Abstract
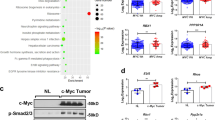
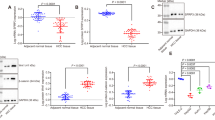
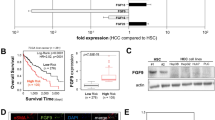
Resistance to growth inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β is a frequent consequence of malignant transformation. On the other hand, serum concentrations of TGF-β, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are elevated as tumor progresses. The molecular mechanism of autocrine TGF-β signaling and its effects on PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unknown. TGF-β signaling involves TGF-β type I receptor-mediated phosphorylation of serine residues within the conserved SSXS motif at the C-terminus of Smad2 and Smad3. To investigate the involvement of autocrine TGF-β signal in cell growth, PAI-1 and VEGF production of HCC, we made stable transfectants of human HCC line (HuH-7 cells) to express a mutant Smad2(3S-A), in which serine residues of SSXS motif were changed to alanine. The transfectants demonstrated an impaired Smad2 signaling. Along with the resistance to growth inhibition by TGF-β, forced expression of Smad2(3S-A) induced endogenous TGF-β secretion. Moreover, this increased TGF-β enhanced ligand-dependent signaling through the activated Smad3 and Smad4 complex, and transcriptional activities of PAI-1 and VEGF genes. In conclusion, distortion of autocrine TGF-β signals in human HCC accelerates their malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelev GI . (1971). Adv. Cancer Res., 14, 295–358.
Bajou K, Noël A, Gerard RD, Masson V, Brunner N, Holst-Hansen C, Skobe M, Fusenig NE, Carmeliet P, Collen D and Foidart JM . (1998). Nat. Med., 4, 923–928.
Danø K, Andreasen PA, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS and Skriver L . (1985). Adv. Cancer Res., 44, 139–266.
Date M, Matsuzaki K, Matsushita M, Sakitani K, Shibano K, Okajima A, Yamamoto C, Ogata N, Okumura T, Seki T, Kubota Y, Kan M, McKeehan WL and Inoue K . (1998). J. Hepatol., 28, 572–581.
de Caestecker MP, Piek E and Roberts AB . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1388–1402.
Derynck R, Zhang Y and Feng X-H . (1998). Cell, 95, 737–740.
Dvorak HF, Sioussat TM, Brown LF, Berse B, Nagy JA, Sotrel A, Manseau EJ, Van de Water L and Senger DR . (1991). J. Exp. Med., 174, 1275–1278.
Engel ME, Datta PK and Moses HL . (1998). J. Cell. Biochem. Suppl., 30/31, 111–122.
Fan G, Ma X, Kren BT and Steer CJ . (1996). Oncogene, 12, 1909–1919.
Feng X-H, Lin X and Derynck R . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 5178–5193.
Ferrara N . (1999). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 237, 1–30.
Gutierrez LS, Schulman A, Brito-Robinson T, Noria F, Ploplis VA and Castellino FJ . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 5839–5847.
Healy AM and Gelehrter TD . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 19095–19100.
Hua X, Liu X, Ansari DO and Lodish HF . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 3084–3095.
Kim S-J, Angel P, Lafyatis R, Hattori K, Kim KY, Sporn MB, Karin M and Roberts AB . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 1492–1497.
Macías-Silva M, Abdollah S, Hoodless PA, Pirone R, Attisano L and Wrana JL . (1996). Cell, 87, 1215–1224.
Massagué J . (1998). Annu. Rev. Biochem., 67, 753–791.
Matsuzaki K, Date M, Furukawa F, Tahashi Y, Matsushita M, Sakitani K, Yamashiki N, Seki T, Saito H, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J and Inoue K . (2000a). Cancer Res., 60, 1394–1402.
Matsuzaki K, Date M, Furukawa F, Tahashi Y, Matsushita M, Sugano Y, Yamashiki N, Nakagawa T, Seki T, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J and Inoue K . (2000b). Hepatology, 32, 218–227.
Matsuzaki K, Yoshitake Y, Miyagiwa M, Minemura M, Tanaka M, Sasaki H and Nishikawa K . (1990). Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 81, 345–354.
Mise M, Arii S, Higashituji H, Furutani M, Niwano M, Harada T, Ishigami S, Toda Y, Nakayama H, Fukumoto M, Fujita J and Imamura M . (1996). Hepatology, 23, 455–464.
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Konishi M, Sakai K, Ishii A, Yasuno M, Hishima T, Koike M, Shitara N, Iwama T, Utsunomiya J, Kuroki T and Mori T . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3098–3103.
Miyazono K, Kusanagi K and Inoue H . (2001). J. Cell Physiol., 187, 265–276.
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Morén A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R, Itoh S, Kawabata M, Heldin N-E, Heldin C-H and ten Dijke P . (1997). Nature, 389, 631–635.
Pedersen H, Brünner N, Francis D, Østerlind K, Ronne E, Hansen HH, Danø K and Grøndahl-Hansen J . (1994a). Cancer Res., 54, 4671–4675.
Pedersen H, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Francis D, Østerlind K, Hansen HH, Danø K and Brünner N . (1994b). Cancer Res., 54, 120–123.
Piek E and Roberts AB . (2001). Adv. Cancer Res., 83, 1–54.
Prunier C, Ferrand N, Frottier B, Pessah M and Atfi A . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 3302–3313.
Riggins GJ, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Thiagalingam S . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 2578–2580.
Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Volpert OV, Bouck NP, Sipos B, Hahn SA, Klein-Scory S, Lüttges J, Kölppel G, Graeven U, Eilert-Micus C, Hintelmann A and Schmiegel W . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 9624–9629.
Shirai Y, Kawata S, Tamura S, Ito N, Tsusima H, Takaishi K, Kiso S and Matsuzawa Y . (1994). Cancer, 73, 2275–2279.
Wrana JL . (2000). Cell, 100, 189–192.
Yakicier MC, Irmak MB, Romano A, Kew M and Ozturk M . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 4879–4883.
Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Toyosaka A, Mitunobu M, Fujihara S, Kato T, Fujimoto J, Oriyama T, Furukawa K and Kawamura E . (1990). Cancer, 65, 1104–1110.
Zhang Y and Derynck R . (1999). Trends Cell Biol., 9, 274–279.
Zhou L, Hayashi Y, Itoh T, Wang W, an Rui J and Itoh H . (2000). Pathol. Int., 50, 392–397.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr SW Qian (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA), Dr R Derynck (University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA), Drs CH Heldin, and K Miyazono (Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research) for providing us with cDNAs of rat TGF-β1, human Smad2, Smad3, Smad4, and human TβRI in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugano, Y., Matsuzaki, K., Tahashi, Y. et al. Distortion of autocrine transforming growth factor β signal accelerates malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 22, 2309–2321 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206305
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The proprotein convertase furin in cancer: more than an oncogene
Oncogene (2022)
-
FOXP3 inhibits angiogenesis by downregulating VEGF in breast cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
TGF-β signal shifting between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis in human chronic liver diseases
Journal of Gastroenterology (2014)
-
Smad phosphoisoform signals in acute and chronic liver injury: similarities and differences between epithelial and mesenchymal cells
Cell and Tissue Research (2012)
-
Opposite functions of HIF-α isoforms in VEGF induction by TGF-β1 under non-hypoxic conditions
Oncogene (2011)