Abstract
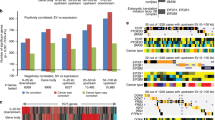
Microarray-based formats offer a high-resolution alternative to conventional, chromosome-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) methods for assessing DNA copy number alteration (CNA) genome-wide in human cancer. For murine tumors, array CGH should provide even greater advantage, since murine chromosomes are more difficult to individually discern. We report here the adaptation and evaluation of a cDNA microarray-based CGH method for the routine characterization of CNAs in murine tumors, using mouse cDNA microarrays representing ∼14 000 different genes, thereby providing an average mapping resolution of 109 kb. As a first application, we have characterized CNAs in a set of 10 primary and recurrent lymphomas derived from a Myc-induced murine lymphoma model. In primary lymphomas and more commonly in Myc-independent relapses, we identified a recurrent genomic DNA loss at chromosome 3G3–3H4, and recurrent amplifications at chromosome 3F2.1–3G3 and chromosome 15E1/E2–15F3, the boundaries of which we defined with high resolution. Further, by profiling gene expression using the same microarray platform, we identified within CNAs the relevant subset of candidate cancer genes displaying comparably altered expression, including Mcl1 (myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1), a highly expressed antiapoptotic gene residing within the chr 3 amplicon peak. CGH on mouse cDNA microarrays therefore represents a reliable method for the high-resolution characterization of CNAs in murine tumors, and a powerful approach for elucidating the molecular events in tumor development and progression in murine models.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGH:
-
comparative genomic hybridization
- CNA:
-
copy number alteration
- TSG:
-
tumor suppressor gene
References
Albertson DG and Pinkel D . (2003). Hum. Mol. Genet., 12 (Spec. No. 2), R145–R152.
Artandi SE, Chang S, Lee SL, Alson S, Gottlieb GJ, Chin L and DePinho RA . (2000). Nature, 406, 641–645.
Barrett MT, Scheffer A, Ben-Dor A, Sampas N, Lipson D, Kincaid R, Tsang P, Curry B, Baird K, Meltzer PS, Yakhini Z, Bruhn L and Laderman S . (2004). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 17765–17770.
Bullinger L, Dohner K, Bair E, Frohling S, Schlenk RF, Tibshirani R, Dohner H and Pollack JR . (2004). N. Engl. J. Med., 350, 1605–1616.
Cai WW, Mao JH, Chow CW, Damani S, Balmain A and Bradley A . (2002). Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 393–396.
Cho-Vega JH, Rassidakis GZ, Admirand JH, Oyarzo M, Ramalingam P, Paraguya A, McDonnell TJ, Amin HM and Medeiros LJ . (2004). Hum. Pathol., 35, 1095–1100.
Chung YJ, Jonkers J, Kitson H, Fiegler H, Humphray S, Scott C, Hunt S, Yu Y, Nishijima I, Velds A, Holstege H, Carter N and Bradley A . (2004). Genome Res., 14, 188–196.
Coleman AE, Forest ST, McNeil N, Kovalchuk AL, Ried T and Janz S . (1999). Leukemia, 13, 1592–1600.
Collins C, Rommens JM, Kowbel D, Godfrey T, Tanner M, Hwang SI, Polikoff D, Nonet G, Cochran J, Myambo K, Jay KE, Froula J, Cloutier T, Kuo WL, Yaswen P, Dairkee S, Giovanola J, Hutchinson GB, Isola J, Kallioniemi OP, Palazzolo M, Martin C, Ericsson C, Pinkel D and Gray JW . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 8703–8708.
Felsher DW and Bishop JM . (1999). Mol. Cell, 4, 199–207.
Felsher DW . (2003). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 3, 375–380.
Giuriato S, Rabin K, Fan AC, Shachaf CM and Felsher DW . (2004). Semin. Cancer Biol., 14, 3–11.
Gollub J, Ball CA, Binkley G, Demeter J, Finkelstein DB, Hebert JM, Hernandez-Boussard T, Jin H, Kaloper M, Matese JC, Schroeder M, Brown PO, Botstein D and Sherlock G . (2003). Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 94–96.
