Abstract
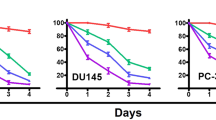
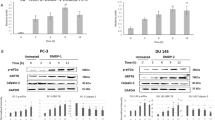
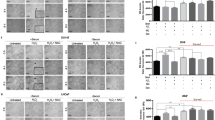
Molecular mechanism of cell cycle arrest caused by diallyl trisulfide (DATS), a garlic-derived cancer chemopreventive agent, has been investigated using PC-3 and DU145 human prostate cancer cells as a model. Treatment of PC-3 and DU145 cells, but not a normal prostate epithelial cell line (PrEC), with growth suppressive concentrations of DATS caused enrichment of the G2–M fraction. The DATS-induced cell cycle arrest in PC-3 cells was associated with increased Tyr15 phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and inhibition of Cdk1/cyclinB1 kinase activity. The DATS-treated PC-3 and DU145 cells also exhibited a decrease in the protein level of Cdc25C and an increase in its Ser216 phosphorylation. The DATS-mediated decrease in protein level and Ser216 phosphorylation of Cdc25C as well as G2–M phase cell cycle arrest were significantly attenuated in the presence of N-acetylcysteine implicating reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cell cycle arrest caused by DATS. ROS generation was observed in DATS-treated PC-3 and DU145 cells. DATS treatment also caused an increase in the protein level of Cdk inhibitor p21, but DATS-induced G2–M phase arrest was not affected by antisense-mediated suppression of p21 protein level. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicate that DATS-induced G2–M phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells is caused by ROS-mediated destruction and hyperphosphorylation of Cdc25C.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal KC . (1996). Med. Res. Rev., 16, 111–124.
Block E . (1992). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 31, 1135–1178.
Bookstein R, Shew J, Chen P, Scully P and Lee W . (1990). Science, 247, 712–715.
Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1998). Science, 282, 1497–1501.
Campbell CL, Savarese DMF, Quesenberry PJ and Savarese TM . (1999). Int. J. Cancer, 80, 868–874.
Challier B, Perarnau JM and Viel JF . (1998). Eur. J. Epidemiol., 14, 737–747.
Charrier-Savournin FB, Chateau M, Gire V, Sedivy J, Piette J and Dulic V . (2004). Mol. Biol. Cell, 15, 3965–3976.
Chen L, Hodge GB, Guarda LA, Welch JL, Greenberg NM and Chai KX . (2001). Prostate, 48, 93–103.
Choi S and Singh SV . (2005). Cancer Res., 65, 2035–2043.
Dausch JG and Nixon DW . (1990). Prev. Med., 19, 346–361.
Draetta G and Eckstein J . (1997). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1332, M53–M63.
Druesne N, Pagniez A, Mayeur C, Thomas M, Cherbuy C, Duee P, Martel P and Chaumontet C . (2004). Carcinogenesis, 25, 1227–1236.
Dulic V, Stein GH, Far DF and Reed SI . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 546–557.
Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuasen RG, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2001). Nature, 410, 842–847.
Filomeni G, Aquilano K, Rotilio G and Ciriolo MR . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 5940–5949.
Freemerman AJ, Vrana JA, Tombes RM, Jiang H, Chellappan SP, Fisher PB and Grant S . (1997). Leukemia, 11, 504–513.
Furnari B, Rhind N and Russell P . (1997). Science, 277, 1495–1497.
Gao CM, Takezaki T, Ding JH, Li MS and Tajima K . (1999). Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 90, 614–621.
Garraway LA, Lin D, Signoretti S, Waltregny D, Dilks J, Bhattacharya N and Loda M . (2003). Prostate, 55, 206–218.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ . (1993). Cell, 75, 805–816.
Herman-Antosiewicz A and Singh SV . (2004). Mutat. Res., 555, 121–131.
Hsing AW, Chokkalingam AP, Gao YT, Madigan MP, Deng J, Gridley G and Fraumeni JF . (2002). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 94, 1648–1651.
Knowles LM and Milner JA . (1998). Nutr. Cancer, 30, 169–174.
Knowles LM and Milner JA . (2000). Carcinogenesis, 21, 1129–1134.
Kwon KB, Yoo SJ, Ryu DG, Yang JY, Rho HW, Kim JS, Park JW, Kim HR and Park BH . (2002). Biochem. Pharmacol., 63, 41–47.
Lan H and Lu Y . (2004). Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 25, 219–225.
Li Y and Lu Y . (2002). DNA Cell Biol., 21, 771–780.
Mailand N, Falck J, Lukas C, Syljuasen RG, Welcker M, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000). Science, 288, 1425–1429.
Matsuoka S, Huang M and Elledge SJ . (1998). Science, 282, 1893–1897.
Milner JA . (2001). J. Nutr., 131, 1027s–1031s.
Mitchell A, Abel P, Ware M, Stamp G and Lalani E . (2000). BJU Int., 85, 932–944.
Molinari M . (2000). Cell Prolif., 33, 261–274.
Molinari M, Mercurio C, Dominguez J, Goubin F and Draetta GF . (2000). EMBO Rep., 1, 71–79.
Nagae S, Ushijima M, Hatono S, Imai J, Kasuga S, Matsuura H, Itakura Y and Higashi Y . (1994). Planta Med., 60, 214–217.
