Abstract
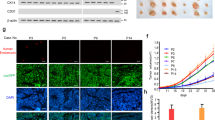
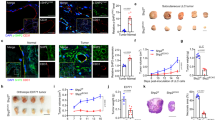
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is required for normal tissue development and pathological conditions such as tumorigenesis. Most solid tumors can not grow beyond a few millimeters without the recruitment of neovessels since cancer cells require access to blood vessels for nutrients and to escape the local environment and metastasize to other tissue and organ sites. Targeting tumor vessel endothelium therefore should serve as an effective therapy for cancers. Maspin is a serpin that exhibits antiangiogenic properties. In this report, we show that when maspin overexpression is targeted in vivo to endothelial cells, it actively induces endothelial cell apoptosis. Intravascular administration of adenovirus-maspin to mice bearing mammary tumors disrupts tumor-induced angiogenesis. Interestingly, tumor neovessels become leaky after maspin treatment, whereas normal mature vessels are not affected by maspin treatment. We further demonstrate that maspin directly induces endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro, and this effect is maspin specific. The induction of apoptosis is accompanied by changes in the expression of Bcl-2 family genes and is blocked by caspase inhibitors. In addition, the apoptotic effect is mediated by intracellular maspin and is dependent on the RSL region of maspin. Furthermore, we have shown that transient overexpression of Bcl-2 protected the HUVECs from maspin-mediated apoptosis, and the presence of both maspin and Bax accelerated the apoptosis process. These findings demonstrate that neovascular endothelial cells are highly sensitive to maspin level inside the cells. This property can be used for targeted therapy against tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird CH, Sutton VR, Sun J, Hirst CE, Novak A, Kumar S, Trapani JA and Bird PI . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 6387–6398.
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X and Wang X . (1999). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 15, 269–290.
Chandra D, Choy G, Deng X, Bhatia B, Daniel P and Tang DG . (2004). Mol. Cell. Biol., 24, 6592–6607.
Cher ML, Biliran Jr HR, Bhagat S, Meng Y, Che M, Lockett J, Abrams J, Fridman R, Zachareas M and Sheng S . (2003). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 100, 7847–7852.
Choi KB, Wong F, Harlan JM, Chaudhary PM, Hood L and Karsan A . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 20185–20188.
Choi WS, Eom DS, Han BS, Kim WK, Han BH, Choi EJ, Oh TH, Markelonis GJ, Cho JW and Oh YJ . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 20451–20460.
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 2905–2927.
Deng Y, Lin Y and Wu X . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 33–45.
Dickinson JL, Norris BJ, Jensen PH and Antalis TM . (1998). Cell. Death Differ., 5, 163–171.
Dimmeler S, Breitschopf K, Haendeler J and Zeiher AM . (1999). J. Exp. Med., 189, 1815–1822.
Ferrari D, Stepczynska A, Los M, Wesselborg S and Schulze-Osthoff K . (1998). J. Exp. Med., 188, 979–984.
Fidler IJ and Ellis LM . (1994). Cell, 79, 185–188.
Folkman J . (1986). Cancer Res., 46, 467–473.
Futscher BW, Oshiro MM, Wozniak RJ, Holtan N, Hanigan CL, Duan H and Domann FE . (2002). Nat. Genet., 31, 175–179.
Gilot D, Loyer P, Corlu A, Glaise D, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Atfi A, Morel F, Ichijo H and Guguen-Guillouzo C . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 49220–49229.
Gurtu V, Kain SR and Zhang G . (1997). Anal. Biochem., 251, 98–102.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell, 100, 57–70.
Juin P, Hueber AO, Littlewood T and Evan G . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1367–1381.
LaVallee TM, Zhan XH, Johnson MS, Herbstritt CJ, Swartz G, Williams MS, Hembrough WA, Green SJ and Pribluda VS . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 468–475.
