Abstract
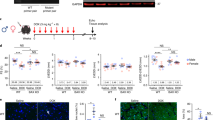
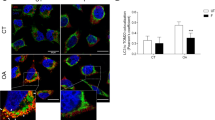
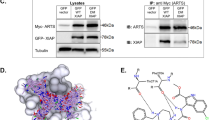
The Bcl-2 family of proteins regulates apoptosis chiefly by controlling mitochondrial membrane permeability. It has previously been shown that the BH4 domain of Bcl-2/Bcl-xL is essential for the prevention of apoptotic mitochondrial changes, including the release of cytochrome c and apoptotic cell death. We have previously reported that BH4 peptide fused to the protein transduction domain of HIV-1 TAT protein (TAT-BH4) significantly inhibits etoposide-induced apoptosis in a cell line. This time, we investigated whether TAT-BH4 peptide was cytoprotective in ex vivo and in vivo rodent models. Intraperitoneal injection of TAT-BH4 peptide greatly inhibited X-ray-induced apoptosis in the small intestine of mice and partially suppressed Fas-induced fulminant hepatitis. In addition, this peptide markedly suppressed heart failure after ischemia–reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart, probably by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. These findings demonstrate that TAT-BH4 peptide exerts anti-apoptotic activity both in vivo and ex vivo, and imply that it may be a useful therapeutic agent for diseases involving mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BH:
-
Bcl-2 homology
- PTD:
-
protein transduction domain
- VDAC:
-
voltage-dependent anion channel
- RCR:
-
respiratory control ratio
- mAST:
-
mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase
References
Adams JM and Cory S . (1998). Science, 281, 1322–1326.
Borner C, Martinou I, Mattmann C, Irmler M, Schaerer E, Martinou JC and Tschopp J . (1994). J. Cell Biol., 126, 1059–1068.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X . (2000). Cell, 102, 33–42.
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B and Martinou JC . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 929–935.
Green DR and Reed JC . (1998). Science, 281, 1309–1312.
Hanada M, Aime-Sempe C, Sato T and Reed JC . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 11962–11969.
Hirotani M, Zhang Y, Fujita N, Naito M and Tsuruo T . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 20415–20420.
Hockenbery DM . (1992). Semin. Immunol., 4, 413–420.
Huang DC, Adams JM and Cory S . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 1029–1039.
Hunter JJ, Bond BL and Parslow TG . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 877–883.
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Latterich M, Schneiter R, Green DR and Newmeyer DD . (2002). Cell, 111, 331–342.
Lee LC, Hunter JJ, Mujeeb A, Turck C and Parslow TG . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23284–23288.
Macho A, Calzado MA, Jimenez-Reina L, Ceballos E, Leon J and Munoz E . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7543–7551.
Martinou JC and Green DR . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2, 63–67.
Niwa H, Yamamura K and Miyazaki J . (1991). Gene, 108, 193–199.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ . (1993). Cell, 74, 609–619.
Park IW, Ullrich CK, Schoenberger E, Ganju RK and Groopman JE . (2001). J. Immunol., 167, 2766–2771.
Saikumar P, Dong Z, Weinberg JM and Venkatachalam MA . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 3341–3349.
Saito M, Korsmeyer SJ and Schlesinger PH . (2000). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 553–555.
Schwarze SR, Hruska KA and Dowdy SF . (2000). Trends Cell Biol., 10, 290–295.
Schwarze SR, Ho A, Vocero-Akbani A and Dowdy SF . (1999). Science, 285, 1569–1572.
Shibasaki F, Kondo E, Akagi T and McKeon F . (1997). Nature, 386, 728–731.
Shimizu S, Kamiike W, Hatanaka N, Nishimura M, Miyata M, Inoue T, Yoshida Y, Tagawa K and Matsuda H . (1994). Transplantation, 57, 144–148.
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kamiike W, Itoh Y, Hasegawa J, Yamabe K, Otsuki Y, Matsuda H and Tsujimoto Y . (1996a). Cancer Res., 56, 2161–2166.
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kamiike W, Matsuda H and Tsujimoto Y . (1996b). Oncogene, 12, 2251–2257.
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y . (1999). Nature, 399, 483–487.
Shimizu S, Ide T, Yanagida T and Tsujimoto Y . (2000a). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 12321–12325.
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Kodama T and Tsujimoto Y . (2000b). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 3100–3105.
Shimizu S, Matsuoka Y, Shinohara Y, Yoneda Y and Tsujimoto Y . (2001). J. Cell Biol., 152, 237–250.
Solem LE and Wallace KB . (1993). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 121, 50–57.
Suzuki K, Sawa Y, Kaneda Y, Ichikawa H, Shirakura R and Matsuda H . (1997). J. Clin. Invest., 99, 1645–1650.
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S . (2000a). FEBS Lett., 466, 6–10.
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S . (2000b). Cell Death Differ., 7, 1174–1181.
Tsujimoto Y . (2003). J. Cell. Physiol., 195, 158–167.
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ and Vaux DL . (2000). Cell, 102, 43–53.
Wang HG, Rapp UR and Reed JC . (1996). Cell, 87, 629–638.
Wang X . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2922–2933.
Wei MC, Lindsten T, Mootha VK, Weiler S, Gross A, Ashiya M, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 2060–2071.
Yamabe K, Shimizu S, Kamiike W, Waguri S, Eguchi Y, Hasegawa J, Okuno S, Yoshioka Y, Ito T, Sawa Y, Uchiyama Y, Tsujimoto Y and Matsuda H . (1998). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 243, 217–223.
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ . (1995). Cell, 80, 285–291.
Zamzami N and Kroemer G . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2, 67–71.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant for Scientific Research on Priority Areas, a grant for Center of Excellence Research, a grant for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan, and by Special Coordination Funds of Promoting Science and Technology from the Science and Technology Agency of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugioka, R., Shimizu, S., Funatsu, T. et al. BH4-domain peptide from Bcl-xL exerts anti-apoptotic activity in vivo. Oncogene 22, 8432–8440 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207180
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of cardiomyocyte DNA damage and cell death by the type 2A protein phosphatase regulatory protein alpha4
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
BH4 domain peptides derived from Bcl-2/Bcl-XL as novel tools against acute pancreatitis
Cell Death Discovery (2018)
-
Alpha 5/6 helix domains together with N-terminus determine the apoptotic potency of the Bcl-2 family proteins
Apoptosis (2016)
-
Inhibition of regulated cell death by cell-penetrating peptides
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2016)
-
Ryanodine receptors are targeted by anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL involving its BH4 domain and Lys87 from its BH3 domain
Scientific Reports (2015)