Hackett CS, Hodgson JG, Law ME, Fridlyand J, Osoegawa K, de Jong PJ, Nowak NJ, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Jain A, Jenkins R, Gray JW and Weiss WA . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 5266–5273.
Hodgson G, Hager JH, Volik S, Hariono S, Wernick M, Moore D, Nowak N, Albertson DG, Pinkel D, Collins C, Hanahan D and Gray JW . (2001). Nat. Genet., 29, 459–464.
Jackson-Grusby L . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 5504–5514.
Kallioniemi A, Kallioniemi OP, Sudar D, Rutovitz D, Gray JW, Waldman F and Pinkel D . (1992). Science, 258, 818–821.
Karlsson A, Giuriato S, Tang F, Fung-Weier J, Levan G and Felsher DW . (2003). Blood, 101, 2797–2803.
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P and Craig RW . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 3516–3520.
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1998). Nature, 396, 643–649.
Li J, Jiang T, Mao JH, Balmain A, Peterson L, Harris C, Rao PH, Havlak P, Gibbs R and Cai WW . (2004). Nat. Genet., 36, 952–954.
Lichter P, Joos S, Bentz M and Lampel S . (2000). Semin. Hematol., 37, 348–357.
Lucito R, Healy J, Alexander J, Reiner A, Esposito D, Chi M, Rodgers L, Brady A, Sebat J, Troge J, West JA, Rostan S, Nguyen KC, Powers S, Ye KQ, Olshen A, Venkatraman E, Norton L and Wigler M . (2003). Genome Res., 13, 2291–2305.
O’Hagan RC, Brennan CW, Strahs A, Zhang X, Kannan K, Donovan M, Cauwels C, Sharpless NE, Wong WH and Chin L . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 5352–5356.
O’Hagan RC, Chang S, Maser RS, Mohan R, Artandi SE, Chin L and DePinho RA . (2002). Cancer Cell, 2, 149–155.
Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C, Sorcinelli MD, Ong CC and Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). Nature, 426, 671–676.
Pinkel D, Segraves R, Sudar D, Clark S, Poole I, Kowbel D, Collins C, Kuo WL, Chen C, Zhai Y, Dairkee SH, Ljung BM, Gray JW and Albertson DG . (1998). Nat. Genet., 20, 207–211.
Pollack JR and Iyer VR . (2002). Nat. Genet., 32 (Suppl), 515–521.
Pollack JR, Perou CM, Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Pergamenschikov A, Williams CF, Jeffrey SS, Botstein D and Brown PO . (1999). Nat. Genet., 23, 41–46.
Pollack JR, Sorlie T, Perou CM, Rees CA, Jeffrey SS, Lonning PE, Tibshirani R, Botstein D, Borresen-Dale AL and Brown PO . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 12963–12968.
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R, Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB and Gray JW . (1999). Nat. Genet., 21, 99–102.
Solinas-Toldo S, Lampel S, Stilgenbauer S, Nickolenko J, Benner A, Dohner H, Cremer T and Lichter P . (1997). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 20, 399–407.
Vrana JA, Bieszczad CK, Cleaveland ES, Ma Y, Park JP, Mohandas TK and Craig RW . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 892–900.
Wang P, Kim Y, Pollack J, Narasimhan B and Tibshirani R . (2005). Biostatistics, 6, 45–58.
Xu Q and Reed JC . (1998). Mol. Cell, 1, 337–346.
Zhou P, Qian L, Bieszczad CK, Noelle R, Binder M, Levy NB and Craig RW . (1998). Blood, 92, 3226–3239.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Mike Fero and the staff of the Stanford Functional Genomic Facility (SFGF) for providing high-quality cDNA microarrays, and to Gavin Sherlock and the staff of the Stanford Microarray Database (SMD) group for providing outstanding database support. We also thank Siegfried Janz who kindly provided us with the lymphoma cell line P388D1, and the RIKEN Genomic Sciences Center for providing microarray cDNA clones. L Bullinger was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bonn, Germany (Forschungsstipendium BU 1339/1), and J Pollack was supported in part by NIH Grant CA97139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sander, S., Bullinger, L., Karlsson, A. et al. Comparative genomic hybridization on mouse cDNA microarrays and its application to a murine lymphoma model. Oncogene 24, 6101–6107 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208751
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208751