Abstract
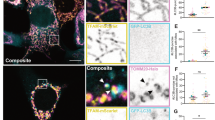
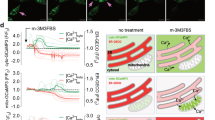
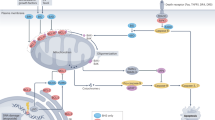
Proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members alter mitochondrial permeability resulting in the release of apoptogenic factors that initiate a caspase cascade. These changes are well described; however, the effects of caspases on mitochondrial function are less well characterized. Here we describe the consequence of caspase-9 and effector caspase inhibition on mitochondrial physiology during intrinsic cell death. Caspase inhibition prevents the complete loss of mitochondrial membrane potential without affecting cytochrome c release. When effector caspases are inhibited, mitochondria become uncoupled and produce reactive oxygen species. Interestingly, the effector caspase-mediated depolarization of the mitochondria occurs independent of the activity of complexes I–IV of the electron transport chain. In contrast, caspase-9 inhibition prevents mitochondrial uncoupling and ROS production and allows for continued electron transport despite the release of cytochrome c. Taken together, these data suggest that activated caspase-9 prevents the accessibility of cytochrome c to complex III, resulting in the production of reactive oxygen species, and that effector caspases may depolarize mitochondria to terminate ROS production and preserve an apoptotic phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrientos A, Kenyon L and Moraes CT . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 14210–14217.
Borner C and Monney L . (1999). Cell Death Differ., 6, 497–507.
Bossy-Wetzel E, Newmeyer DD and Green DR . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 37–49.
Bratton SB, Walker G, Roberts DL, Cain K and Cohen GM . (2001). Cell Death Differ., 8, 425–433.
Burlacu A, Jinga V, Gafencu AV and Simionescu M . (2001). Cell Tissue Res., 306, 409–416.
Cai J and Jones DP . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 11401–11404.
Chandel NS and Schumacker PT . (1999). FEBS Lett., 454, 173–176.
Chandra J, Samali A and Orrenius S . (2000). Free Radic. Biol. Med., 29, 323–333.
Cheng EH, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA, Mak TW, Lindsten T and Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 705–711.
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell, 116, 205–219.
Deshmukh M, Kuida K and Johnson Jr EM . (2000). J. Cell. Biol., 150, 131–143.
Fearnhead HO, McCurrach ME, O’Neill J, Zhang K, Lowe SW and Lazebnik YA . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 1266–1276.
Garcia-Calvo M, Peterson EP, Leiting B, Ruel R, Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 32608–32613.
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI and Green DR . (2000). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 156–162.
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ . (1999a). Genes Dev., 13, 1899–1911.
Gross A, Yin XM, Wang K, Wei MC, Jockel J, Milliman C, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Korsmeyer SJ . (1999b). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 1156–1163.
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, Potter J, Yoshida R, Kaufman SA, Lowe SW, Penninger JM and Mak TW . (1998). Cell, 94, 339–352.
Higuchi M, Honda T, Proske RJ and Yeh ET . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 2753–2760.
Higuchi Y and Yoshimoto T . (2002). Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 400, 133–140.
Johnson BW, Cepero E and Boise LH . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 31546–31553.
Kim TH, Zhao Y, Barber MJ, Kuharsky DK and Yin XM . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 39474–39481.
Kluck RM, Esposti MD, Perkins G, Renken C, Kuwana T, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldberg M, Allen T, Barber MJ, Green DR and Newmeyer DD . (1999). J. Cell. Biol., 147, 809–822.
Kokiszka JE, Waymire KG, Levy SE, Sligh JE, Cai J, Jones DP, MacGregor GR and Wallace DC . (2004). Nature, 427, 461–465.
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X . (1997). Cell, 91, 479–489.
Lowe SW, Cepero E and Evan G . (2004). Nature, 432, 307–315.
