Abstract
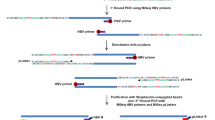
Although the integration of hepatitis B virus (HBV) into human DNA has been found to be associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the molecular mechanism remains unclear. In order to obtain additional insight into the correlation of HBV integration and HCC development, integrated HBV in 14 primary HCC cases was isolated and characterized by sequencing analysis. Our findings in this study showed that: (1) none of the known cellular oncogene or tumor suppressor gene was affected by the HBV integration; (2) although the integration of HBV is random, the integration site was often within or close to human repetitive sequences; (3) integrated HBV may possess the capacity to transpose to another chromosome region through reintegration; (4) rearrangements of HBV sequence were observed in all the 14 integrants, involving (most frequently) X (12/14 integrants), P (8/14), S (7/14), and C (7/14) genes; and (5) 3′-deleted X gene and consequent C-terminal truncated X protein caused by HBV integration was observed in 10 cases. These deletions cause the losses of p53-dependent transcriptional repression binding site, transcription factor Sp1 binding site, and growth-suppressive effect domain, leading to cell proliferation and transformation. This finding suggests that 3′-deleted X gene caused by the HBV integration may play an important role in the HCC development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnot P, Capovilla A and Kew M . (2000). J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 15, 357–368.
Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC and Chien CS . (1981). Lancet, 2, 1129–1133.
Billet O, Grimber G, Levrero M, Seye KA, Briand P and Joulin V . (1995). J. Virol., 69, 5912–5916.
Brechot C, Gozuacik D, Murakami Y and Brechot PP . (2000). Semin. Cancer Biol., 10, 211–231.
Buendia MA . (1992). Adv. Cancer Res., 59, 167–226.
Chami M, Gozuacik D, Saigo K, Capiod T, Falson P, Lecoeur H, Urashima T, Beckmann J, Gougeon ML, Claret M, Maire M, Brechot C and Paterlini-Brechot P . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 2877–2886.
Diao J, Garces R and Richardson CD . (2001). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 12, 189–205.
Grozuacik D, Murakami Y, Saigo K, Chami M, Mugnier C, Lagorec D, Okanoue T, Urashima T, Brechot C and Paterlini-Brechot P . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 6233–6240.
Hansen LJ, Tennant BC, Seeger C and Ganem D . (1993). Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 659–635.
Jaspers NGJ and Hoeijmakers JHJ . (1995). Curr. Biol., 5, 700–702.
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T and Jay G . (1991). Nature, 351, 317–320.
Lee H, Kim HT and Yun Y . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 19786–19791.
Li J and Ou J-H . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 8400–8406.
Madden CR, Finegold MJ and Slagle BL . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 3851–3858.
Matsubara K and Tokino T . (1990). Mol. Biol. Med., 7, 243–260.
Murakami S . (2001). J. Gastroenterol., 36, 651–660.
Natoli G, Avantaggiati ML, Chirillo P, Puri PL, Ianni A, Balsano C and Levrero M . (1994). Oncogene, 9, 2837–2843.
Peterson MC, Inostroza J, Maxon ME, Flores O, Admon A, Reinberg D and Tjian R . (1991). Nature, 354, 369–373.
Reifenberg K, Lohler J, Pudollek HP, Schmitteckert E, Spindler G, Kock J and Schlicht HJ . (1997). J. Hepatol., 26, 119–130.
Robinson WS . (1994). Ann. Rev. Med., 45, 297–323.
Sirma H, Giannini C, Poussin K, Paterlini P, Kremsdorf D and Brechot C . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 4848–4859.
Su TS, Hwang WL and Yauk YK . (1998). DNA Cell Biol., 17, 415–425.
Terradillos O, Pollicino T, Lecoeur H, Tripodi M, Gougeon ML, Tiollais P and Buendia MA . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 2115–2123.
Tokino T and Matsubara K . (1991). J. Virol., 65, 6761–6764.
Tu H, Bonura C, Giannini C, Mouly H, Soussan P, Kew M, Paterlini-Brechot P, Brechot C and Kremsdorf D . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 7803–7810.
Urano Y, Watanabe K, Lin C, Hino O and Tamaoki T . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 1460–1464.
Wang HP and Rogler CE . (1988). Science, 48, 72.
Wang J, Chenivesse X, Henglein B and Brechot C . (1990). Nature, 343, 555–557.
Wang XW, Gibson MK, Vermeulen W, Yeh H, Forrester K, Sturzbecher HW, Hoeijmakers JH and Harris CC . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 6012–6016.
Yeh CT . (2000). J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 15, 339–341.
Yu DY, Moon HB, Son JK, Jeong S, Yu SL, Yoon H, Han YM, Lee CS, Park JS, Lee CH and Hyun BH . (1999). J. Hepatol., 31, 123–132.
Ziemer M, Garcia P, Shaul Y and Rutter WJ . (1985). J. Virol., 53, 885–892.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported in part by the Leung Kwok Tze Foundation and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 30171046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lau, S., Sham, JT. et al. Characterization of HBV integrants in 14 hepatocellular carcinomas: association of truncated X gene and hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Oncogene 23, 142–148 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206889
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206889
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tumor suppressive role of mitochondrial sirtuin 4 in induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
C-terminal-truncated HBV X promotes hepato-oncogenesis through inhibition of tumor-suppressive β-catenin/BAMBI signaling
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2016)
-
An update on viral association of human cancers
Archives of Virology (2013)
-
Association Between the Various Mutations in Viral Core Promoter Region to Different Stages of Hepatitis B, Ranging of Asymptomatic Carrier State to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
American Journal of Gastroenterology (2011)
-
Comparison of hepatitis B X gene mutation between patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and patients with chronic hepatitis B
Virus Genes (2011)