Abstract
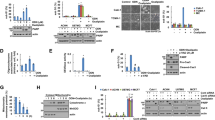
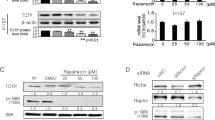
Geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitors (GGTIs) represent a new class of anticancer drugs. However, the mechanism by which GGTIs inhibit tumor cell growth is still unclear. Here, we demonstrate that GGTI-298 and GGTI-2166 induce apoptosis in both cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian epithelial cancer cells by inhibition of PI3K/AKT and survivin pathways. Following GGTI-298 or GGTI-2166 treatment, kinase levels of PI3K and AKT were decreased and survivin expression was significantly reduced. Ectopic expression of constitutively active AKT2 and/or survivin significantly rescue human cancer cells from GGTI-298-induced apoptosis. Previous studies have shown that Akt mediates growth factor-induced survivin, whereas p53 inhibits survivin expression. However, constitutively active AKT2 failed to rescue the GGTIs downregulation of survivin. Further, GGTIs suppress survivin expression and induce programmed cell death in both wild-type p53 and p53-deficient ovarian cancer cell lines. These data indicate that GGTI-298 and GGTI-2166 induce apoptosis by targeting PI3K/AKT and survivin parallel pathways independent of p53. Owing to the fact that upregulation of Akt and survivin as well as inactivation of p53 are frequently associated with chemoresistance, GGTIs could be valuable agents to overcome antitumor drug resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnane J, Bizouarn FA, Qian Y, Hamilton AD and Sebti SM . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 6962–6970.
Altieri DC . (2003). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 3, 46–54.
Arboleda MJ, Lyons JF, Kabbinavar FF, Bray MR, Snow BE, Ayala R, Danino M, Karlan BY and Slamon DJ . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 196–206.
Bolick SC, Landowski TH, Boulware D, Oshiro MM, Ohkanda J, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM and Dalton WS . (2003). Leukemia, 17, 451–457.
Brazil DP, Park J and Hemmings BA . (2002). Cell, 111, 293–303.
Chen Z, Sun J, Pradines A, Favre G, Adnane J and Sebti SM . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 17974–17978.
Cheng JQ, Godwin AK, Bellacosa A, Taguchi T, Franke TF, Hamilton TC, Tsichlis PN and Testa JR . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 9267–9271.
Cheng JQ, Jiang X, Fraser M, Li M, Dan HC, Sun M and Tsang BK . (2002). Drug Resist. Update, 5, 131–146.
Cheng JQ, Ruggeri B, Klein WM, Sonoda G, Altomare DA, Watson DK and Testa JR . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 3636–3641.
Clark AS, West K, Streicher S and Dennis PA . (2002). Mol. Cancer Ther., 1, 707–717.
Datta K, Bellacosa A, Chan TO and Tsichlis PN . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 30835–30839.
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 2905–2927.
Deveraux QL and Reed JC . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 239–252.
Du W, Lebowitz PF and Prendergast GC . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 1831–1840.
Franke TF, Yang SL, Chan TO, Datta K, Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR and Tsichlis PN . (1995). Cell, 81, 727–736.
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J and Murphy M . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 3247–3257.
Jiang K, Coppola D, Crespo NC, Nicosia SV, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM and Cheng JQ . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 139–148.
Kane LP, Mollenauer MN, Xu Z, Turck CW and Weiss A . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 5962–5974.
Kohl NE, Mosser SD, deSolms SJ, Giuliani EA, Pompliano DL, Graham SL, Smith RL, Scolnick EM, Oliff A and Gibbs JB . (1993). Science, 260, 1934–1937.
Li F and Altieri DC . (1999). Biochem. J., 344, 305–311.
Liu AX, Testa JR, Hamilton TC, Jove R, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 2973–2977.
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Schottelius AJ, Baldwin Jr AS and Mayo MW . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 1626–1638.
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry TN, Wu Q, Ashar H, Black S, Wen SF, Wang L, Kirschmeier P, Bishop WR and Nielsen LL . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 2613–2622.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Schlossman R, Akiyama M, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Treon SP, Munshi NC, Richardson PG and Anderson KC . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 5673–5683.
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM and Donner DB . (1999). Nature, 401, 82–85.
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb RG, O’Connor DS, Li F, Altieri DC and Sessa WC . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 9102–9105.
Prendergast GC . (2001). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 1, 162–168.
Reed JC . (2001). J. Clin. Invest., 108, 965–969.
Reiss Y, Goldstein JL, Seabra MC, Casey PJ and Brown MS . (1990). Cell, 62, 81–88.
Sasaki H, Sheng Y, Kotsuji F and Tsang BK . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 5659–5666.
Sebti SM and Hamilton AD . (1997). Pharmacol. Ther., 74, 103–114.
Sebti SM and Hamilton AD . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6584–6593.
Singh B, Reddy PG, Goberdhan A, Walsh C, Dao S, Ngai I, Chou TC, O-Charoenrat P, Levine AJ, Rao PH and Stoffel A . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 984–993.
Song K, Li Z, Seth P, Cowan KH and Sinha BK . (1997). Oncol. Res., 9, 603–609.
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, Lin Y, Snow B, Jang Y, Benchimol S and Mak TW . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 317–325.
Sun J, Blaskovich MA, Knowles D, Qian Y, Ohkanda J, Bailey RD, Hamilton AD and Sebti SM . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 4919–4926.
Sun J, Qian Y, Chen Z, Marfurt J, Hamilton AD and Sebti SM . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 6930–6934.
Tran J, Master Z, Yu JL, Rak J, Dumont DJ and Kerbel RS . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 4349–4354.
Yuan Z, Sun M, Feldman RI, Wang G, Ma X, Coppola D, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 2324–2330.
Yuan ZQ, Feldman RI, Sun M, Olashaw NE, Coppola D, Sussman GE, Shelley SA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 29973–29982.
Zaffaroni N, Pennati M, Colella G, Perego P, Supino R, Gatti L, Pilotti S, Zunino F and Daidone MG . (2002). Cell Mol. Life Sci., 59, 1406–1412.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Jian-dong Chen for GST-p53 plasmid and Benjamin K Tsang for ovarian cancer cell lines. We are also grateful to the Molecular Biology DNA Sequence Facility at H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center for sequencing Survivin constructs. This work was supported by National Cancer Institute Grants CA085709, CA67771, CA89242 and Department of Defense DAMD 17-01-1-0394 and DAMD17-02-1-0670.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dan, H., Jiang, K., Coppola, D. et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/AKT and survivin pathways as critical targets for geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23, 706–715 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207171
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interactions between tumor-derived proteins and Toll-like receptors
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Protein prenylation: unique fats make their mark on biology
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2016)
-
Geranylgeranylation signals to the Hippo pathway for breast cancer cell proliferation and migration
Oncogene (2015)
-
Oncogenes associated with drug resistance in ovarian cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2015)
-
The same and not the same: heterogeneous functional activation of prostate tumor cells by TLR ligation
Cancer Cell International (2014)