Martinou I, Desagher S, Eskes R, Antonsson B, Andre E, Fakan S and Martinou JC . (1999). J. Cell Biol., 144, 883–889.
Marzo I, Brenner C, Zamzami N, Susin SA, Beutner G, Brdiczka D, Remy R, Xie ZH, Reed JC and Kroemer G . (1998a). J. Exp. Med., 187, 1261–1271.
Marzo I, Susin SA, Petit PX, Ravagnan L, Brenner C, Larochette N, Zamzami N and Kroemer G . (1998b). FEBS Lett., 427, 198–202.
Mootha VK, Wei MC, Buttle KF, Scorrano L, Panoutsakopoulou V, Mannella CA and Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). EMBO J., 20, 661–671.
Nagata S . (1997). Cell, 88, 355–365.
Raha S and Robinson BH . (2001). Am. J. Med. Genet., 106, 62–70.
Rathmell JC, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, Frauwirth KA and Thompson CB . (2000). Mol. Cell., 6, 683–692.
Rego AC, Vesce S and Nicholls DG . (2001). Cell Death Differ., 8, 995–1003.
Ricci JE, Gottlieb RA and Green DR . (2003). J. Cell. Biol., 160, 65–75.
Ricci JE, Munoz-Pinedo C, Fitzgerald P, Bailly-Maitre B, Perkins GA, Yadava N, Scheffler IE, Ellisman MH and Green DR . (2004). Cell, 117, 773–786.
Ryan CA, Stennicke HR, Nava VE, Burch JB, Hardwick JM and Salvesen GS . (2002). Biochem. J., 366, 595–601.
Saraste M . (1999). Science, 283, 1488–1493.
Samali A, Nordgren H, Zhivotovsky B, Peterson E and Orrenius S . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 255, 6–11.
Scorrano L, Ashiya M, Buttle K, Weiler S, Oakes SA, Mannella CA and Korsmeyer SJ . (2002). Dev. Cell, 2, 55–67.
Shi Y . (2002). Mol. Cell, 9, 459–470.
Shimizu S and Tsujimoto Y . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 577–582.
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT and Thompson CB . (1997). Cell, 91, 627–637.
Vander Heiden MG, Plas DR, Rathmell JC, Fox CJ, Harris MH and Thompson CB . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 5899–5912.
von Ahsen O, Renken C, Perkins G, Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E and Newmeyer DD . (2000). J. Cell. Biol., 150, 1027–1036.
Waterhouse NJ, Goldstein JC, von Ahsen O, Schuler M, Newmeyer DD and Green DR . (2001). J. Cell. Biol., 153, 319–328.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). Science, 292, 727–730.
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A, Hakem R, Penninger JM and Mak TW . (1998). Cell, 94, 739–750.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Carlos Moraes, Yuri Lazebnik, Colin Duckett, Bryan Johnson, Esther Obeng, Robert Levy, Jennifer McCafferty and Kelvin Lee for reagents, advice and a critical review of the manuscript. This work was supported by F31 GM20435 (EC) and R01 GM65813 (LHB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cepero, E., King, A., Coffey, L. et al. Caspase-9 and effector caspases have sequential and distinct effects on mitochondria. Oncogene 24, 6354–6366 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208793
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208793
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Glyoxal-derived advanced glycation end-products, Nε-carboxymethyl-lysine, and glyoxal-derived lysine dimer induce apoptosis-related gene expression in hepatocytes
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Effects of Remifentanil Preconditioning Attenuating Oxidative Stress in Human Dermal Fibroblast
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2017)
-
Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate induced oxidative damage involving FasL-associated apoptotic pathway in mouse spermatogenic GC-2spd cells
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2016)
-
A modified thymosin alpha 1 inhibits the growth of breast cancer both in vitro and in vivo: suppressment of cell proliferation, inducible cell apoptosis and enhancement of targeted anticancer effects
Apoptosis (2015)
-
Preconditioning with pitavastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, attenuates C-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced apoptosis
Acta Neurochirurgica (2015)