Abstract
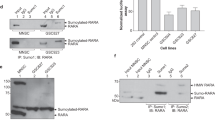
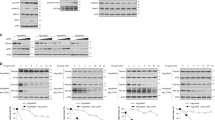
Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates signaling from the insulin-like growth factor type-I receptor. We found that all-trans retinoic acid (RA) decreases IRS-1 protein levels in MCF-7, T47-D, and ZR75.1 breast cancer cells, which are growth arrested by RA, but not in the RA-resistant MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells. Based on prior reports of ubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRS-1, we investigated the ubiquitination of IRS-1 in RA-treated breast cancer cells. Two proteasome inhibitors, MG-132 and lactacystin, blocked the RA-mediated degradation of IRS-1, and RA increased ubiquitination of IRS-1 in the RA-sensitive breast cancer cells. In addition, we found that RA increases serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. To elucidate the signaling pathway responsible for this phosphorylation event, pharmacologic inhibitors were used. Two PKC inhibitors, but not a MAPK inhibitor, blocked the RA-induced degradation and serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. We demonstrate that RA activates PKC-δ in the sensitive, but not in the resistant cells, with a time course that is consistent with the RA-induced decrease of IRS-1. We also show that: (1) RA-activated PKC-δ phosphorylates IRS-1 in vitro, (2) PKC-δ and IRS-1 interact in RA-treated cells, and (3) mutation of three PKC-δ serine sites in IRS-1 to alanines results in no RA-induced in vitro phosphorylation of IRS-1. Together, these results indicate that RA regulates IRS-1 levels by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, involving a PKC-sensitive mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando S, Panno ML, Salerno M, Sisci D, Mauro L, Lanzino M and Surmacz E . (1998). Bioch. Biophys. Res. Commun., 253, 315–319.
Blobe GC, Obeid LM and Hannun YA . (1994). Cancer Metast. Rev., 13, 411–431.
Boylan JM and Gruppuso PA . (2002). Endocrinology, 143, 4178–4183.
Boyle JO, Langenfeld J, Lonardo F, Sekula D, Reczek P, Rusch V, Dawson MI and Dmitrovsky E . (1999). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 91, 373–379.
Brouillard F and Cremisi CE . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 39509–39516.
Buren J, Liu HX, Jensen J and Eriksson JW . (2002). Eur. J. Endocrinol., 146, 419–429.
Burks DJ and White MF . (2001). Diabetes, 50, S140–S145.
Chan TW, Pollak M and Huynh H . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 2545–2554.
Chang Q, Li Y, White MF, Fletcher JA and Xiao S . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 6035–6038.
Chernov MV, Bean LJ, Lerner N and Stark GR . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 31819–31824.
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N . (1987). Anal. Biochem., 162, 156–159.
del Rincón SV, Rousseau C, Samanta R and Miller Jr WH . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 3353–3360.
Dow R, Hendley J, Pirkmaier A, Musgrove EA and Germain D . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 45945–45951.
Egawa K, Nakashima N, Sharma PM, Maegawa H, Nagai Y, Kashiwagi A, Kikkawa R and Olefsky JM . (2000). Endocrinology, 141, 1930–1935.
Gonzalez C, Alonso A, Grueso NA, Diaz F, Esteban MM, Fernandez S and Patterson AM . (2001). J. Pancreas, 2, 140–149.
Greene MW, Morrice N, Garofalo RS and Roth RA . (2004). Biochem. J., 378, 105–116.
Greene MW, Sakaue H, Wang L, Alessi DR and Roth RA . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 8199–8211.
Haruta T, Uno T, Kawahara J, Takano A, Egawa K, Sharma PM, Olefsky JM and Kobayashi M . (2000). Mol. Endocrinol., 14, 783–794.
Hirashima Y, Tsuruzoe K, Kodama S, Igata M, Toyonaga T, Ueki K, Kahn CR and Araki E . (2003). J. Endocrinol., 179, 253–266.
Huang X, Vaag A, Hansson M and Groop L . (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 87, 255–259.
Ito T, Sasaki Y and Wands J . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 943–951.
Iwao K, Kawasaki H, Taira K and Yokoyama KK . (1999). Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser., 42, 207–208.
Kambhampati S, Li Y, Verma A, Sassano A, Majchrzak B, Deb DK, Parmar S, Giafis N, Kalvakolanu DV, Rahman A, Uddin S, Minucci S, Tallman MS, Fish EN and Platanias LC . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 32544–32551.
Kim HJ and Lotan R . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 2439–2448.
Langenfeld J, Kiyokawa H, Sekula D, Boyle J and Dmitrovsky E . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12070–12074.
Lavan BE, Lane WS and Lienhard GE . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 11439–11443.
Lee AV, Gooch JL, Oesterreich S, Guler RL and Yee D . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 1489–1496.
