Abstract
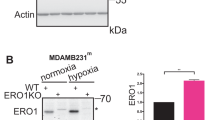
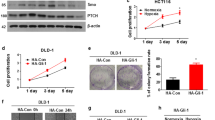
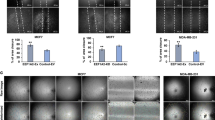
Oxygen is the ultimate source of oxidizing power for disulfide bond formation, suggesting that under limiting oxygen proper protein folding might be compromised. We show that secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein with multiple disulfide bonds, was indeed impeded under hypoxia and was partially restored by artificial increase of oxidizing equivalents with diamide. Physiologically, the oxireductase endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin-1 (Ero1)-Lα, but not other proteins in the relay of disulfide formation, was strongly upregulated by hypoxia and independently by hypoglycemia, two known accompaniments of tumors. Further, we provide genetic evidence that induction of Ero1-Lα by hypoxia and hypoglycemia is mediated by the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) but is independent of p53. In natural human tumors, Ero1-Lα mRNA was specifically induced in hypoxic microenvironments coinciding with that of upregulated VEGF expression. To establish a physiological relevance to modulations in Ero1-Lα levels, we showed that even a modest, two- to three-fold reduction in Ero1-Lα production via siRNA leads to significant inhibition of VEGF secretion, a compromised proliferation capacity and enhanced apoptosis. Together, these findings demonstrate that hypoxic induction of Ero1-Lα is the key adaptive response in a previously unrecognized HIF-1-mediated pathway that operates to improve protein secretion under hypoxia and might be harnessed for inhibiting tumor growth via inhibiting VEGF-driven angiogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An WG, Kanekal M, Simon MC, Maltepe E, Blagosklonny MV and Neckers LM . (1998). Nature, 392, 405–408.
Barash Y, Elidan G, Kaplan T and Friedman N . (2004). Bioinformatics, Sep 28 [Epub ahead of print].
Benda P, Lightbody J, Sato G, Levine L and Sweet W . (1968). Science, 161, 370–371.
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R, Maxwell P, Koch CJ, Ratcliffe P, Moons L, Jain RK, Collen D, Keshert E and Keshet E . (1998). Nature, 394, 485–490.
Claffey KP, Senger DR and Spiegelman BM . (1995). Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1246, 1–9.
Czyzyk-Krzeska MF . (1997). Respir. Physiol., 110, 99–111.
Ellgaard L and Frickel EM . (2003). Cell Biochem. Biophys., 39, 223–247.
Endoh H, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Konishi H, Osada H, Tajima K, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T . (2004). J. Clin. Oncol., 22, 811–819.
Ferrari DM and Soling HD . (1999). Biochem. J., 339 (Part 1), 1–10.
Firth JD, Ebert BL, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 6496–6500.
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD and Semenza GL . (1996). Mol. Cell Biol., 16, 4604–4613.
Frand AR and Kaiser CA . (1998). Mol. Cell, 1, 161–170.
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y and Ben-Sasson SA . (1992). J. Cell Biol., 119, 493–501.
Gess B, Hofbauer KH, Wenger RH, Lohaus C, Meyer HE and Kurtz A . (2003). Eur. J. Biochem., 270, 2228–2235.
Graeber TG, Osmanian C, Jacks T, Housman DE, Koch CJ, Lowe SW and Giaccia AJ . (1996). Nature, 379, 88–91.
Halterman MW, Miller CC and Federoff HJ . (1999). J. Neurosci., 19, 6818–6824.
Ikeda E, Achen MG, Breier G and Risau W . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 19761–19766.
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin Jr WG . (2001). Science, 292, 464–468.
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ . (2001). Science, 292, 468–472.
Kuwabara K, Matsumoto M, Ikeda J, Hori O, Ogawa S, Maeda Y, Kitagawa K, Imuta N, Kinoshita T, Stern DM, Yanagi H and Kamada T . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 5025–5032.
Maltepe E, Schmidt JV, Baunoch D, Bradfield CA and Simon MC . (1997). Nature, 386, 403–407.
Mazzarella RA, Srinivasan M, Haugejorden SM and Green M . (1990). J. Biol. Chem., 265, 1094–1101.
Motro B, Itin A, Sachs L and Keshet E . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 3092–3096.
Muller YA, Li B, Christinger HW, Wells JA, Cunningham BC and de Vos AM . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 7192–7197.
Pagani M, Fabbri M, Benedetti C, Fassio A, Pilati S, Bulleid NJ, Cabibbo A and Sitia R . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 23685–23692.
Potgens AJ, Lubsen NH, van Altena MC, Vermeulen R, Bakker A, Schoenmakers JG, Ruiter DJ and de Waal RM . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 32879–32885.
Rutkowski DT and Kaufman RJ . (2004). Trends. Cell Biol., 14, 20–28.
Ryan HE, Poloni M, McNulty W, Elson D, Gassmann M, Arbeit JM and Johnson RS . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 4010–4015.
Sciandra JJ, Subjeck JR and Hughes CS . (1984). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 81, 4843–4847.
Semenza GL . (1999). Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol., 15, 551–578.
Semenza GL . (2000). J. Appl. Physiol., 88, 1474–1480.
Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM and Wang GL . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 23757–23763.
Sevier CS, Cuozzo JW, Vala A, Aslund F and Kaiser CA . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 874–882.
Shima DT, Deutsch U and D'Amore PA . (1995). FEBS Lett., 370, 203–208.
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D and Keshet E . (1992). Nature, 359, 843–845.
Stein I, Itin A, Einat P, Skaliter R, Grossman Z and Keshet E . (1998). Mol. Cell Biol., 18, 3112–3119.
Stein I, Neeman M, Shweiki D, Itin A and Keshet E . (1995). Mol. Cell Biol., 15, 5363–5368.
Sullivan DC, Huminiecki L, Moore JW, Boyle JJ, Poulsom R, Creamer D, Barker J and Bicknell R . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 47079–47088.
Tu BP and Weissman JS . (2002). Mol. Cell, 10, 983–994.
Tu BP and Weissman JS . (2004). J. Cell Biol., 164, 341–346.
Tu BP, Ho-Schleyer SC, Travers KJ and Weissman JS . (2000). Science, 290, 1571–1574.
Walter DH, Hink U, Asahara T, Van Belle E, Horowitz J, Tsurumi Y, Vandlen R, Heinsohn H, Keyt B, Ferrara N, Symes JF and Isner JM . (1996). Lab. Invest., 74, 546–556.
Wang GL and Semenza GL . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 4304–4308.
Wang GL, Jiang BH and Semenza GL . (1995b). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 212, 550–556.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL . (1995a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 5510–5514.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Belfer Foundation and from Quark Biotech Inc. We thank Yevgeni Kazanov and David Belenki for preparation of anti-Ero-1La antibodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
May, D., Itin, A., Gal, O. et al. Ero1-Lα plays a key role in a HIF-1-mediated pathway to improve disulfide bond formation and VEGF secretion under hypoxia: implication for cancer. Oncogene 24, 1011–1020 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208325
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208325
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction, UPRmt signaling, and targeted therapy in metastasis tumor
Cell & Bioscience (2021)
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment
Nature Reviews Cancer (2021)
-
Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a dynamic duo in multiple myeloma
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Unfolded protein response (UPR) integrated signaling networks determine cell fate during hypoxia
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2020)
-
Integrating microarray-based spatial transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-seq reveals tissue architecture in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas
Nature Biotechnology (2020)