Abstract
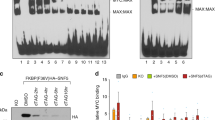
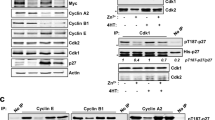
USF and c-Myc are basic helix–loop–helix transcription factors with similar DNA-binding specificities, but antagonistic effects on cellular transformation. In order to determine how these opposite functions correlate with the transcriptional activities of the two factors on particular downstream targets, we investigated the roles of USF and c-Myc in expression of CDK4, a known direct target of c-Myc. Overexpression of either c-Myc or USF2, but not USF1, stimulated the expression of CDK4 promoter-driven reporter genes in the non-tumorigenic mammary epithelial MCF-10A cells. Dominant-negative mutants specific to either Myc or USF family proteins inhibited reporter gene activity as well as endogenous CDK4 expression, demonstrating involvement of both USF and Myc in CDK4 transcriptional control. In contrast, in two different breast cancer cell lines where USF is transcriptionally inactive and c-Myc is overexpressed, CDK4 promoter activity was no longer responsive to either transcription factor. Accordingly, chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed significantly lower levels of both USF and c-Myc bound to the endogenous CDK4 promoter in breast cancer cells than in MCF-10A cells, with a concomitant decrease in associated histone H3 acetylation. These results suggest that a major switch in the transcriptional control of CDK4 occurs during breast carcinogenesis, with likely alteration of cell cycle regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An H-X, Beckmann MW, Reifenberger G, Bender HG and Niederacher D . (1999). Am. J. Pathol., 154, 113–118.
Athanikar JN and Osborne TF . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 4935–4940.
Beckmann H, Su LK and Kadesch T . (1990. Genes Dev., 4, 167–179.
Bendall AJ and Molloy PL . (1994). Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 2801–2810.
Boyd KE and Farnham P . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 8393–8399.
Dang CV . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 1–11.
Eilers M, Schirm S and Bishop JM . (1991). EMBO J., 10, 133–141.
Eisenman RN . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2023–2030.
Fisher DE, Carr CS, Parent LA and Sharp PA . (1991). Genes Dev., 5, 2342–2352.
Hadsell DL, Bonnette S, George J, Torres D, Klementidis Y, Gao S, Haney P, Summy-Long J, Soloff M, Parlow AF, Sirito M and Sawadogo M . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 2251–2267.
Harbour JW, Luo RX, Dei Santi A, Postigo AA and Dean DC . (1999). Cell, 98, 859–869.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ . (1993). Cell, 75, 805–816.
Hermeking H, Rago C, Schuhmacher M, Li Q, Barrett JF, Obaya AJ, O'Connell BC, Mateyak MK, Tam W, Kohlhuber WF, Dang CV, Sedivy JM, Eick D, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 2229–2234.
Hurlin PJ, Zhou ZQ, Toyo-Oka K, Ota S, Walker WL, Hirotsune S and Wynshaw-Boris A . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 4584–4596.
Ismail PM, Lu T and Sawadogo M . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 5582–5591.
Ito Y, Kobayashi T, Takeda T, Komoike Y, Wakasugi E, Tamaki Y, Umeshita K, Monden T and Monden M . (1996). Breast Cancer, 3, 93–104.
Kirschbaum BJ, Pognonec P and Roeder RG . (1992). Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 5094–5101.
Krylov D, Kasai K, Echlin DR, Taparowsky EJ, Arnheiter H and Vinson C . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12274–12279.
Land H, Chen AC, Morgenstren JP, Parada LF and Weinberg RA . (1986). Mol. Cell. Biol., 6, 1917–1925.
Lazarov M, Kubo Y, Cai T, Dajee M, Tarutani M, Lin Q, Fang M, Tao S, Green CL and Khavari PA . (2002). Nat. Med., 8, 1105–1114.
Luo X and Sawadogo M . (1996a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 1308–1313.
Luo X and Sawadogo M . (1996b). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 1367–1375.
Matsushime H, Ewen ME, Strom D K, Kato JY, Hanks SK, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ . (1992). Cell, 71, 323–334.
Maxam AM and Gilbert W . (1977). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 74, 560–564.
Mizzen CA, Yang XJ, Kokubo T, Brownell JE, Bannister AJ, Owen-Hughes T, Workman J, Wang L, Berger SL, Kouzarides T, Nakatani Y and Allis CD . (1996). Cell, 87, 1261–1270.
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M . (2002). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1602, 73–87.
Persson H, Gray HE and Godeau F . (1985). Mol. Cell. Biol., 5, 2903–2912.
Polyak K, Lee M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P and Massague J . (1994). Cell, 78, 59–66.
Qyang Y, Luo X, Lu T, Ismail PM, Krylov D, Vinson C and Sawadogo M . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 1508–1517.
Rane SG, Dubus P, Mettus RV, Galbreath EJ, Boden G, Reddy EP and Barbacid M . (1999). Nat. Genet., 22, 44–52.
Rodriguez-Puebla ML, de Marval PL, LaCava M, Moons DS, Kiyokawa H and Conti CJ . (2002). Am. J. Pathol., 161, 405–411.
Sasano H, Frost AR, Saitoh R, Taniyama Y, Nagura H, Matsunaga G, Takehana K, Kimura M and Silverberg SG . (1997). Anticancer Res., 17, 3685–3690.
Sawadogo M . (1988). J. Biol. Chem., 263, 11994–12001.
Sawadogo M and Roeder RG . (1985). Cell, 43, 165–175.
Sherr CJ and Roberts DM . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1501–1512.
Sirito M, Lin Q, Deng JM, Behringer RR and Sawadogo M . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 3758–3763.
Sirito M, Lin Q, Maity T and Sawadogo M . (1994). Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 427–433.
Sotillo R, Dubus P, Martin J, de la Cueva E, Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M . (2001). EMBO J., 20, 6637–6647.
Swanson HI and Yang JH . (1999). Nucleic Acids Res., 27, 3205–3212.
Szentirmay MN, Yang HX, Pawar SA, Vinson C and Sawadogo M . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 37231–37240.
Tsutsui T, Hesabi B, Moons DS, Pandolfi PP, Hansel KS, Koff A and Kiyokawa H . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 7011–7019.
Van Dyke MW, Sirito M and Sawadogo M . (1992). Gene, 111, 99–104.
Weissman JD, Howcroft TK and Singer DS . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 10160–10167.
Yasumoto K, Yokoyama K, Shibata K, Tomita Y and Shibahara S . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 8058–8070.
Zou X, Ray D, Aziyu A, Christov K, Boiko AD, Gudkov AV and Kiyokawa H . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 2923–2934.
Acknowledgements
The technical help by Hui-Xin Yang for FACS analysis and immunoblotting is gratefully acknowledged. Grants 9866 from the Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation, CA79578 from the National Institutes of Health, and G-1195 from the Robert A Welch Foundation supported this work. The MD Anderson Cancer Center DNA-sequencing and FACS facilities are supported by Grant CA16672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawar, S., Szentirmay, M., Hermeking, H. et al. Evidence for a cancer-specific switch at the CDK4 promoter with loss of control by both USF and c-Myc. Oncogene 23, 6125–6135 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207806
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207806
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulatory network changes between cell lines and their tissues of origin
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
Association of CDK4 and CCND1 mRNA overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas occurs without CDK4 amplification
Virchows Archiv (2007)
-
Tumor-suppression function of transcription factor USF2 in prostate carcinogenesis
Oncogene (2006)