Abstract
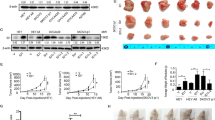
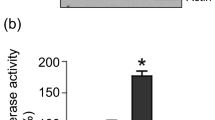
The growth-promoting effect of Id-1 (inhibitor of differentiation/DNA binding) has been demonstrated in a number of human cancers. However, the mechanisms responsible for its action are not clear. In this study, we report that in prostate cancer cells, Id-1 promotes cell survival through activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling pathway. After stable expression of Id-1 protein in LNCaP cells, we found that the Id-1 transfectants showed increased resistance to apoptosis induced by TNFα through inactivation of Bax and caspase 3. In addition, in the LNCaP cells expressing ectopic Id-1 protein, we also observed increased NF-κB transactivation activity and nuclear translocation of the p65 and p50 proteins, which was accompanied by upregulation of their downstream effectors Bcl-xL and ICAM-1. These results indicate that the Id-1-induced antiapoptotic effect may be via NF-κB signalling transduction pathway in these cells. In addition, inactivation of Id-1 by its antisense oligonucleotide and retroviral construct in DU145 cells resulted in the decrease of nuclear level of p65 and p50 proteins, which was associated with increased sensitivity to TNFα-induced apoptosis. Our results strongly suggest that Id-1 may be one of the upstream regulators of NF-κB and activation of NF-κB signalling pathway may be essential for Id-1 induced cell proliferation through protection against apoptosis. Our findings also suggest a potential therapeutic strategy in which inactivation of Id-1 may lead to sensitization of prostate cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alani RM, Hasskarl J, Grace M, Hernandez MC, Israel MA and Munger K . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 9637–9641.
Alani RM, Young AZ and Shifflett CB . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 7812–7816.
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D . (1996). Cell, 87, 13–20.
Baldwin Jr AS . (1996). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 14, 649–683 .
Baldwin Jr AS, Azizkhan JC, Jensen DE, Beg AA and Coodly LR . (1991). Mol. Cell. Biol., 11, 4943–4951.
Barone MV, Pepperkok R, Peverali FA and Philipson L . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 4985–4988.
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL and Weintraub H . (1990). Cell, 61, 49–59.
Chen F, Castranova V and Shi X . (2001). Am. J. Pathol., 159, 387–397.
Desprez PY, Hara E, Bissell MJ and Campisi J . (1995). Mol Cell. Biol., 15, 3398–3404.
Desprez PY, Lin CQ, Thomasset N, Sympson CJ, Bissell MJ and Campisi J . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 4577–4588.
Dhanalakshmi S, Singh RP, Agarwal C and Agarwal R . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 1759–1767.
DiDonato J, Mercurio F, Rosette C, Wu-Li J, Suyang H, Ghosh S and Karin M . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 1295–1304.
Gupta S, Afaq F and Mukhtar H . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 3727–3738.
Gurumurthy S, Vasudevan KM and Rangnekar VM . (2001). Cancer Metastasis Rev., 20, 225–243.
Florio M, Hernandez MC, Yang H, Shu HK, Cleveland JL and Israel MA . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 5435–5444.
Hara E, Uzman JA, Dimri GP, Nehlin JO, Testori A and Campisi J . (1996). Dev. Genet., 18, 161–172.
Hara E, Yamaguchi T, Nojima H, Ide T, Campisi J, Okayama H and Oda K . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 2139–2145.
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD and Fidler IJ . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 4188–4197.
Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y, Davidson NE and Poirier GG . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 3976–3985.
Kebebew E, Treseler PA, Duh QY and Clark OH . (2000). Surgery, 128, 952–957.
Kim BY, Gaynor RB, Song K, Dritschilo A and Jung M . (2002a). Oncogene, 21, 4490–4497.
Kim D, Xu M, Nie L, Peng XC, Jimi E, Voll RE, Nguyen T, Ghosh S and Sun XH . (2002b). Immunity, 16, 9–21.
Kleeff J, Ishiwata T, Friess H, Buchler MW, Israel MA and Korc M . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 3769–3772.
Langlands K, Down GA and Kealey T . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 5929–5933.
Li X and Stark GR . (2002). Exp. Hematol., 30, 285–296.
