Abstract
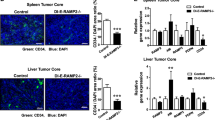
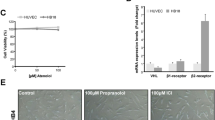
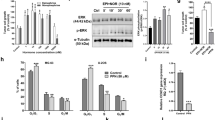
Since it is reported that adrenomedullin (AM) upregulated by hypoxia inhibits hypoxic cell death, we examined the effects of AM antagonist (AM C-terminal fragment; AM(22–52)) on the growth of pancreatic cancer cells. We, for the first time, demonstrated that AM antagonist significantly reduced the in vivo growth of the pancreatic cancer cell line. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that the mean diameter of blood vessels was significantly smaller in the tumor tissues treated with AM antagonist than in those treated with AM N-terminal fragment (AM(1–25)), and that the PCNA-labeling index was lower in the former than in the latter. Then we demonstrated that AM antagonist showed no effect on the in vitro growth of the pancreatic cancer cell line. These results showed that AM played an important role in the growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vivo, suggesting that AM antagonist might be a useful tool for treating pancreatic cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akakura N, Kobayashi M, Horiuchi I, Suzuki A, Wang J, Chen J, Niizeki H, Kawamura K, Hosokawa M and Asaka M . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6548–6554.
Browder T, Folkman J and Pirie-Shepherd S . (2000). J Biol. Chem., 275, 1521–1524.
Carmeliet P . (2000). Nat. Med., 6, 389–395.
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R, Maxell P, Koch CJ, Ratcliffe P, Moons F, Jain RK, Collen D and Keshet E . (1998). Nature, 394, 485–490.
Choi S, Kobayashi M, Wang J, Habellhah H, Okada F, Hamada J, Moriuchi T, Totsuka Y and Hosokawa M . (2000). Clin. Exp. Metast., 18, 45–50.
Cormier-Regard S, Nguyen SV and Claycomb WC . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 1787–1792.
Drake CJ and Little CD . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 7657–7661.
Eguchi S, Hirata Y, Iwasaki H, Sato K, Watanabe TX, Inui T, Nakajima K, Sakakibara S and Marumo F . (1994). Endocrinology, 135, 2454–2458.
Folkman J . (1995). Nat. Med., 1, 27–31.
Garayoa M, Martinez A, Lee S, Pio R, An WG, Neckers L, Trepel J, Montuenga LM, Ryan H, Johnson R, Gassmann M and Cuttitta F . (2000). Mol. Endocrinol., 14, 848–862.
Hayakawa H, Hirata Y, Kakoki M, Suzuki Y, Nishimatsu H, Nagata D, Suzuki E, Kikuchi K, Nagano T, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Sugimoto T and Omata M . (1999). Hypertension, 33, 689–693.
Kato H, Shichiri M, Marumo F and Hirata Y . (1997). Endocrinology, 138, 2615–2620.
Kerbel RS . (2000). Carcinogenesis, 21, 505–515.
Miller MJ, Martinez A, Unsworth EJ, Thiele CJ, Moody TW, Elsasser T and Cuttitta F . (1996). J Biol. Chem., 271, 23345–23351
Muff R, Born W and Fischer JA . (2001). Peptides, 22, 1765–1772.
Nakayama M, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Shirato K and Shibahara S . (1998). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 243, 514–517.
Niizeki H, Kobayashi M, Horiuchi I, Akakura N, Chen J, Wang J, Hamada J, Seth P, Katoh H, Watanabe H, Raz A and Hosokawa M . (2002). Br. J. Cancer, 86, 1914–1919.
Nuki C, Kawasaki H, Kitamura K, Takenaga M, Kangawa K, Eto T and Wada A . (1993). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 196, 245–251.
Oehler MK, Hague S, Rees MC and Bicknell R . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 2815–2821.
Oehler MK, Norbury C, Hague S, Rees MC and Bicknell R . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 2937–2945.
Ouafik L, Sauze S, Boudouresque F, Chinot O, Delfino C, Fina F, Vuaroqueaux V, Dussert C, Palmari J, Dufour H, Grisoli F, Casellas P, Brunner N and Martin PM . (2002). Am. J. Pathol., 160, 1279–1292.
Rocchi P, Boudouresque F, Zamora AJ, Muracciole X, Lechevallier E, Martin PM and Ouafik L . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 1196–1206.
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH, Sato TN and Yancopoulos GD . (1998). Science, 282, 468–471.
Watanabe TX, Itahara Y, Inui T, Yoshizawa-Kumagaye K, Nakajima K and Sakakibara S . (1996). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 219, 59–63.
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ and Holash J . (2000). Nature, 407, 242–248.
Zhao L, Brown LA, Owji AA, Nunez DJ, Smith DM, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR and Wilkins MR . (1996). Am. J. Physiol., 271, 622–629.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. We appreciate Dr Hiroshi Ishikura (The First Department of Pathology, Hokkaido University School of Medicine) and Dr Yutaka Shimada (Department of Surgery & Surgical Basic Science, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University) for providing us with a pancreatic cancer cell line. We thank Ms M Yanome for assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, T., Chen, J., Wang, J. et al. Adrenomedullin antagonist suppresses in vivo growth of human pancreatic cancer cells in SCID mice by suppressing angiogenesis. Oncogene 22, 1238–1242 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206207
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations
BMC Cancer (2018)
-
Reduced Adrenomedullin Parallels Microtubule Dismantlement in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Increased Levels of Brain Adrenomedullin in the Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Adrenomedullin promotes angiogenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer through upregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Small molecules related to adrenomedullin reduce tumor burden in a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer
Scientific Reports (2017)