Nakagawa H, Tsuta K, Kiuchi K, Senzaki H, Tanaka K, Hioki K and Tsubura A . (2001). Carcinogenesis, 22, 891–897.
Nakamoto T, Chang C, Li A and Chodak GW . (1992). Cancer Res., 52, 571–577.
Narayanan PK, Goodwin EH and Lehnert BE . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 3963–3971.
Peng CY, Graves PR, Ogg S, Thoma RS, Byrnes MJ, Wu Z, Stephenson MT and Piwnica-Worms H . (1998). Cell Growth Differ., 9, 197–208.
Peng CY, Graves PR, Thoma RS, Wu Z, Shaw AS and Piwnica-Worms H . (1997). Science, 277, 1501–1505.
Pines J and Hunter T . (1991). J. Cell Biol., 115, 1–17.
Reddy BS, Rao CV, Rivenson A and Kelloff G . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 3493–3498.
Robert V, Mouille B, Mayeur C, Michaud M and Blachier F . (2001). Carcinogenesis, 22, 1155–1161.
Rothe G and Valet GJ . (1990). J. Leukoc. Biol., 47, 440–448.
Sanchez Y, Wong C, Thoma RS, Richman R, Wu Z, Piwnica-Worms H and Elledge SJ . (1997). Science, 277, 1497–1501.
Savitsky PA and Finkel T . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 20535–20540.
Schaffer EM, Liu JZ, Green J, Dangler CA and Milner JA . (1996). Cancer Lett., 102, 199–204.
Sherwood SW, Rush DF, Kung AL and Schimke RT . (1994). Exp. Cell Res., 211, 275–281.
Shirin H, Pinto JT, Kawabata Y, Soh JW, Delohery T, Moss SF, Murty V, Rivlin RS, Holt PR and Weinstein IB . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 725–731.
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV, Lew KL, Srivastava SK, Kamath R, Brown KD, Zhang L and Baskaran R . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 25813–25822.
Sparnins VL, Barany G and Wattenberg LW . (1988). Carcinogenesis, 9, 131–134.
Sumiyoshi H and Wargovich MJ . (1990). Cancer Res., 50, 5084–5087.
Sundaram SG and Milner JA . (1996). Carcinogenesis, 17, 669–673.
Suzui N, Sugie S, Rahman KM, Ohnishi M, Yoshimi N, Wakabayashi K and Mori H . (1997). Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 88, 705–711.
Takahashi S, Hakoi K, Yada H, Hirose M, Ito N and Fukushima S . (1992). Carcinogenesis, 13, 1513–1518.
Taylor WR and Stark GR . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 1803–1815.
Vogt A, Tamura K, Watson S and Lazo JS . (2000). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therapeut., 294, 1070–1075.
Wargovich MJ . (1987). Carcinogenesis, 8, 487–489.
Wargovich MJ, Woods C, Eng VWS, Stephens LC and Gray K . (1988). Cancer Res., 48, 6872–6875.
Wattenberg LW, Sparnins VL and Barany G . (1989). Cancer Res., 49, 2689–2692.
Webber M, Bello D and Quader S . (1997a). Prostate, 30, 58–64.
Webber M, Bello D and Quader S . (1997b). Prostate, 30, 136–142.
Widrow RJ, Rabinovitch PS, Cho K and Laird CD . (1997). Cytometry, 27, 250–254.
Winters ZE, Ongkeko WM, Harris AL and Norbury CJ . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 673–684.
Xiao D, Choi S, Johnson DE, Vogel VG, Johnson CS, Trump DL, Lee YJ and Singh SV . (2004). Oncogene, 23, 5594–5606.
Xiao D, Pinto JT, Soh JW, Deguchi A, Gundersen GG, Palazzo AF, Yoon JT, Shirin H and Weinstein IB . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 6825–6837.
Xiao D and Singh SV . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 3615–3619.
You WC, Blot WJ, Chang YS, Ershow A, Yang ZT, An Q, Henderson BE, Fraumeni JF and Wang TG . (1989). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 81, 162–164.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by United States Public Health Service Grants RO1 CA113363-01, RO1 CA101753-02 and RO1 CA076348-07 (to SVS) awarded by the National Cancer Institute, and a Developmental Research Grant from the UPCI Lung Cancer SPORE. We thank Karen Lew and Yan Zeng for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, D., Herman-Antosiewicz, A., Antosiewicz, J. et al. Diallyl trisulfide-induced G2–M phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells is caused by reactive oxygen species-dependent destruction and hyperphosphorylation of Cdc25C. Oncogene 24, 6256–6268 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208759
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208759
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of hydrogen sulfide gasotransmitter limits the proven benefits of garlic
Phytochemistry Reviews (2019)
-
Redox Modulation at Work: Natural Phytoprotective Polysulfanes From Alliums Based on Redox-Active Sulfur
Current Pharmacology Reports (2018)
-
Synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation of thiosulfinate derivatives for the treatment of human multidrug-resistant breast cancer
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2017)
-
Diallyl trisulfide inhibits proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis of glioma cells by inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Cell and Tissue Research (2017)
-
Curcumin analog WZ35 induced cell death via ROS-dependent ER stress and G2/M cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2015)