Abstract
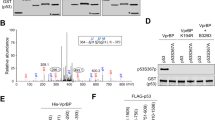
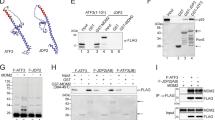
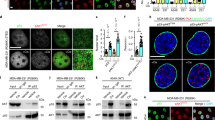
The p53 tumor suppressor protein plays a critical role in mediating cellular response to stress. Upon DNA damage, post-translational modifications stabilize and activate this nuclear phosphoprotein. To determine the effect of phosphorylation site mutants in the context of the whole p53 protein, we performed reporter assays in p53 and MDM2 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts transfected with full-length p53 constructs. We show that mutation of S37 causes a decrease in p53 transcriptional activity compared to wild-type p53. Our data further suggest that the dephosphorylation of p53 at S37 is a regulated event involving protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). Coimmunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence microscopy studies demonstrate that PP2A and p53 associate with one another in vivo following γ-irradiation. Consistent with these observations, phosphorylated S37 accumulates in cell extracts prepared from γ-irradiated Molt-4 cells in the presence of okadaic acid. Furthermore, in vitro phosphatase assays show that PP2A dephosphorylates p53 at S37. These results suggest that dephosphorylation of p53 at S37 plays a role in the transcriptional regulation of the p53 protein in response to DNA damage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal ML, Taylor MV, Chernov MV, Chernova OB and Stark GR . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 1–4.
Ashcroft M and Vousden KH . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7637–7643.
Baharians Z and Schonthal AH . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 19019–19024.
Bean LJ and Stark GR . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 1076–1084.
Bialojan C and Takai A . (1988). Biochem. J., 256, 283–290.
Bryant JC, Westphal RS and Wadzinsky BE . (1999). Biochem. J., 339, 241–246.
Canettieri G, Morantte I, Guzman E, Asahara H, Herzig S, Anderson SD, Yates JR and Montminy M . (2003). Nat. Struct. Biol., 10, 175–181.
Chen J, Martin Bl and Brautignan DL . (1992). Science, 257, 1261–1264.
Cohen P . (1991). Methods Enzymol., 201, 389–397.
Cohen P and Cohen PTW . (1989). J. Biol. Chem., 264, 21435–21438.
Cohen P, Klumpp S and Schelling DL . (1989). FEBS Lett., 254, 596–600.
Dumaz N and Meek DW . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 7002–7010.
El-Deiry WS, Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1992). Nat. Genet., 1, 45–49.
Elbi C, Misteli T and Hager GL . (2002). Mol. Biol. Cell, 13, 2001–2015.
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE, Vande Woude GF, O'Connor PM and Appella E . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 6048–6058.
Funk WD, Pak DT, Karas RH, Wright WE and Shay JW . (1992). Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 2866–2871.
Gotz J, Probst A, Ehler E, Hemmings B and Kues W . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 12370–12375.
Guy GR, Cao X, Chua SP and Tan YH . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 1846–1852.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ . (1993). Cell, 75, 805–816.
Juven T, Barak Y, Zauberman A, George DL and Oren M . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 3411–3416.
Kastan MB, Zhan Q, El-Deiry WS, Carrier F, Jacks T, Walsh W, V, Plunkett BS, Vogelstein B and Fornace AJJ . (1992). Cell, 71, 587–597.
Kawabe T, Muslin AJ and Korsmeyer SJ . (1997). Nature, 385, 454–458.
Kimura SH and Nojima H . (2002). Genes Cells, 7, 869–880.
Ko LJ and Prives C . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 1054–1072.
Lambert FP, Kashanchi F, Radonovitch MF, Shiekhattar R and Brady JN . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 33048–33053.
Lees-Miller SP, Chen Y-R and Anderson CW . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 6472–6481.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 323–331.
Li L, Ljungman M and Dixon JE . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2410–2414.
Miyashita T and Reed JC . (1995). Cell, 80, 293–299.
Mumby M and Walter G . (1993). Physiol. Rev., 73, 673–699.
Okamoto K, Kamibayashi C, Serrano M, Prives C, Mumby MC and Beach D . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 6593–6602.
Okamoto K, Li H, Jensen MR, Zhang T, Taya Y, Thorgeirsson SS and Prives C . (2002). Mol. Cell, 9, 761–771.
Pise-Masison CA, Mahieux R, Jiang H, Ashcroft M, Radonovich M, Duvall J, Guillerm C and Brady JN . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3377–3386.
Ruediger R, Van Wart Hood JE, Mumby M and Walter G . (1991). Mol. Cell. Biol., 11, 4282–4285.
Sakaguchi K, Herrera JE, Saito S, Miki T, Bustin M, Vassilev A, Anderson CW and Appella E . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2831–2841.
Scheidtmann KH, Mumby MC, Rundell K and Walter G . (1991). Mol. Cell. Biol., 11, 1996–2003.
Schonthal AH . (1998). Front. Biosci., 3, 1262–1273.
Shieh S-Y, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C . (1997). Cell, 91, 325–334.
Shieh S-Y, Taya Y and Prives C . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1815–1823.
Siliciano JD, Canman CE, Taya Y, Sakaguchi K, Appella E and Kastan MB . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 3471–3481.
Takenaka I, Morin F, Seizinger BR and Kley N . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 5405–5411.
Van Steensel B, van Binnendijk EP, Hornsby CD, Van der Voort HT, Krozowski Z, De Kloet ER and Van Driel R . (1996). J. Cell Sci., 109, 787–792.
Wera S and Hemmings BA . (1995). Biochem. J., 311, 17–29.
Wilson NJ, Moss ST, Csar XF, Ward AC and Hamilton JA . (1999). Biochem. J., 339, 517–524.
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D and Levine AJ . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 1126–1132.
Yan Y, Shay JW, Wright WE and Mumby MC . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 15220–15226.
Zuo Z, Dean N and Honkanen RE . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 12250–12258.
Acknowledgements
We thank Michael Radonovich for preparation of γ-irradiated cells, Dr Tom Misteli for technical suggestions on image processing and Dr Cynthia Pise-Masison for helpful discussions. Microscopy images in this article were generated in the imaging facility of Tom Misteli and processed in the NIH, NCI Core Imaging Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dohoney, K., Guillerm, C., Whiteford, C. et al. Phosphorylation of p53 at serine 37 is important for transcriptional activity and regulation in response to DNA damage. Oncogene 23, 49–57 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207005
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207005
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Altering phosphorylation in cancer through PP2A modifiers
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
Regulation of cardiomyocyte DNA damage and cell death by the type 2A protein phosphatase regulatory protein alpha4
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Serine/threonine protein phosphatases in DNA damage response
Chinese Science Bulletin (2011)
-
Serine/threonine phosphatases in the DNA damage response and cancer
Oncogene (2010)
-
Protein phosphatase-1 regulates Akt1 signal transduction pathway to control gene expression, cell survival and differentiation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2010)