Lin CQ, Singh J, Murata K, Itahana Y, Parrinello S, Liang SH, Gillett CE, Campisi J and Desprez PY . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 1332–1340.
Ling MT, Wang X, Tsao SW and Wong YC . (2002a). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1570, 145–152.
Ling MT, Wang X, Ouyang X, Lee TKW, Fan T, Xu K, Tsao SW and Wong YC . (2002b). Oncogene, 21, 8498–8505.
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, Yan W, Gerald W, O'Reilly R, Bader BL, Hynes RO, Zhuang Y, Manova K and Benezra R . (1999). Nature, 401, 670–677.
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Schottelius AJ, Baldwin Jr AS and Mayo MW . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 1626–1638.
Maruyama H, Kleeff J, Wildi S, Friess H, Buchler MW, Israel MA and Korc M . (1999). Am. J. Pathol., 155, 815–822.
Norton JD and Atherton GT . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 2371–2381.
Ohtani N, Zebedee Z, Huot TJ, Stinson JA, Sugimoto M, Ohashi Y, Sharrocks AD, Peters G and Hara E . (2001). Nature, 409, 1067–1070.
Ouyang XS, Wang X, Lee DT, Tsao SW and Wong YC . (2001). Carcinogenesis, 22, 965–973.
Ouyang XS, Wang X, Lee DT, Tsao SW and Wong YC . (2002a). J. Urol., 167, 2598–2602.
Ouyang XS, Wang X, Ling MT, Wong HL, Tsao SW and Wong YC . (2002b). Carcinogenesis, 23, 721–725.
Palayoor ST, Youmell MY, Calderwood SK, Coleman CN and Price BD . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7389–7394.
Parrinello S, Lin CQ, Murata K, Itahana Y, Singh J, Krtolica A, Campisi J and Desprez PY . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 39213–39219.
Pise-Masison CA, Mahieux R, Jiang H, Ashcroft M, Radonovich M, Duvall J, Guillerm C and Brady JN . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3377–3386.
Polsky D, Young AZ, Busam KJ and Alani RM . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6008–6011.
Raffo AJ, Kim AL and Fine RL . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6216–6228.
Schindl M, Oberhuber G, Obermair A, Schoppmann SF, Karner B and Birner P . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 5703–5706.
Sevilla L, Zaldumbide A, Pognonec P and Boulukos KE . (2001). Histol. Histopathol., 16, 595–601.
Shao J, Fujiwara T, Kadowaki Y, Fukazawa T, Waku T, Itoshima T, Yamatsuji T, Nishizaki M, Roth JA and Tanaka N . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 726–736.
Stennicke HR and Salvesen GS . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 25719–25723.
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Fujisawa K, Nasu K and Miyakawa I . (2001). Cancer Lett., 165, 185–193.
Tanaka K, Pracyk JB, Takeda K, Yu ZX Ferrans VJ, Desphande SS, Ozaki M, Hwang PM, Lowenstein CJ, Irani K and Finkel T . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 25922–25928.
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D and Miyamoto S . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 2723–2735.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV and Baldwin Jr AS . (1998). Science, 281, 1680–1683.
Wilson JW, Deed RW, Inoue T, Balzi M, Becciolini A, Faraoni P, Potten CS and Norton JD . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 8803–8810.
Wu MX, Ao Z, Prasad KV, Wu R and Schlossman SF . (1998). Science, 281, 998–1001.
Zhong H, Voll RE and Ghosh S . (1998). Mol. Cell, 1, 661–671.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by RGC grants to YC Wong (HKU 7186/99 M, HKU 7314/01 M and HKU 7490/03M) and Area of Excellence Scheme (Project No. AoE/P-10/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, MT., Wang, X., Ouyang, XS. et al. Id-1 expression promotes cell survival through activation of NF-κB signalling pathway in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 22, 4498–4508 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206693
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206693
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ID1 marks the tumorigenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mouse and human
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Retraction Note to: Id-1 stimulates cell proliferation through activation of EGFR in ovarian cancer cells
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
The role of leukemia inhibitory factor in pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia: molecular and cell signaling approach
Journal of Molecular Histology (2021)
-
Cinchonine induces apoptosis of HeLa and A549 cells through targeting TRAF6
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2017)
-
Id-1 promotes migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells through activating NF-κB signaling pathway
Journal of Biomedical Science (2017)