Abstract
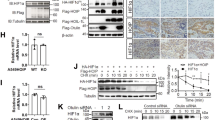
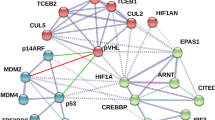
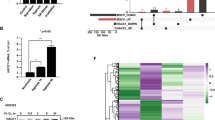
In the present study, the role of the C-terminal α-helical domain (amino acid (aa) 195–208) of the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumour suppressor was investigated. Deletions of the VHL C-terminus up to the naturally occurring 195-Gln-Term resulted in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α downregulation in renal cell carcinoma (RCC)4 cells during normoxia, suggesting that this domain is not an absolute requirement for the ubiquitination of HIF-1α. However, detailed investigation of the ubiquitin protein isopeptide ligase ubiquitin ligase properties of VHL revealed C-terminal deletions to cause a significant impairment of HIF-1α ubiquitination, which is shown to be due to a loss in high-affinity binding to the target substrate. When VHL regulation of both HIF-1α N- and C-terminal oxygen-dependent degradation domains (HIF-ODDD) was investigated, it was found that only ubiquitination of the C-terminal HIF-ODDD was affected by the deletion of the VHL C-terminus. When RCC4 cells expressing C-terminal truncations of VHL were exposed to graded hypoxia, differences in the induction of HIF-1α were observed in comparison with full-length VHL, with a shift in the maximal induction of HIF-1α to a higher oxygen tension. These changes were accompanied by increased glucose transporter 1 expression, p300 CH1 domain binding and HIF-mediated reporter activity. We have thus defined a role for the C-terminal α-helical domain of VHL in the regulation of HIF-1α.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VHL:
-
von Hippel–Lindau
- HIF:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor
- HLF:
-
HIF-like factors
- Cul-2:
-
Cullin-2
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- GLUT1:
-
glucose transporter 1
- E3:
-
ubiquitin protein isopeptide ligase
- aa:
-
amino acids
- TIMP:
-
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases
- MCS:
-
multiple cloning site
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulphoxide
- RCC:
-
renal cell carcinoma
- HRE:
-
HIF response element
- EF-IRES:
-
elongation factor promoter-internal ribosome entry site
- NES:
-
nuclear export signal
- NLS:
-
nuclear localization signal
- DRB:
-
5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole ribososide
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- FCS:
-
foetal calf serum
References
Clifford SC and Maher ER . (2000). Adv. Cancer Res., 82, 85–105.
Clifford SC, Cockman ME, Smallwood AC, Mole DR, Woodward ER, Maxwell PH, Ratcliffe PJ and Maher ER . (2001). Hum. Mol. Genet., 10, 1029–1038.
Crossey PA, Richards FM, Foster K, Green JS, Prowse A, Latif F., Lerman MI, Zbar B, Affara NA and Ferguson-Smith MA . (1994). Hum. Mol. Genet., 3, 1303–1308.
Ema M, Taya S, Yokotani N, Sogawa K, Matsuda Y and Fujii-Kuriyama Y . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 94, 4273–4278.
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O'Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, Tian YM, Masson N, Hamilton DL, Jaakkola P, Barstead R, Hodgkin J, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ and Ratcliffe PJ . (2001). Cell, 107, 43–54.
Hewitson KS, McNeill LA, Riordan MV, Tian YM, Bullock AN, Welford RW, Elkins JM, Oldham NJ, Bhattacharya S, Gleadle JM, Ratcliffe PJ, Pugh CW and Schofield CJ . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 26351–26355.
Hoffman MA, Ohh M, Yang H, Klco JM, Ivan M and Kaelin Jr W . (2001). Hum. Mol. Genet., 10, 1019–1027.
Hon WC, Wilson MI, Harlos K, Claridge TD, Schofield CJ, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Ratcliffe PJ, Stuart DI and Jones EY . (2002). Nature, 417, 975–978.
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R and Semenza GL . (1996b). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 17771–17778.
Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C and Marti HH . (1996a). Am. J. Physiol., 271, C1172–C1180.
Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML and Bruick RK . (2002b). Genes Dev., 16, 1466–1471.
Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ and Whitelaw ML . (2002a). Science, 295, 858–861.
Lisztwan J, Imbert G, Wirbelauer C, Gstaiger M and Krek W . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1822–1833.
Lonergan KM, Iliopoulos O, Ohh M, Kamura T, Conaway RC, Conaway JW and Kaelin Jr W . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 732–741.
Mahon PC, Hirota K and Semenza GL . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2675–2686.
Masson N, Willam C, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ . (2001). EMBO J., 20, 5197–5206.
Min JH, Yang H, Ivan M, Gertler F, Kaelin Jr WG and Pavletich NP . (2002). Science, 296, 1886–1889.
Ohh M and Kaelin Jr W . (1999). Mol. Med. Today, 5, 257–263.
Ohh M, Yauch RL, Lonergan KM, Whaley JM, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Louis DN, Gavin BJ, Kley N, Kaelin Jr W and Iliopoulos O . (1998). Mol. Cell, 1, 959–968.
Roberts BJ and Whitelaw ML . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 36351–36356.
Stebbins CE, Kaelin Jr W and Pavletich NP . (1999). Science, 284, 455–461.
Whaley JM, Naglich J, Gelbert L, Hsia YE, Lamiell JM, Green JS, Collins D, Neumann HP, Laidlaw J and Li FP . (1994). Am. J. Hum. Genet., 55, 1092–1102.
Zbar B, Kishida T, Chen F, Schmidt L, Maher ER, Richards FM, Crossey PA, Webster AR, Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Brauch H, Glavac D, Neumann HP, Tisherman S, Mulvihill JJ, Gross DJ, Shuin T, Whaley J, Seizinger B, Kley N, Olschwang S, Boisson C, Richard S, Lips CH, Linehan M and Lerman M . (1996). Hum. Mutat., 8, 348–357.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Project Grant: 10365, awarded to BJ Roberts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, M., Roberts, B. Role of the C-terminal α-helical domain of the von Hippel–Lindau protein in its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Oncogene 23, 2315–2323 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207384
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207384
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mutation of the proline P81 into a serine modifies the tumour suppressor function of the von Hippel–Lindau gene in the ccRCC
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
HIF-1α and EPAS ubiquitination mediated by the VHL tumour suppressor involves flexibility in the ubiquitination mechanism, similar to other RING E3 ligases
Oncogene (2007)
-
Role of the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein in the regulation of HIF-1α and its oxygen-regulated transactivation domains at high cell density
Oncogene (2005)