Li H, Kolluri SK, Gu J, Dawson MI, Cao X, Hobbs PD, Lin B, Chen G, Lu J, Lin F, Xie Z, Fontana JA, Reed JC and Zhang X . (2000). Science, 289, 1159–1164.
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J . (1998). Cell, 94, 491–501.
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X . (1997). Cell, 91, 479–489.
Li X, Marani M, Mannucci R, Kinsey B, Andriani F, Nicoletti I, Denner L and Marcelli M . (2001a). Cancer Res., 61, 1699–1706.
Li Y, Tondravi M, Liu J, Smith E, Haudenschild CC, Kaczmarek M and Zhan X . (2001b). Cancer Res., 61, 6906–6911.
Liu J, Yin S, Reddy N, Spencer C and Sheng S . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 1703–1711.
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X . (1998). Cell, 94, 481–490.
McGettrick AF, Barnes RC and Worrall DM . (2001). Eur. J. Biochem., 268, 5868–5875.
Risau W . (1997). Nature, 386, 671–674.
Sanchez I, Xu CJ, Juo P, Kakizaka A, Blenis J and Yuan J . (1999). Neuron, 22, 623–633.
Sheng S, Pemberton PA and Sager R . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 30988–30993.
Shi HY, Liang R, Templeton NS and Zhang M . (2002). Mol. Ther., 5, 755–761.
Shi HY, Zhang W, Liang R, Abraham S, Kittrell FS, Medina D and Zhang M . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6945–6951.
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB, Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri ES, Green DR and Martin SJ . (1999). J. Cell Biol., 144, 281–292.
Soengas MS, Capodieci P, Polsky D, Mora J, Esteller M, Opitz-Araya X, McCombie R, Herman JG, Gerald WL, Lazebnik YA, Cordon-Cardo C and Lowe SW . (2001). Nature, 409, 207–211.
Suminami Y, Nagashima S, Vujanovic NL, Hirabayashi K, Kato H and Whiteside TL . (2000). Br. J. Cancer, 82, 981–989.
Tang D, Lahti JM and Kidd VJ . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 9303–9307.
Tewari M and Dixit VM . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 3255–3260.
Tewari M, Beidler DR and Dixit VM . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 18738–18741.
Tuxhorn JA, McAlhany SJ, Yang F, Dang TD and Rowley DR . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 6021–6025.
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X . (1997). Science, 275, 1129–1132.
Yuan Y, Liao L, Tulis DA and Xu J . (2002). Circulation, 105, 2653–2659.
Zhang M, Maass N, Magit D and Sager R . (1997a). Cell Growth Differ., 8, 179–186.
Zhang M, Magit D and Sager R . (1997b). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 5673–5678.
Zhang M, Shi Y, Magit D, Furth PA and Sager R . (2000a). Oncogene, 19, 6053–6058.
Zhang M, Volpert O, Shi YH and Bouck N . (2000b). Nat. Med., 6, 196–199.
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, Thor A, Neveu M, Sheng S, Rafidi K, Seftor E and Sager R . (1994). Science, 263, 526–529.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr RD Gerard at UT Southwestern Medical School for kindly providing us with the Ad-PAI-1 and Ad-PAI-2, and Dr RJ Youle at NIH for kindly providing us with the Bcl-2-EGFP and Bax-EGFP expression constructs. This study is supported by a NIH Grant CA79736 to MZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Shi, H. & Zhang, M. Targeted expression of maspin in tumor vasculatures induces endothelial cell apoptosis. Oncogene 24, 2008–2019 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208449
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208449
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Maspin impairs the function of endothelial cells: an implying pathway of preeclampsia
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2017)
-
RGD and polyhistidine tumor homing peptides potentiates the action of human Maspin as an antineoplastic candidate
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2016)
-
Nuclear location of tumor suppressor protein maspin inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells without affecting proliferation of normal epithelial cells
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
Maspin expression and melanoma progression: a matter of sub-cellular localization
Modern Pathology (2014)
-
Maspin is not required for embryonic development or tumour suppression
Nature Communications (2014)