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK and Yee D . (1999). Mol. Endocrinol., 13, 787–796.
Lindahl T, Landberg G, Ahlgren J, Nordgren H, Norberg T, Klaar S, Holmberg L and Bergh J . (2004). Carcinogenesis, 25, 375–380.
Molloy CA, May FE and Westley BR . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 12565–12571.
Morelli C, Garofalo C, Bartucci M and Surmacz E . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 4007–4016.
Rechsteiner M and Rogers SW . (1996). Trends Biochem. Sci., 21, 267–271.
Rocha RL, Hilsenbeck SG, Jackson JG, VanDenBerg CL, Weng Cn, Lee AV and Yee D . (1997). Clin. Cancer Res., 3, 103–109.
Rosenauer A, Nervi C, Davison K, Lamph WW, Mader S and Miller Jr WH . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5110–5116.
Rosenauer A, Raelson JV, Nervi C, Eydoux P, DeBlasio A and Miller Jr W . (1996). Blood, 88, 2671–2682.
Salerno M, Sisci D, Mauro L, Guvakova MA, Ando S and Surmacz E . (1999). Int. J. Cancer, 81, 299–304.
Shepherd PR, Withers D and Siddle K . (1998). Biochem. J., 333, 471–490.
Smith LK, Bradshaw M, Croall DE and Garner CW . (1993). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 196, 767–772.
Spinella MJ, Freemantle SJ, Sekula D, Chang JH, Christie AJ and Dmitrovsky E . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 22013–22018.
Sueoka N, Lee HY, Walsh GL, Hong WK and Kurie JM . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 3838–3844.
Sun H, Tu X, Prisco M, Wu A, Casiburi I and Baserga R . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 472–486.
Sun XJ, Goldberg JL, Qiao LY and Mitchell JJ . (1999). Diabetes, 48, 1359–1364.
Sun XJ, Rothenberg P, Kahn CR, Backer JM, Araki E, Wilden PA, Cahill DA, Goldstein BJ and White MF . (1991). Nature, 352, 73–77.
Surmacz E and Burgaud JL . (1995). Clin. Cancer Res., 1, 1429–1436.
Tanaka T, Rodriguez de la Concepcion ML and De Luca LM . (2001). Biochem. Pharmacol., 61, 1347–1355.
Treier M, Staszewski LM and Bohmann D . (1994). Cell, 78, 787–798.
Tu X, Batta P, Innocent N, Prisco M, Casaburi I, Belletti B and Baserga R . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 44357–44365.
Turnbow MA, Keller SR, Rice KM and Garner CW . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 2516–2520.
van der Burg B, van der Leede BM, Kwakkenbos-Isbrucker L, Salverda S, de Laat SW and van der Saag PT . (1993). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 91, 149–157.
Wang LM, Myers Jr MG, Sun XJ, Aaronson SA, White M and Pierce JH . (1993). Science, 261, 1591–1594.
Wang TC, Cardiff RD, Zukerberg L, Lees E, Arnold A and Schmidt EV . (1994). Nature, 369, 669–671.
White MF . (1997). Diabetologia, 40, S2–S17.
Yoshida H, Kitamura K, Tanaka K, Omura S, Miyazaki T, Hachiya T, Ohno R and Naoe T . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 2945–2948.
Zhande R, Mitchell JJ, Wu J and Sun XJ . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 1016–1026.
Zhang H, Hoff H and Sell C . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 22558–22562.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Chris Sell for providing all FLAG-tagged IRS-1 constructs used in this manuscript. We thank Dr Dirk Bohmann for providing the HA-tagged ubiquitin construct. We extend our kindest thanks to Dr Richard A Roth for providing the GST-IRS-1288−678WT and GST-IRS-1288−678MUT constructs. We also thank Dr C Ronald Khan for his generous gift of human IRS-1 cDNA. This work was supported by a predoctoral fellowship award from the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Breast Cancer Research Program (Award number DAMD1701-1-0320 to SV del Rincón) and a grant from the Canadian Breast Cancer Research Initiative. Wilson H Miller Jr is an Investigator of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rincón, S., Guo, Q., Morelli, C. et al. Retinoic acid mediates degradation of IRS-1 by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, via a PKC-dependant mechanism. Oncogene 23, 9269–9279 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208104
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2
Diabetologia (2012)
-
Depletion of insulin receptor substrate 2 reverses oncogenic transformation induced by v-src
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)
-
Targeting PKCδ-mediated topoisomerase IIβ overexpression subverts the differentiation block in a retinoic acid-resistant APL cell line
Leukemia (2010)
-
Nuclear insulin receptor substrate-1 activates promoters of cell cycle progression genes
Oncogene (2008)
-
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway is essential for the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells
Oncogene (2006)