and Griffin JD . (1997). J. Clin. Invest., 100, 46–57.
Schleuning M, Mittermuller J and Kolb HJ . (1999). Eur. J. Haematol., 62, 149–154.
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB and McGlave PB . (1992). J. Clin. Invest., 90, 1232–1241.
Wang JC, Lapidot T, Cashman JD, Doedens M, Addy L, Sutherland DR, Nayar R, Laraya P, Minden M, Keating A, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ and Dick JE . (1998). Blood, 91, 2406–2414.
Wertheim JA, Forsythe K, Druker BJ, Hammer D, Boettiger D and Pear WS . (2002). Blood, 99, 4122–4130.
Wertheim JA, Perera SA, Hammer DA, Ren R, Boettiger D and Pear WS . (2003). Blood, 102, 2220–2228.
Zhao RC, Jiang Y and Verfaillie CM . (2001). Blood, 97, 2406–2412.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Warren Pear (University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA) for the gift of the pMig210 retroviral vector; Dr Brian Druker (OHSU, Portland, OH, USA) for the 32D and 32Dp210 cell lines; Dr Elizabeth Buchdunger (Novartis Pharma, Basel, Switzerland) for imatinib mesylate; Gary Warnes and Katy Smith for their excellent flow sorting service; Phil Muckett for helpful advice regarding the care and welfare of mice, and Dr Richard Szydlo for invaluable help with statistical analyses. This work was supported by the Leukaemia Research Fund of Great Britain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, D., Schultheis, B., Adedeji, S. et al. Dose-dependent effects of Bcr-Abl in cell line models of different stages of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 24, 6432–6440 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208796
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208796
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparative expression analysis of dasatinib and ponatinib-regulated lncRNAs in chronic myeloid leukemia and their network analysis
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Beyond BCR-ABL1
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2018)
-
Clonal competition in BcrAbl-driven leukemia: how transplantations can accelerate clonal conversion
Molecular Cancer (2017)
-
CIP2A is overexpressed and involved in the pathogenesis of chronic myelocytic leukemia by interacting with breakpoint cluster region-Abelson leukemia virus
Medical Oncology (2014)
-
Do we have to kill the last CML cell?
Leukemia (2011)